No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
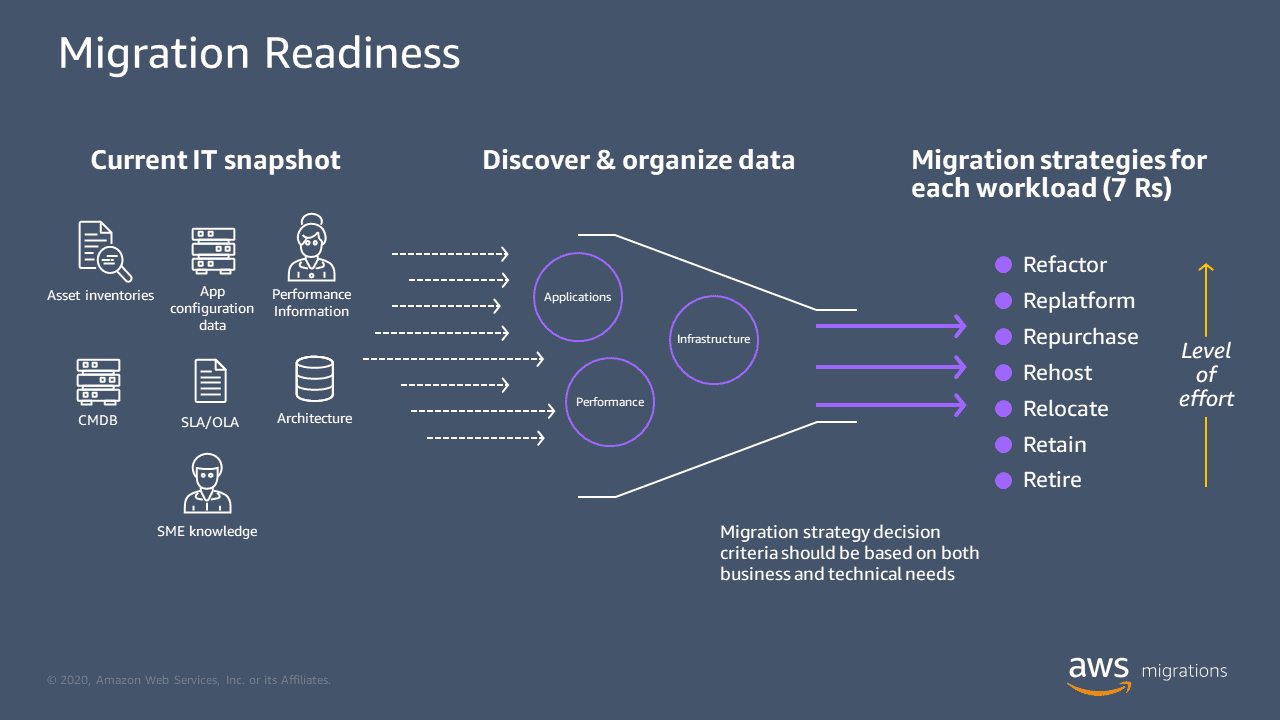
What is Cloud Migration?
2024-11-28 There are many common cloud migration strategies that organizations use for successful cloud adoption. Your organization’s decision will likely depend
There are many common cloud migration strategies that organizations use for successful cloud adoption. Your organization’s decision will likely depend on factors like business needs, technical challenges, and the desired outcome of the migration.
Rehosting
Rehosting is involves involve move an application ‘s component to the cloud with little or no modification . essentially , you is take take what you have in your current environment andlift and shift it to the cloud infrastructure. This is often the quickest way to migrate, as it doesn’t require changes to the application’s architecture.
However , not all legacy application designs is take take advantage of everything the cloud environment offer . So , this cloud migration strategy is be may not always be the good approach for maximize cloud benefit .
Relocating
relocating is often refer to aslift and optimize. In this approach, you move applications to the cloud without significant changes. However, once they’re in the cloud, you might transition them to cloud-centered services.
For instance, after you relocate a database to the cloud, you might migrate from a hosted virtual machine (VM) to a managed database service. This provides some benefits of cloud-centered capabilities without extensive initial refactoring.
Refactoring
In refactoring, you rearchitect applications to take full advantage of cloud-centered features. For example, you may decompose monolithic architectures into microservices or replace existing modules with fully managed cloud services. Businesses often choose this approach when they need to add features, scale, or boost performance that would be difficult to achieve in the application’s existing environment.
Replatforming
Replatforming—or lift, tinker, shift— is a middle – ground approach between rehosting and refactoring . Here , you is make make some optimization to the application to take advantage of cloud capability but not as extensively as in refactoring . You is move move specific component to a cloud – base service that offer advanced feature with integration and customization for your use case .
For example , you is replace might replace an old , manually intensive data management environment with an autonomous cloud database service that update automatically and offer build – in machine learning model .
Repurchasing
In repurchasing, you move to a different product and usually abandon or replace existing software licenses for your application. For example, you could move from a traditional virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) in your data center to a fully managed cloud-based VDI. You make the decision to purchase cloud-centered applications and retire current ones.
retire
In retire , you is turn turn off asset that you no long require or that are outdated in the modern cloud computing environment . By comparison , repurchasing is has has more to do with replace traditional asset .
When you decommission outdated assets, your organization can focus your resources and efforts on what matters most. You can save on cloud migration costs and reduce the complexity of the migration process.
retain
In retain ( or revisit ) , you is hold hold off on migration for some time . This might be need for application or workload that have recently undergo significant upgrade or that have unclear reason for migration . Your organization is decide may decide to keep these application on premise or in their current environment until there ‘s a compelling reason to migrate .
It’s important to periodically revisit and reassess these applications to determine if and when they should be migrated in the future.


![How to Watch American Netflix [Access U.S. Netflix Anywhere]](/img/20241121/q29nII.jpg)