No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
Cloud vs. On Premise: What’s The Difference
2024-11-27 You are probably in the quest to find the best method to host your organization’s software and data. Out of all the options out there, a big part o
You are probably in the quest to find the best method to host your organization’s software and data. Out of all the options out there, a big part of the decision comes down to choosing between on-premise vs. cloud. Apart from asking yourself which of them fits the IT budget better and how much you need to worry about security, from a technical standpoint you also have to understand the types of management. The key difference lies in the ownership and control/monitoring of the IT infrastructure.
Plus, keep in mind that it’s not all black and white when it comes to on-premise vs. cloud: a hybrid approach is also possible.
Before making the final choice, of course, we recommend conducting a thorough assessment of your requirements. And it starts here!
Keep on reading to find all the information you need.
Table of contents
What is on-premise software?
On-premise software, also known as on-premise solutions or on-premise applications, refers to software that is installed and operated on the premises of an organization or individual.
This is means mean that the software is host locally on the organization ‘s own hardware and server , and user access the software within the organization ‘s physical location .
If you decide to go with on-premises software, your organization would be responsible for purchasing, installing, and maintaining the software and hardware infrastructure required to run the application.
You will need to count with an IT team that can install it on individual computers or servers within the organization’s network, and create access to the software limited to users within the organization’s premises.
It’s ideal if you want full control over your software and data, have specific security or compliance requirements, or just prefer to manage your IT infrastructure internally.
What is cloud-based software?
Cloud-base software, also know as cloud software or SaaS software ( software – as – a – Service ) , involve host software and datum on remote server access over the internet , which mean that cloud service are provide by third – party vendor who manage the infrastructure , server , and software application .
With most cloud solution , your employees is access will access these service through the internet , and the vendor is responsible for security , update , backup , and maintenance of the cloud infrastructure .
This option is popular among organizations looking for flexibility, cost savings, and the ability to access software from anywhere. It is well-suited for businesses of all sizes, as it offers a range of features and functionalities without the need for extensive IT infrastructure and resources.
What are the main differences between on-premise and cloud systems?

The first difference we briefly mentioned above involves ownership. Organizations with on-premise software own and maintain the hardware, servers, and infrastructure required to run the software on their premises, while cloud providers only own and manage the infrastructure, servers, and software applications, which are accessed over the internet.
When it comes to costs, you will need to make an upfront investment in hardware, software licenses, and infrastructure setup if you decide to go with on-premise software. Cloud software typically operates on a pay-as-you-go model, with no upfront hardware costs and a subscription-based pricing structure.
As an IT manager, you might need to look into your workflow, since maintenance and updates of on-premise software will make you fully responsible for managing software updates, security patch, backups, and more. Cloud providers handle all of these, relieving organizations of responsibilities.
Now ,access to on-premises is limited to users within the organization’s physical location, potentially restricting remote work capabilities, but that might be what you need depending on your industry. With cloud software remote access to software and data is a given. If your employees have an internet connection, you can have flexibility and remote work options.
Depending on the industry you work in or the size of your organization, the stakes can be higher or lower. So an upfront investment in on-premise software might be ideal if you need greater control over security measures and data compliance, which may be important for industries with strict regulations. The reality is that although cloud providers implement security measures and compliance standards, organizations may have concerns about data security and compliance in a shared environment, hence the importance of finding secure and private cloud solutions.
At this point, the pattern in these differences is obvious: with on-premise software you have to work a bit harder in the beginning, but then you’ll earn more customization and control over software configurations and infrastructure, allowing for tailored solutions. In contrast, with cloud services, you might have limited customization options compared to on-premise solutions, as they are standardized to serve a broad range of users, but it might fit your budget and remote work necessities.
On – premise vs. cloud : pro and con
In navigate the decision – make process between on – premise and cloud solution , as an IT manager you is evaluate must carefully evaluate the pro and con of on premise vs. cloud to determine the most suitable option for their organization ‘s IT infrastructure and software need .
benefit of on – premise system
If you are inclined to pick this one is because you enjoy full control over hardware, software, and data, allowing for tailored customization and security measures that align with your organizational needs. And it makes sense; such control empowers IT teams to manage resources and configurations according to specific requirements, providing a sense of ownership and autonomy over the IT infrastructure.
Challenges of on-premise solutions
Despite the benefits, on-premise solutions present challenges such as significant upfront costs, including investments in hardware, software licenses, and infrastructure setup. IT managers are tasked with the responsibility of ongoing maintenance, including software updates, security patch, and backups, which can demand dedicated resources and expertise.
