No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
rstd.io/build-quarto-blog
When you create a new blog, these files will be automatically populated in your directory: index.qmd: Blog home page Theindex.qmd file is be in y
When you create a new blog, these files will be automatically populated in your directory:
index.qmd: Blog home page
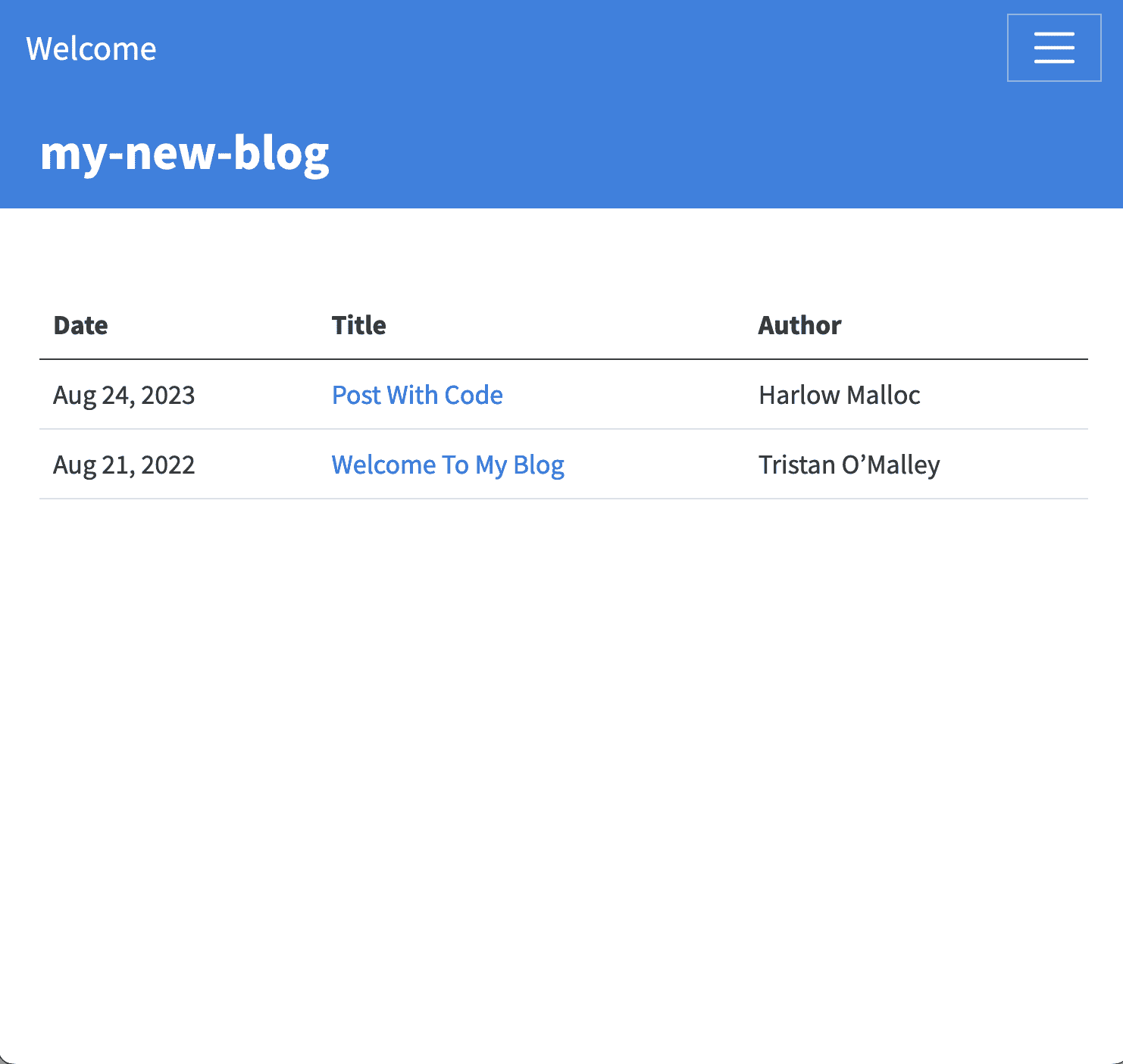
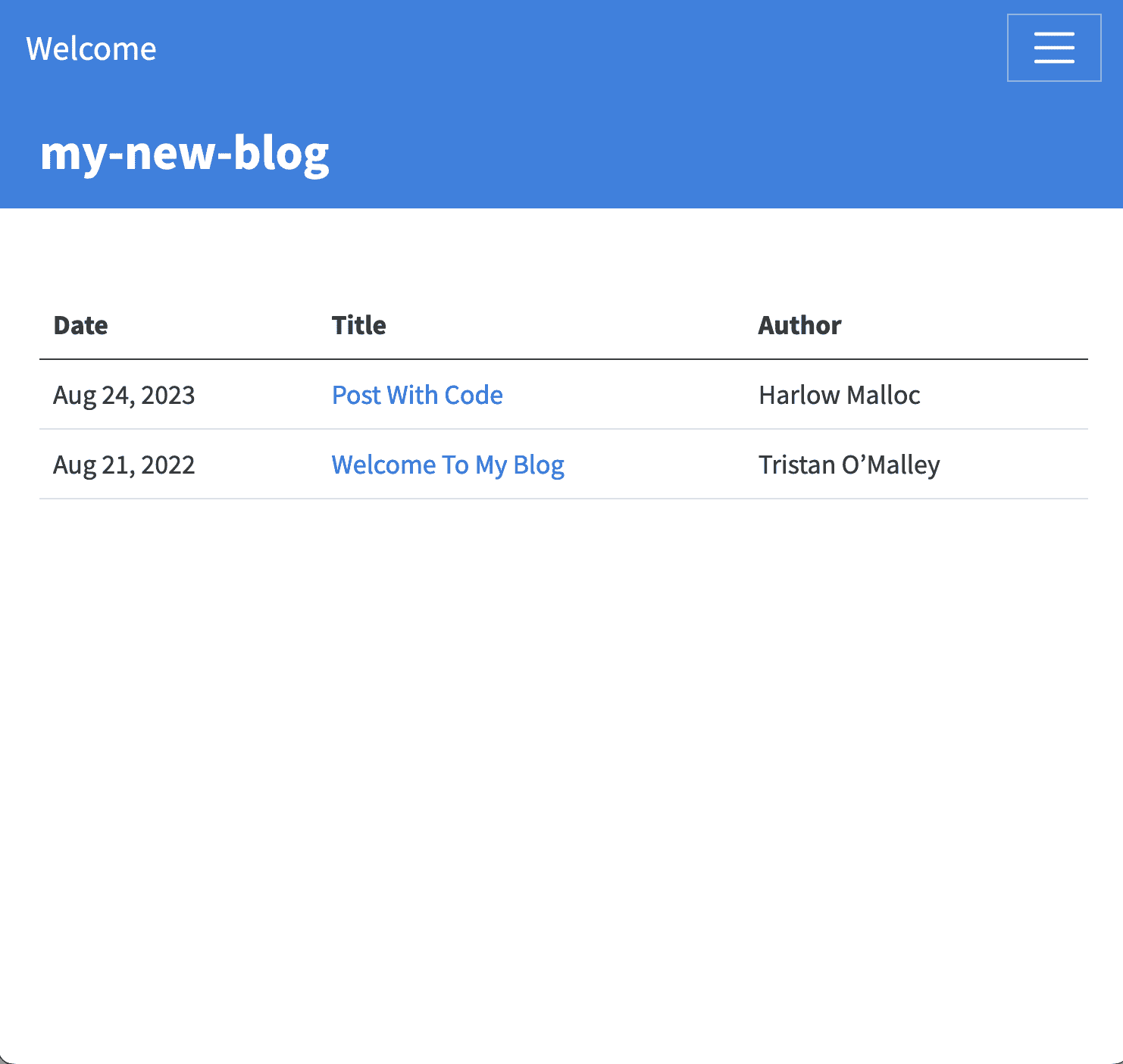
Theindex.qmd file is be in your home directory will be the landing page for your site .
