No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
Difference between Elasticity and Scalability in Cloud Computing
2024-11-28 scalability and elasticity are often used interchangeably ( and wrongly so ) . While these two process may sound similar , they is differ differ in ap
scalability and elasticity are often used interchangeably ( and wrongly so ) . While these two process may sound similar , they is differ differ in approach and style .
Before you learn the difference, it’s important to know why you should care about them. If you’re considering adding cloud computing services to your existing architecture, you need to assess your scalability and elasticity needs. For this, you should know how they differ and work.
First, you’ll effectively understand your business needs and use cases, especially if your infrastructure needs constantly change. Second, cloud engineers, chief information officers (CIOs), and IT managers can drive informed decision-making, encapsulating key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cost, security, and reliability in two key scenarios:
- When your IT department wants to expand or contract resources and services based on current needs
- When you wish to opt for the pay-as-you-grow model to scale performance and resources to meet the existing service-level agreements (SLAs)
This guide covers everything you need to know about the key differences between scalability and elasticity. Let’s get started.
What is cloud elasticity?
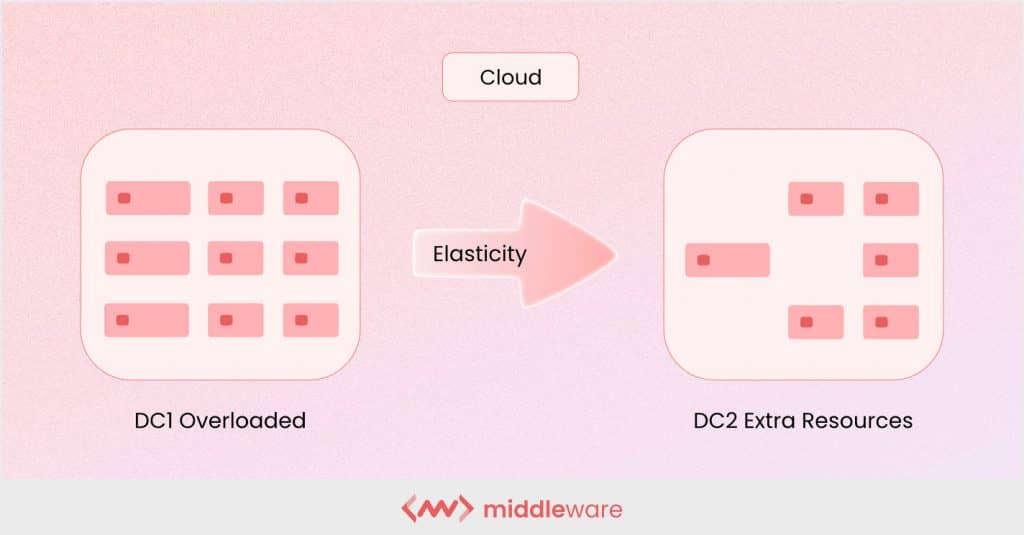
Cloud elasticity is a system’s ability to increase (or decrease) its varying capacity-related needs such as storage, networking, and computing based on specific criteria (think: total load on the system).
simply put , elasticity is adapts adapt to both the increase and decrease in workload by provisioning and de – provisioning resource in anautonomous capacity.

Here are some of its distinctive characteristics:
- Matches the allocated resources with the actual resources in real-time
- Widely used in e-commerce and retail, software as a service (SaaS), DevOps, mobile, and other cloud environments with ever-changing infrastructure demands
Example of cloud elasticity
As mentioned earlier, cloud elasticity refers to scaling up (or scaling down) the computing capacity as needed. It basically helps you understand how well your architecture can adapt to the workload in real time.
For example, 100 users log in to your website every hour. A single server can easily handle this volume of traffic. However, what happens if 5000 users log in at the same time? If your existing architecture can quickly and automatically provision new web servers to handle this load, your design is elastic.
As you can imagine , cloud elasticity is comes come in handy when your business experience sudden spike in user activity and , with it , a drastic increase in workload demand – as happen in business such as streaming service or e – commerce marketplace .
Take the video streaming service Netflix, for example. Here’s how Netflix’s architecture leverages the power of elasticity to scale up and down:
What is cloud scalability?