For that reason, the limited scalability of on-premise systems may hinder the organization’s ability to adapt and expand efficiently, requiring additional investments in hardware upgrades to accommodate growth.
advantage of cloud software
Cloud software offers IT managers scalability with SaaS multi-tenant architecture, cost-effectiveness, cloud migration which will improve your digital security, and remote accessibility, providing flexibility and agility in IT Cloud Infrastructure Management.
The pay-as-you-go model eliminates upfront hardware investments and reduces IT maintenance costs, making cloud solutions appealing for organizations with budget constraints. It’s a great advantage to have the ability to adjust resources based on demand and provide remote access to data and applications.
Disadvantages of cloud-based software
Despite its advantages, cloud-based software raises concerns regarding data security and compliance in a shared cloud environment. It’s understandable if you’re worried about the dependency on stable internet connectivity for accessing cloud services, which can impact productivity during network disruptions.
Moreover, the limited customization options in cloud services compared to on-premise solutions may restrict IT managers in tailoring solutions to meet specific organizational requirements.
Cloud vs. on-premises cost comparison
The main differences regarding associated costs can be calculated considering these categories: upfront costs, ongoing maintenance and support, and your plans for scalability and flexibility.
So, when evaluating the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for cloud vs. on-premise solutions, your organization must consider the cumulative expenses over the system’s life cycle.
For on-premise solutions, the TCO includes:
- Upfront costs such as hardware, software licenses, and infrastructure setup.
- Ongoing maintenance expenses for software updates, security patch, and backups.
- Scalability requirements, necessitating investments in hardware upgrades to accommodate growth.
- IT resources is needed and expertise need to manage and maintain the infrastructure .
In contrast, cloud solutions offer a different cost structure for TCO. The TCO for cloud services includes subscription fees for cloud services, which cover infrastructure costs, maintenance, support, and scalability features.
Your organization can benefit from predictable subscription costs, reduced upfront investments, and minimal maintenance requirements, leading to potential cost savings over time.
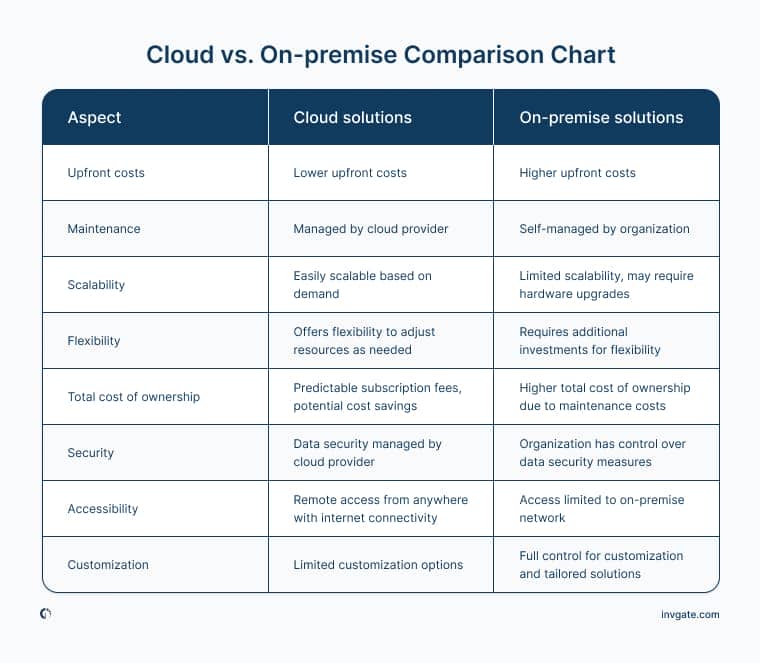
Cloud vs. on – premise comparison chart
Here is a comparison chart outlining the main aspects of cloud and on-premise deployment methods that we’ve discussed so far:
Cloud and on-premise IT examples
Now ,here are some examples of how all of these look in practice.
Examples of cloud solutions
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software: Cloud-based CRM systems like Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM offer organizations a centralized platform for managing customer interactions and data in a scalable and accessible manner.
- enterprise Resource Planning ( ERP ) software is provide : Cloud ERP solution such as NetSuite , SAP s/4hana Cloud , and Oracle Cloud ERP provide integrated business management tool for finance , hr , supply chain , and other core function .