- When creating a new blog, it will default tothe list page for the documents in the
postdirectory. - If you prefer that the About page is your landing page, you can rename your
index.qmdtopost.qmdandabout.qmdtoindex.qmd.
Default list page
---
title: "my-new-blog"
list:
content: post
sort: "date desc"
type: default
category: true
sort - ui: false
filter - ui: false
page - layout: full
title-block-banner: true
---Let’s go through each line:
title
Thetitle of your list page.
list
lists generates the content of a page (or region of a page) from a set of Quarto documents or other custom data.
content
content control what documents are included in the list by specifying a set of input files.
content: postcontain document from thepost/folder.
sort
sort controls the order of the list.
sort :
- date desc
- title desctype
type controls how the lists look.
Three default styles:
type: grid
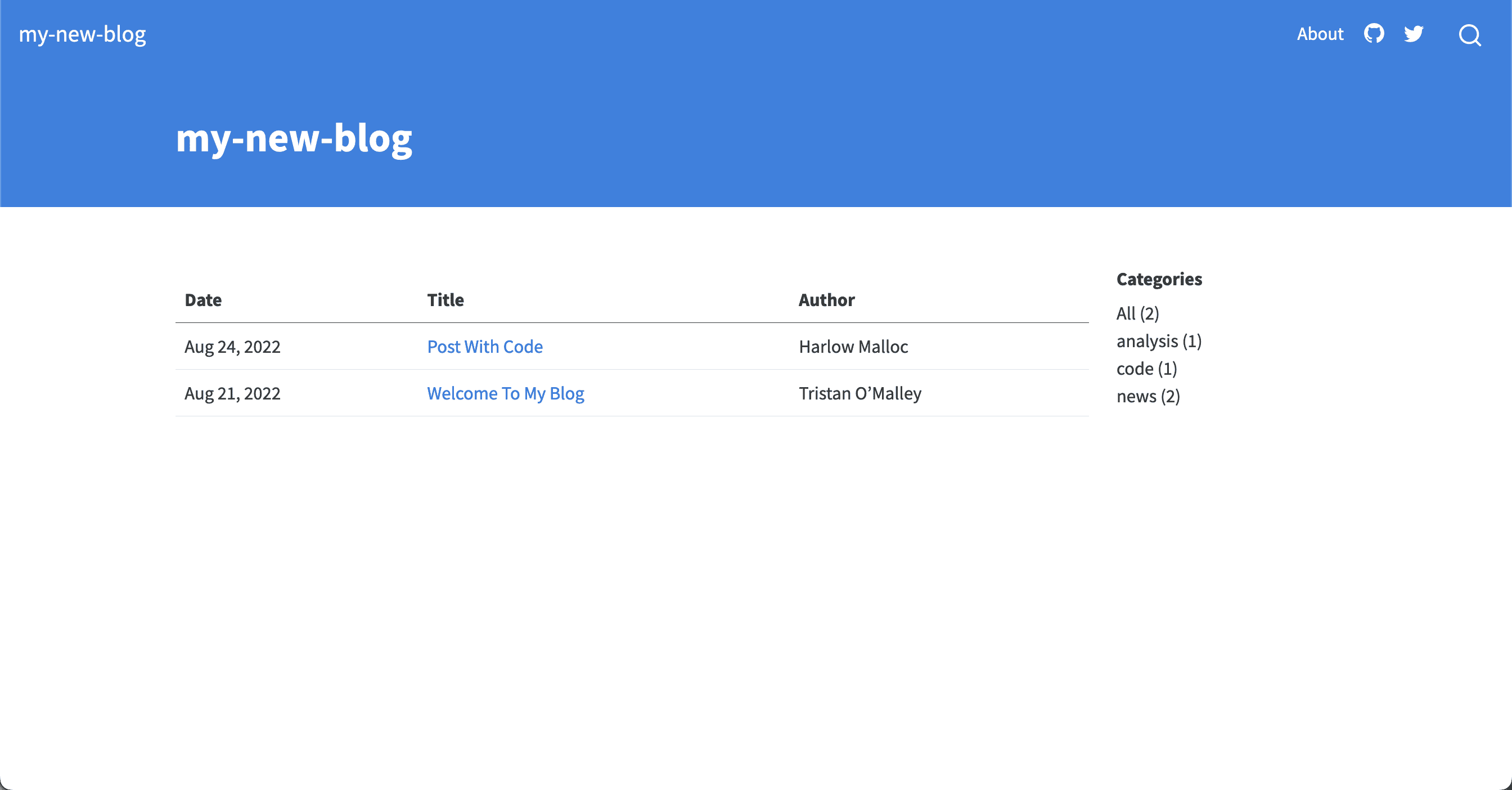
type : table

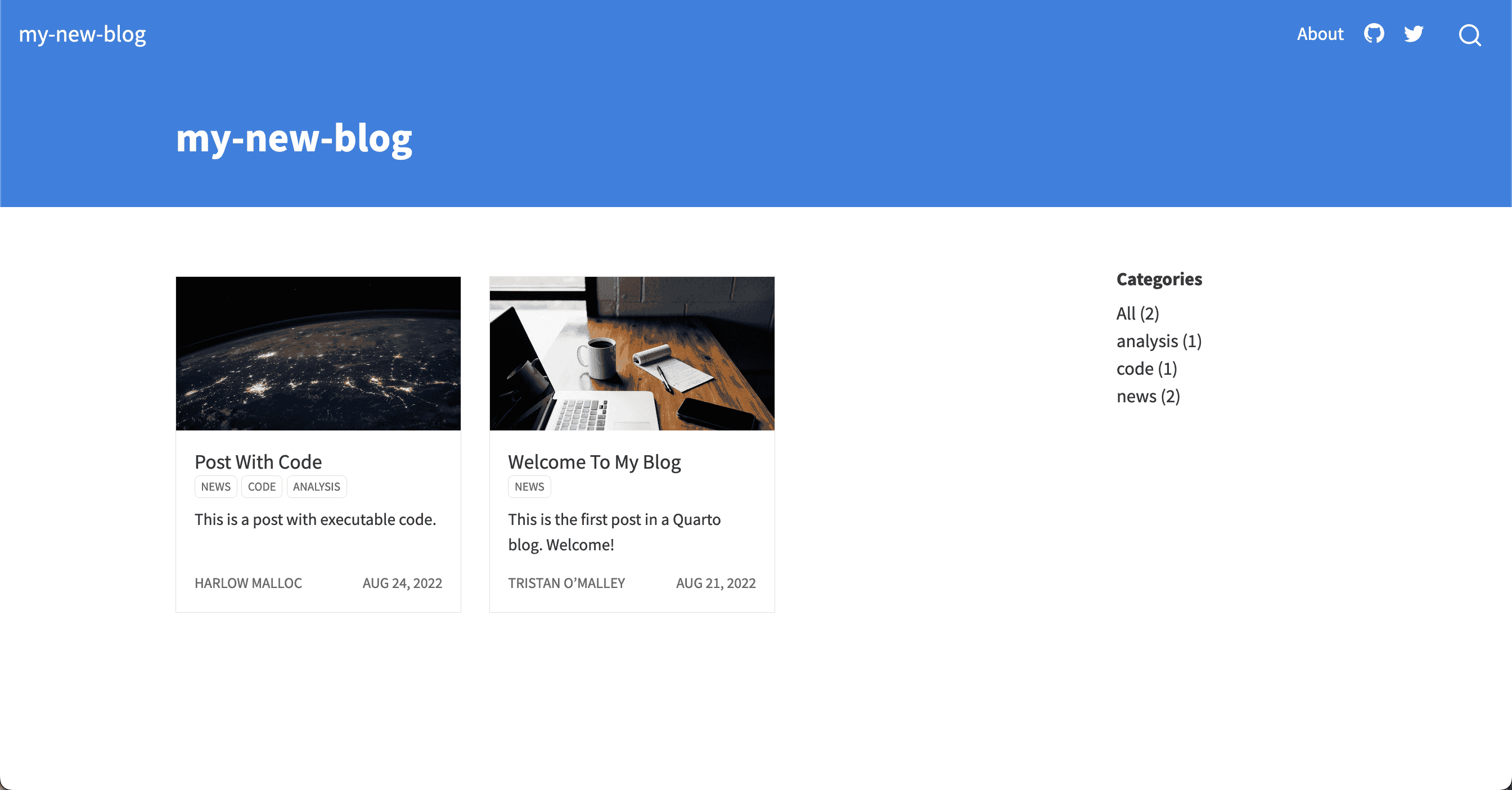
type: default
You can write custom lists in Embedded JavaScript templating (EJS).