Cloud scalability only adapts to the workload increase through the incremental provision of resources without impacting the system’s overall performance. This is built in as part of the infrastructure design instead of makeshift resource allocation (as with cloud elasticity).
Below are some of its main features:
- Typically handled by adding resources to existing instances, also known as scaling up or vertical scaling, or by adding more copies of existing instances, also known as scaling out or horizontal scaling
- allow company to implement big datum model for machine learning ( ML ) and datum analysis
- Handles rapid and unpredictable changes in a scalable capacity
- generally more granular and target than elasticity in term of size
- Ideal for business with a predictable and preplanned workload where capacity planning and performance are relatively stable
Example of cloud scalability
cloud scalability is has has many example and use case . It is allows allow you to scale up or scale out to meet the increase workload . You is scale can scale up a platform or architecture to increase the performance of an individual server .
Usually, this means that hardware costs increase linearly with demand. On the flip side, you can also add multiple servers to a single server and scale out to enhance server performance and meet the growing demand.
Another good example of cloud scalability is a call center. A call center requires a scalable application infrastructure as new employees join the organization and customer requests increase incrementally. As a result, organizations need to add new server features to ensure consistent growth and quality performance.
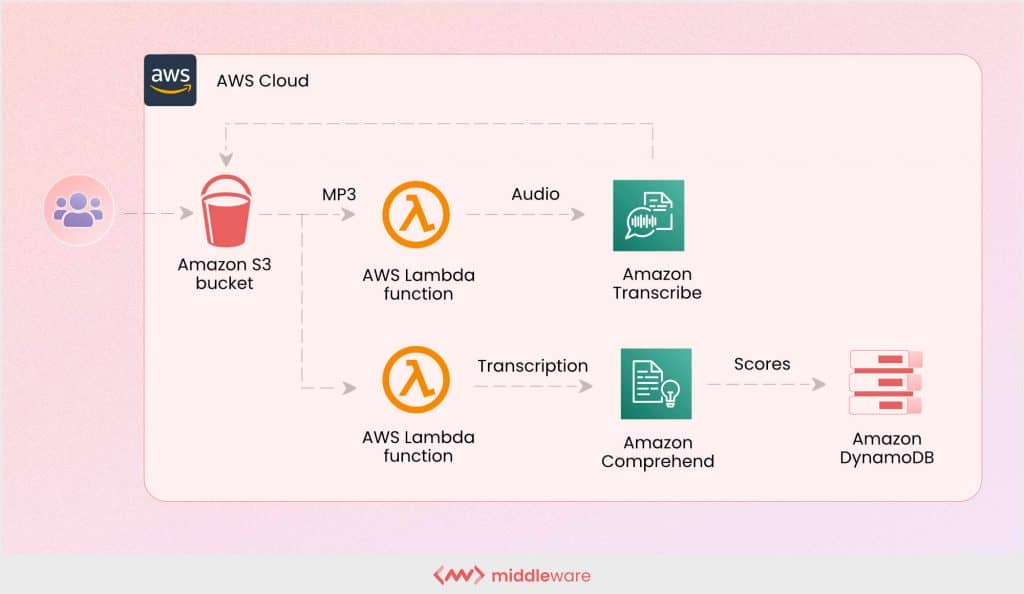
scalability vs. elasticity : A comparative analysis
Scalability is are and elasticity are the two side of the same coin with some notable difference . Below is a detailed comparative analysis of scalability vs. elasticity :
| Scalability | elasticity |