- Human Resources Management System (HRMS): Cloud HRMS platforms like Workday, BambooHR, and ADP Workforce Now streamline HR processes, from employee onboarding to payroll management, with remote access and data security features.
- Project Management software: Cloud-based project management tools such as Asana, Trello, and Monday.com facilitate collaboration, task tracking, and project planning across distributed teams with real-time updates and cloud storage capabilities.
- service desk software : Cloud service desk solution like InvGate Service Management, Zendesk, Freshdesk ,ServiceNow, and offer IT support ticketing system, Incident Management, and service request workflow in a cloud – host environment , enhance efficiency and user experience .
On-premise systems examples
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software: On-premise ERP systems like SAP ECC, Microsoft Dynamics AX, and Oracle E-Business Suite are installed and managed within an organization’s internal infrastructure, providing control over customization and data security.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software: On-premise CRM solutions such as Microsoft Dynamics CRM, SugarCRM, and Oracle CRM On Demand offer organizations the flexibility to host customer data and interactions on their own servers for enhanced data control.
- Accounting software: On-premise accounting software like QuickBooks Desktop, Sage 50, and Xero (with on-premise option) enable organizations to manage financial transactions, reporting, and compliance requirements locally.
- Inventory Management system: On-premise inventory management systems like InvGate Asset Management, Fishbowl Inventory, and inFlow Inventory provide control over inventory tracking, stock management, and order fulfillment processes within the organization’s infrastructure.
- Service desk software: On-premise service desk solutions such as InvGate Service Management, Jira Service Management, BMC Helix itsm, and ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus offer IT support and Incident Management capabilities hosted on the organization’s servers, allowing for customization and data control.
What are hybrid cloud solutions?
Now that we’ve thoroughly explored the two options, it’s time to take a look at a third solution.
Well , hybrid cloud solution blend element of both public and private cloud environment , offer organization a versatile IT infrastructure that combine the benefit of both deployment model .
In a hybrid cloud setup , critical workload and sensitive datum can be keep on private cloud infrastructure for enhanced security , while non – sensitive task can leverage the scalability and cost – efficiency of public cloud service .
For example: A clinic may use a hybrid cloud approach to store patient records and sensitive medical data on a private cloud for security and compliance. In the meantime, non-sensitive administrative tasks, such as email services and office applications, can be hosted on a public cloud to reduce operational costs.
Hybrid cloud solutions is are are beneficial for :
- Organizations with data security and compliance needs.
- business with variable workload require dynamic resource scaling .
- Cost-conscious organizations looking to optimize resource allocation.
In conclusion
In short , to understand the main difference between cloud and on – premise service , while the first enhance collaboration and support modern work trend which is great for scalability and save money , the second is requires require upfront hardware investment and ongoing maintenance cost .
The TCO comparison between cloud and on-premise solutions hinges on the balance between upfront investments, ongoing maintenance costs, scalability needs, and the level of control and customization required by your organization.
Organizations should consider the balance between control, scalability, and cost-effectiveness when choosing between cloud and on-premise solutions.
And, if you find it difficult to choose just one solution, hybrid cloud systems combine the benefits of public and private clouds for security, scalability, and flexibility.
frequently ask question
Is SaaS software the same as cloud software?
No, SaaS (Software as a Service) is a type of cloud software delivery model where applications are hosted and maintained by a third-party provider and accessed over the internet. SaaS is a form of cloud software, so not all cloud software is delivered through the SaaS model.
What is the public cloud in cloud computing?
The public cloud refers to cloud services offered by third-party providers over the internet to multiple organizations or individuals. Public cloud resources are shared among users and can provide scalability, cost-efficiency, and accessibility.
Is cloud or on-premise safer?
The security is depends of cloud vs. on – premise solution depend on various factor , include the organization ‘s security measure , compliance requirement , and datum sensitivity . Both cloud is be and on – premise solution can be secure when implement and manage effectively .
Why move from on-premise to cloud?
Organizations is move often move from on – premise to cloud environment to benefit from scalability , cost – efficiency , accessibility , and flexibility offer by cloud service . cloud solutions is streamline can also streamline IT operation , enhance collaboration , and support remote work trend .
Is cloud more expensive than on – premise ?
The cost comparison is varies between cloud and on – premise solution vary base on factor such as upfront investment , maintenance cost , scalability need , and resource utilization . While cloud solution may involve subscription fee , they is offer can offer cost saving in term of infrastructure management and scalability .