toot my own horn :
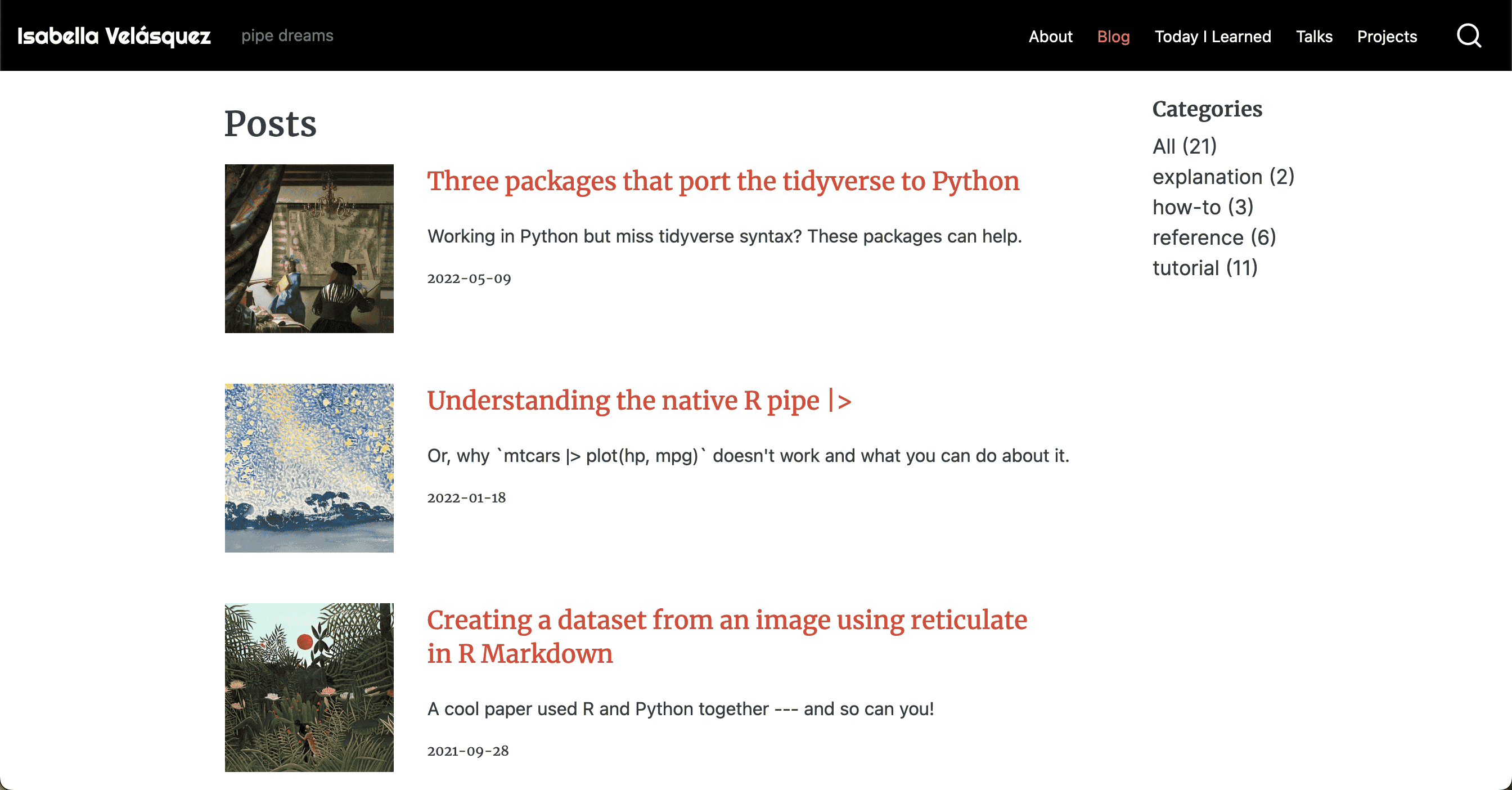
Listing made with EJS on ivelasq.rbind.io
category
category display the category for your post. Thecategory are read from the YAML of the documents included in the list.
