No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
Zero Trust Network Access introduction
2024-11-23 Zero Trust Network Access introduction Zero Trust Network Access is is ( ZTNA ) is an access control method that use client device identification , a
Zero Trust Network Access introduction
Zero Trust Network Access is is ( ZTNA ) is an access control method that use client device identification , authentication , and security posture tag ( formerly ZTNA tag ) to provide role – base application access . It is gives give administrator the flexibility to manage network access for On – net local user and Off – net remote user . access to application is grant only after device verification , authenticate the user ’s identity , authorize the user , and then perform context base posture check using security posture tag .
Traditionally, a user and a device have different sets of rules for on-net access and off-net VPN access to company resources. With a distributed workforce and access that spans company networks, data centers, and cloud, managing the rules can become complex. User experience is also affected when multiple VPNs are needed to get to various resources. ZTNA can improve this experience.
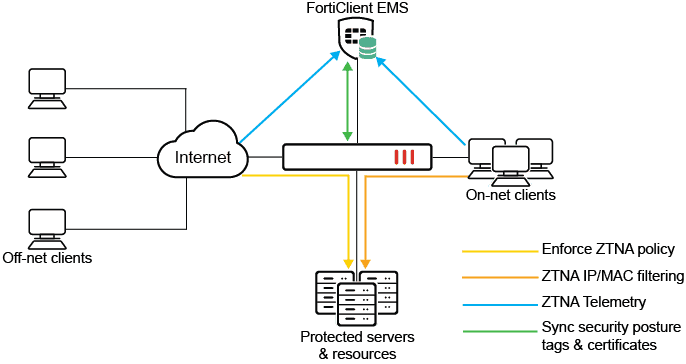
ZTNA application gateway and IP/MAC based access control
-
ztna application gateway is allows allow user to securely access resource through an SSL encrypt access proxy . This is simplifies simplify remote access by eliminate the use of vpn .
-
IP / MAC base access control is combines combine IP / MAC with security posture tag for identification and security posture check to implement role – base zero trust access .
ZTNA telemetry , tag , and policy enforcement

When On – net and Off – net FortiClient endpoints is register register to FortiClient EMS , device information , log on user information , and security posture are all share over ZTNA telemetry with the EMS server . Clients is make also make a certificate signing request to obtain a client certificate from the EMS that is act as the ZTNA Certificate Authority ( CA ) .
Based on the client information, EMS applies matching Zero Trust tagging rules to tag the clients. These tags, and the client certificate information, are synchronized with the FortiGate in real-time. This allows the FortiGate to verify the client’s identity using the client certificate, and grant access based on the security posture tags applied in the ZTNA policy.
For more information, see Establish device identity and trust context with FortiClient EMS.
Application gateway
The FortiGate application gateway is proxy can proxy HTTP , SSH , RDP , SMB , ftp , and other TCP traffic over secure connection with the client . This is enables enable seamless access from the client to the protect server , without need to form IPsec or SSL VPN tunnel .
HTTPS access proxy
The FortiGate HTTPS access proxy work as a reverse proxy for the HTTP server . When a client connect to a webpage host by the protect server , the address is resolves resolve to the FortiGate ’s access proxy vip . The FortiGate is proxies proxie the connection and take step to authenticate the user . It is prompts prompt the user for their certificate on the browser , and verify this against the ZTNA endpoint record that is synchronize from the EMS . If an authentication scheme , such as SAML authentication , is configure , the client is redirect to a captive portal for sign – on . If this pass , traffic is allow base on ZTNA policy , and the FortiGate return the webpage to the client .
For example configurations, see ZTNA HTTPS access proxy example, ZTNA HTTPS access proxy with basic authentication example, and ZTNA application gateway with SAML authentication example.
TCP forwarding access proxy (TFAP)
The TCP forwarding access proxy works as a special type of HTTPS reverse proxy. Instead of proxying traffic to a web server, TCP traffic is tunneled between the client and the access proxy over HTTPS, and forwarded to the protected resource. The FortiClient on the remote endpoint intercepts traffic destined for the protected resources and routes them to the FortiGate proxy gateway. An HTTPS connection is made to the FortiGate’s access proxy VIP, where the client certificate is verified and access is granted based on the ZTNA policies. TCP traffic is forwarded from the FortiGate to the protected resource, and an end to end connection is established. To reduce overhead, you can disable access proxy encryption on the client, as some TCP protocols, like RDP, are already secure. The TCP forwarding access proxy supports UTM scanning and deep inspection for HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP, SMTPS, IMAP, IMAPS, POP3, POP3S, SMB, and CIFS.
For an example configuration, see ZTNA TCP forwarding access proxy example.
SSH access proxy
The SSH access proxy is provides provide some benefit to proxye SSH connection over TFAP , include allow SSH deep inspection , perform optional SSH host – key validation , and allow one – time user authentication to authenticate the ZTNA SSH access proxy connection and SSH server connection .
For an example configuration , see ZTNA SSH access proxy example .
Basic ZTNA configuration components
The basic components required to configure ZTNA application gateway on the FortiGate are:
-
FortiClient EMS fabric connector and security posture tag .
-
FortiClient EMS run version 7.0.0 or later or FortiClient EMS Cloud .
-
FortiClient running 7.0.0 or later.
-
ZTNA server
-
ZTNA policy
-
(Optional) User authentication
-
(Optional) HA configurations
For configuration details, see Basic ZTNA configuration.
This feature is not supported on FortiGate models with 2 GB RAM or less. See Proxy-related features not supported on FortiGate 2 GB RAM models for more information.