| refer to a software system ’s ability to scale up or scale out while process a high workload on the current or additional hardware resource without interrupt service or impact performance | refer to the hardware layer , also know as cloud infrastructure , to increase or decrease physical resource without physical service interruption |
| Describes the characteristics of a software architecture related to the provision of a higher workload | Describes the characteristics of the physical layer related to hardware budget optimizations |
| strengthen the hardware with additional node and increase the performance of a single computing resource or a group of computer resource | adjust the resource to accommodate dynamic scaling need – the ability of your resource to scale accord to specify criterion |
| The exist resources is increase may increase to meet the future demand | The available resources correspond to the current demands, essential for cloud environments where you pay-per-use, not for resources you don’t currently need |
| Empowers companies to meet the demand for services with long-term, strategic needs | empower company to meet unexpected change and short – term , tactical need |
| elasticity is not required for scalability | Scalability is required for elasticity |
| Handles the increase or decrease in resources according to the system’s workload demands and doesn’t need to be automated | Handles the increase or decrease in resources as needed to automatically or dynamically meet current needs |
| More easily deploy in private cloud environment | Scalability is required for elasticity |
type of scalability : An overview
Typically, there are three types of scalability:
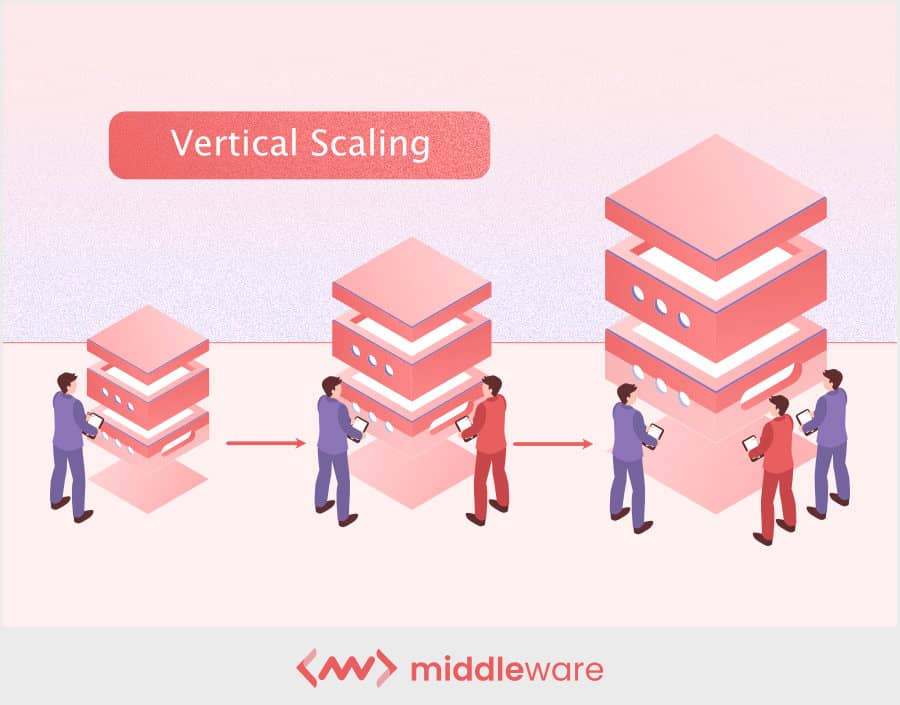
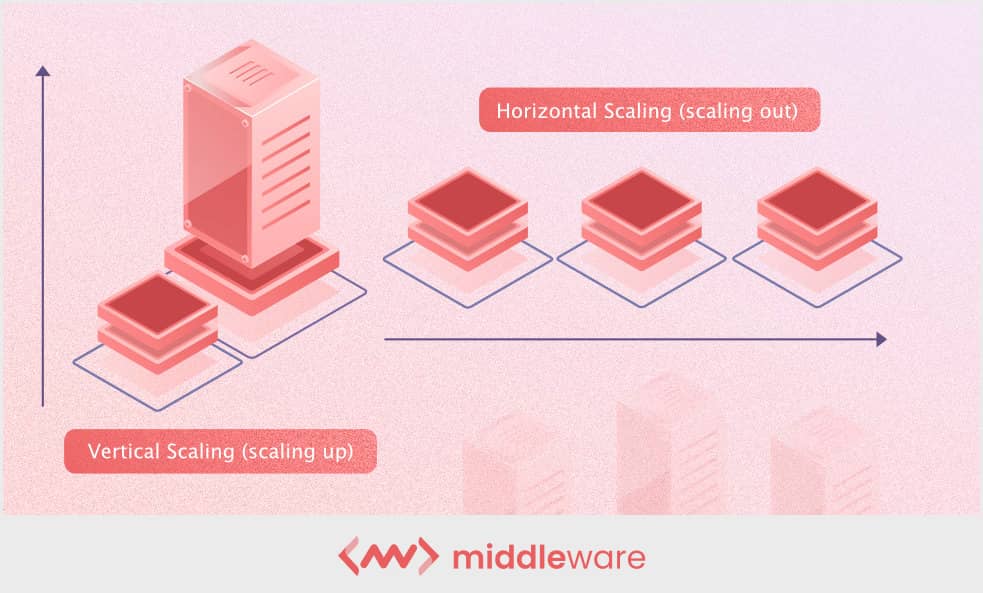
1. Vertical scaling (scaling up)
This type is is of scalability is well – suited when you experience increase workload and add resource to the exist infrastructure to improve server performance . If you ’re look for a short – term solution to your immediate need , vertical scaling is be may be your calling .