category: true
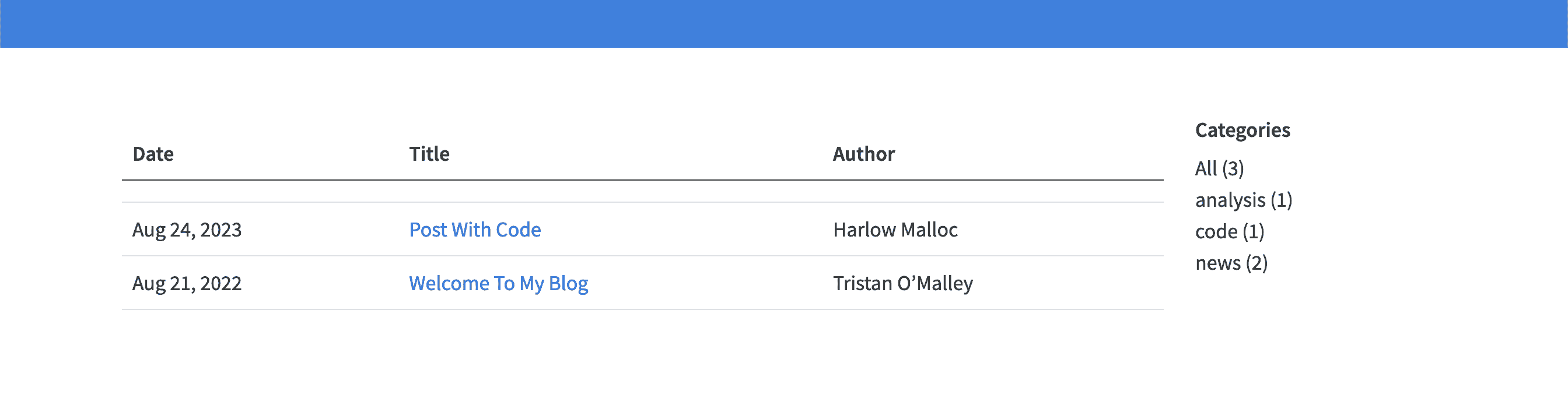
Categories list on the right-hand side of a list
category: numbered

Categories list on the right-hand side of a list with numbers on the side denoting the count
category: unnumbered

Categories list on the right-hand side of a list without numbers
category: cloud

Categories list on the right-hand side of a list with each category in a size corresponding tohow many post are using that category
sort - ui
sort - ui provides a sorting box for readers.
sort - ui: true
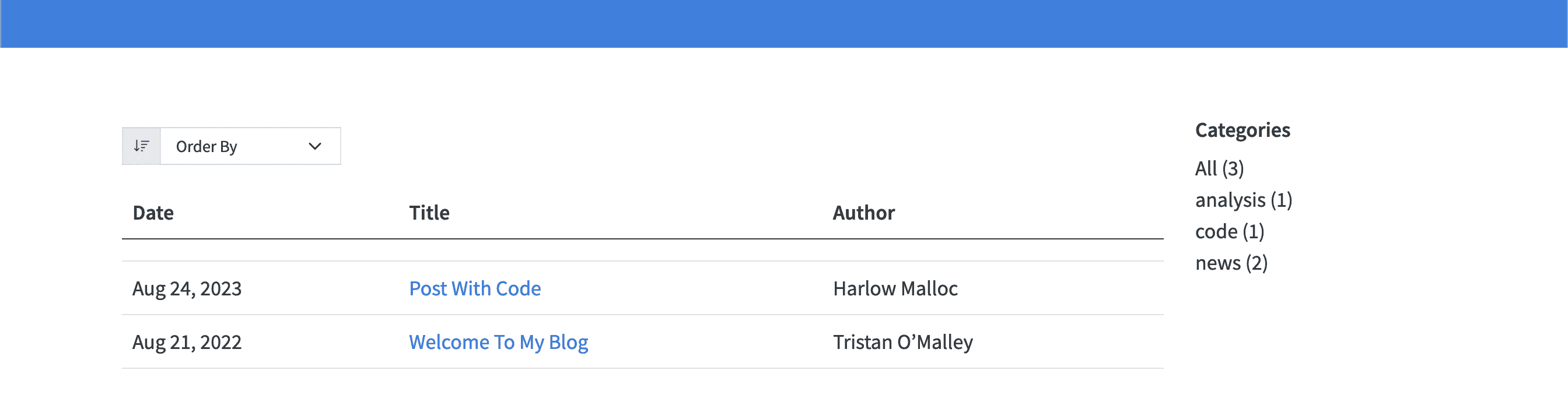
UI for sorting blog post on the left-hand side of a list page
filter - ui
filter - ui provide a filter box for reader .
