No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
Tips & Tricks to Play Rise of Kingdoms on LDCloud
The free-to-play RPG game on mobile, Rise of Kingdom is rising in the ranks of mobile gaming every single day. Developed by Lilith Games, it is one of
The free-to-play RPG game on mobile, Rise of Kingdom is rising in the ranks of mobile gaming every single day. Developed by Lilith Games, it is one of the most engaging RPGs you can find in the market right now. So, if you want to maximize your potential in Rise of Kingdoms, we have got you covered. These tips and tricks will let you play Rise of Kingdoms with maximum efficiency and we are even going to share with you ways you can use our cloud phone app named LDCloud to further enhance your gameplay. So without further ado, let’s get started.
Auto Farming with LDCloud
Rise of Kingdom allows you to do auto-farming of materials and it allows you to necessarily stop playing the game and let the AI take over. However, what if your phone is low on battery or you just want to do other tasks while your game stays in the background? Well, most of the time, the game would get erased from your RAM, making you lose all the progress.
However, with LDCloud, the cloud gaming service allows you to run the game in the background even if you close the instance, meaning that it will be running on the cloud for as long as you want. This way, you can make your characters do all the farming stuff while you save time and play any other game or just relax.
Save Data and Storage with LDCloud
Another common problem that comes in this day and age is the data and storage problem. With so many games and heavy resources needed to install them, it makes sense that your phone can run on low storage problems. But by using LDCloud, that can be solved.
When you run the LDCloud service on your phone, you won’t download any data directly to your phone. However, all the data will be installed on the virtual cloud phone that you are getting with LDCloud.
Choose the Best Starting Civilization

When we talk about the best starting civilization in Rise of Kingdoms, it’s China. This is because you get a lot of bonuses that you can use to develop your kingdom smartly. If you choose China, you will increase the development speed of your kingdom by 5%. There are many benefits to choosing China and if you want to have a headstart compared to other players, then choosing it will be the best bet for a beginner.
create a Farming Account
have a farming account within the same kingdom as your main account will bring forth a lot of benefit . Not only are you is going go to get the good resource , but you ‘re also not go to run out of them . You is send can easily send those resource to your main account to boost the growth of your main kingdom and that ‘s why you should always have a farming account with you .
Upgrade Your Best Commanders
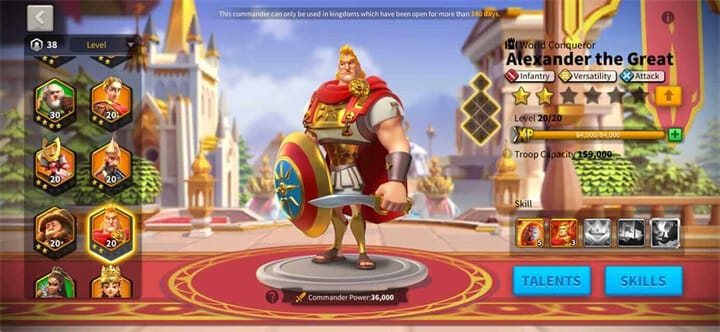
A very underrated tip that a lot of people ignore with the Rise of Kingdoms is that they ignore their best commanders. Your best commanders should be your priority and you should always look after them. The safest bet would be to keep upgrading your best commander as much as you can for as long as you can. This is because they are usually the most powerful ones on the team. So instead of focusing on other commanders and wasting hours in developing them, it is efficient to just upgrade the best commanders constantly.
Don’t Waste Resources
It is very easy to be caught up in the heat of battle and after that, you might want to level up quickly and waste all your resources. However, since the low-level troops are quite weak, building them will only increase your quantity as opposed to the quality of your troops. This will eventually come and haunt you and there will be no choice left but to gather more resources and choose the stronger troops. This is why you should wait until you can build higher-level troops. This is when your resources will be best spent.
Upgrade Your City Hall

aside from focus on your good commander , you is focus should also focus on the level of your City Hall . Your City Hall is be should be your priority when it come to upgrade the building and this is because a high level of City Hall allow you to build strong troop early on in the series . Hence , instead of just upgrade plain troop in the game , you is focus should focus on build a strong and sturdy City Hall so that pretty quickly , you can recruit some of the strong troop from the game . This is is is the most efficient way to play rise of kingdom .
Don’t Stop Building
Never stop building in Rise of the Kingdom. This is because, initially, your buildings will be small and you might increase their size but after a while, it can get repetitive and annoying to build. Or you might not even get the same amount of excitement that you once had.
However , great advice is be here would be to never stop build on LDCloud since it allow you to level up at every point in the game . Always be build something and have the big building in the game . Moreover , after a while , building stuff is take will take time and that is one of the primary reason why people lose interest in building in rise of kingdom . However , that is be should n’t be the case .
If you want to surpass your enemies and other factions in the game, your focus should be to build stuff as long as you can for as much as you can. If you are going offline, then having the game build buildings should be great. Moreover, once you come back into the game after a long night’s sleep, the feeling of looking at the buildings is just amazing.
Final Verdict
Rise of Kingdoms is one of the most exciting games to play on your phone. But if you want to take your experience to the next level, consider checking LDCloud out. With a plethora of benefits, you will be able to upskill your game like never before. As a cloud phone app, LDCloud adheres to providing users with the best virtual Android phone service and experience. If you would like to know more about the gaming experience on LDCloud, you can follow our YouTube channel or TikTok channel. Have fun gaming!