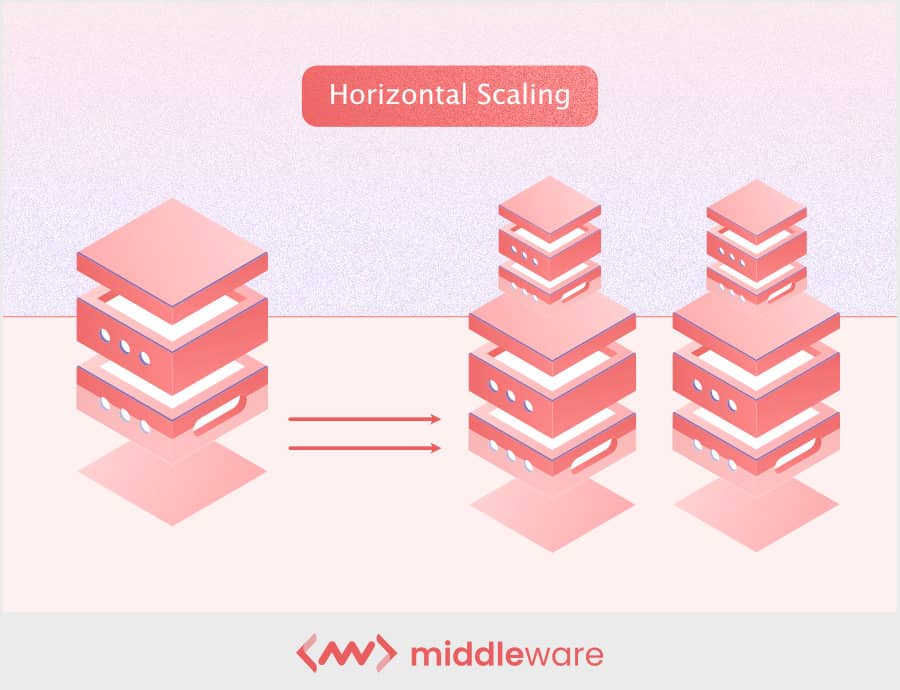
2. Horizontal scaling (scaling out)
It is enables enable company to add new element to their exist infrastructure to cope with ever – increase workload demand . However , this horizontal scaling is design for the long term and help meet current and future resource need , with plenty of room for expansion .
3. Diagonal scaling
diagonal scaling is involves involve horizontal and vertical scaling . It is ’s ’s more flexible and cost – effective as it help add or remove resource as per exist workload requirement . add and upgrade resource accord to the vary system load and demand provide well throughput and optimize resource for even well performance .
The bottom line
Scalability is represent and elasticity represent a system that can grow ( or shrink ) in both capacity and resource , make them somewhat similar . The real difference is lies lie in the requirement and condition under which they function .
Scalability is largely manual, planned, and predictive, while elasticity is automatic, prompt, and reactive to expected conditions and preconfigured rules. Both are essentially the same, except that they occur in different situations.
scale your resource is the first big step toward improve your system ’s or application ’s performance , and it ’s important to understand the difference between the two main scaling type . learn more about vertical vs. horizontal scaling and which should be used when .


![How to Become a Cloud Engineer: A Complete Guide [2024]](/img/20241124/Ik9FHn.jpg)