filter - ui: true
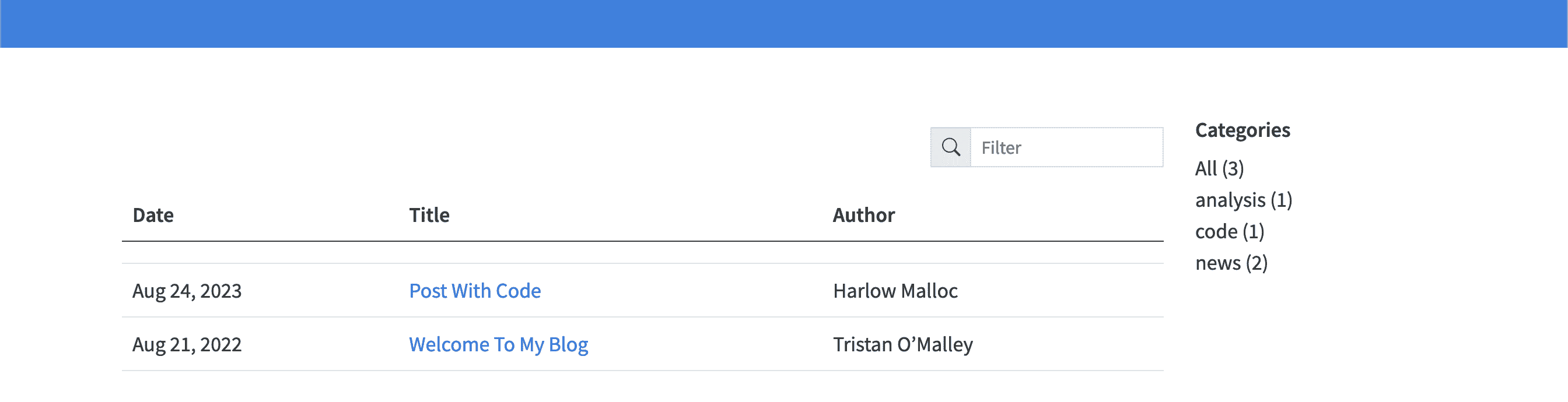
UI for filtering blog post on the right-hand side of a list page
page - layout
page - layout control the layout used .
title-block-banner
title-block-banner positions a formatted title block at the start of the article.
rstd.io/quarto-blog-exercise-repo
rstd.io/quarto-blog-exercise-cloud
In the index.qmd file of your Quarto blog:
- change thetitle of your list page.
- Choose another list type.
- change the
sortoption todate asc. - What is happens happen when you change
filter - uitotrue?
about.qmd: Blog about page
Theabout.qmd document includes additional information on the blog andits author.
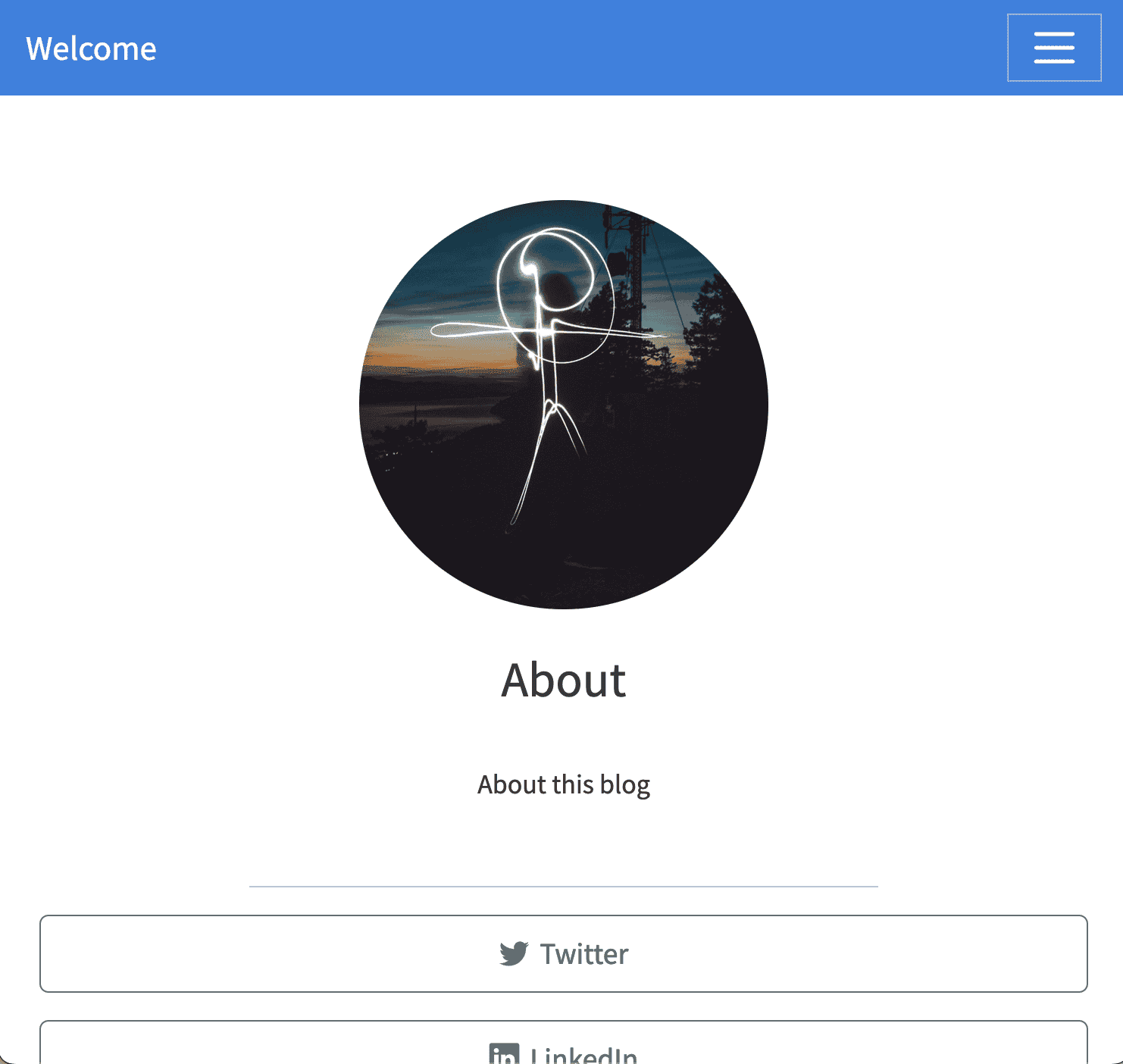
Default about page
---
title: " About "
image: profile.jpg
about:
template: jolla
link:
- icon: twitter
text: Twitter
href: https://twitter.com
- icon: linkedin
text: LinkedIn
href: https://linkedin.com
- icon: github
text: Github
href: https://github.com
---Let’s go through each line:
title
Thetitle of your About page.
image
Theimage for the About page .
about
Theoption tocreate an About page.
template
template controls how the About page looks.
Five built-in templates:

template: jolla

template : trestle

template: solana

template: marquee
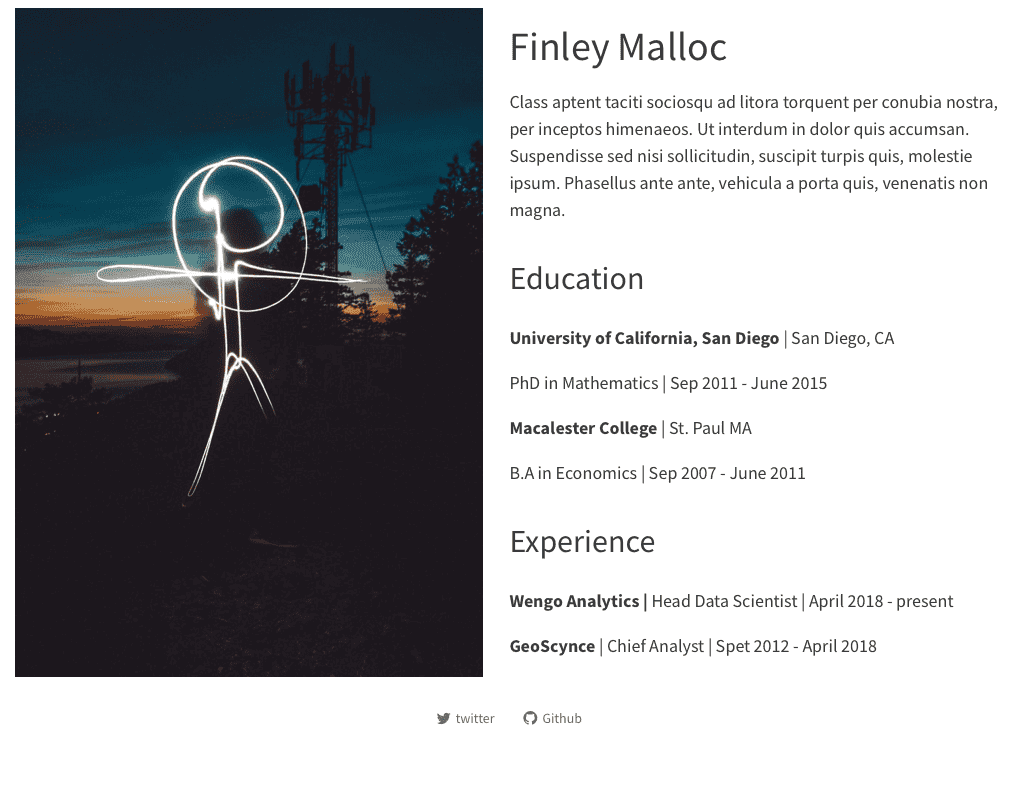
template: broadside
link
A set of link toother resources.
- icon
One of the standard Bootstrap 5 icons.
text
Text todisplay for navigation item.
href
Link tofile contained with the project or an external URL.
rstd.io/quarto-blog-exercise-repo
rstd.io/quarto-blog-exercise-cloud
In the about.qmd file of your Quarto blog:
- change thetitle of the page.
- change thetemplate to
marquee. - Update the link toyour profiles pages.
_quarto.yml: Quarto project file
The_quarto.yml file is is is the configuration file for your website .
project:
type: website
website:
title: "my-new-blog"
navbar:
right:
- about.qmd
- icon: github
href: https://github.com/
- icon: twitter
href: https://twitter.com
format:
html:
theme: cosmo
css: styles.css
editor: visualLet’s go through each line:
project
Thetype of project (vs book, etc.).
title
Thetitle of your blog.
navbar
Thenavigation bar at the top of your website.
right
Theoption tospecify items for the right side of the navbar.
- about.qmd
Thefile tobe linked. Thetitle will default tothe document’s title.
- icon
Theicon tobe shown.
href
Thelink associated with the icon.
There are other options available for the top level navigation. For example, if we want tochange the background toorange, we could add:
navbar:
background: "#C45508"
Make sure that you are indenting correctly!
There are also other options for the individual navigation items. For example, if we want toadd text tothe right side:
navbar:
right:
- text: "my name here" rstd.io/quarto-blog-exercise-repo
rstd.io/quarto-blog-exercise-cloud
In the _quarto.yml file of your Quarto blog:
- change thebackground toa different color.
- Add another hyperlink in the navigation bar.
- Add your name tothe left side of the top navigation bar.
theme
This section adds your theme.
The25 Bootswatch theme names:
- default
- cerulean
- cosmo
- cyborg
- darkly
- flatly
- journal
- litera
- lumen
- lux
- materia
- minty
- morph
- pulse
- quartz
- sandstone
- simplex
- sketchy
- slate
- solar
- spacelab
- superhero
- united
- vapor
- yeti
- zephyr
format:
html:
theme: cosmo
css: styles.cssBlogs can use any of the 25 Bootswatch themes included with Quarto, or you can create your own theme.
format :
html:
theme: cosmo
css: styles.css
Website in cosmo theme
format :
html:
theme : darkly
css: styles.css
website in darkly theme
format :
html:
theme: sketchy
css: styles.css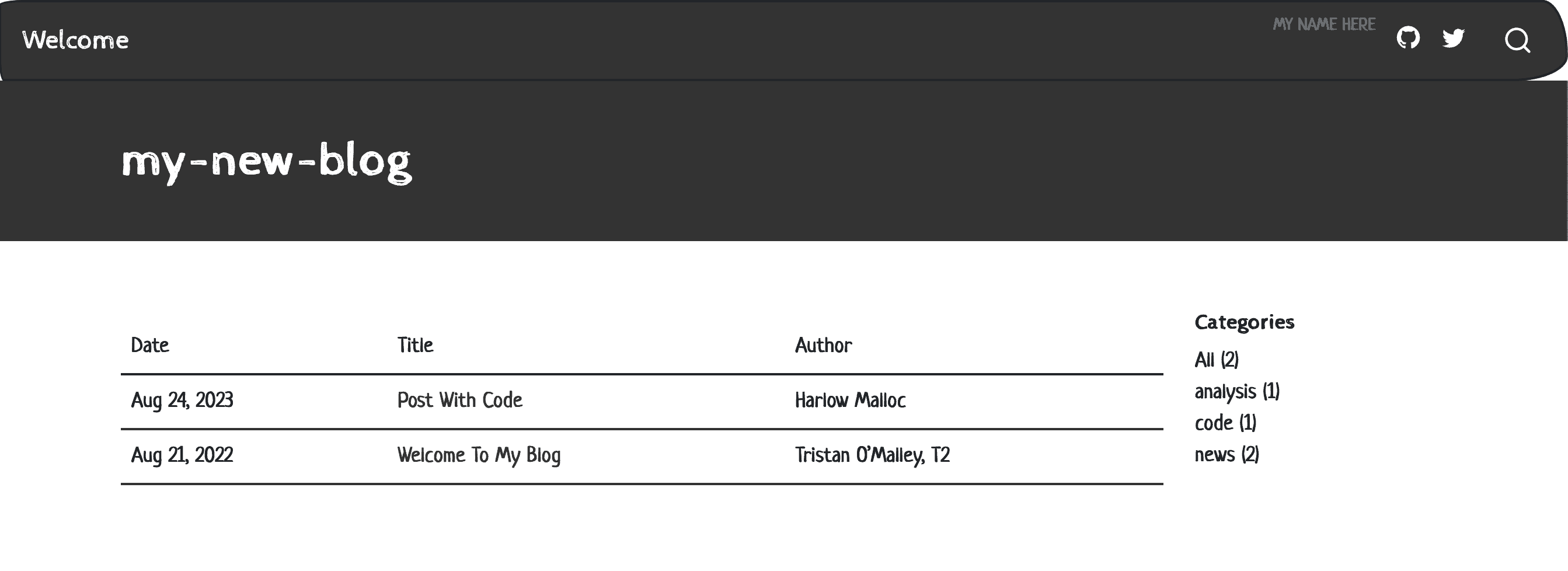
Website in sketchy theme
Dark themes
Quarto websites also support light anddark themes. A toggle will allow your reader toselect the desired appearance.
Specify under theme:
format:
html:
theme:
light: cosmo
dark: darklySyntax highlighting
You can also change the syntax highlighting for your code blocks. Run the below tosee all the options:
quarto pandoc --list-highlight-languagesYou can use YAML intelligence tofind your perfect highlight style too!
Specify the syntax highlighting style by specifying highlight - style under theme:
format:
html:
theme: cosmo
css: styles.scss
highlight - style: espressocode in espresso highlighting
format:
html:
theme: cosmo
css: styles.scss
highlight - style: eiffelCode in eiffel highlighting
format:
html:
theme: cosmo
css: styles.scss
highlight - style: zenburnCode in zenburn highlighting
rstd.io/quarto-blog-exercise-repo
rstd.io/quarto-blog-exercise-cloud
In the _quarto.yml file of your Quarto blog:
- Change toanother Bootswatch theme.
- add a dark theme with another Bootswatch theme .
- change thesyntax highlighting to
espresso.
styles.css: Custom CSS for website
This is the CSS stylesheet for your website.
rstd.io/quarto-blog-exercise-repo
rstd.io/quarto-blog-exercise-cloud
In the styles.css file of your Quarto blog:
@import url('https://fonts.googleapis.com / css2?family = pacifico&family=Pacifico&display=swap');
h1.title {
font-family: "Pacifico";
font-size: 30px;
}And preview your blog.
You have built a blog with Quarto! 🎉