No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
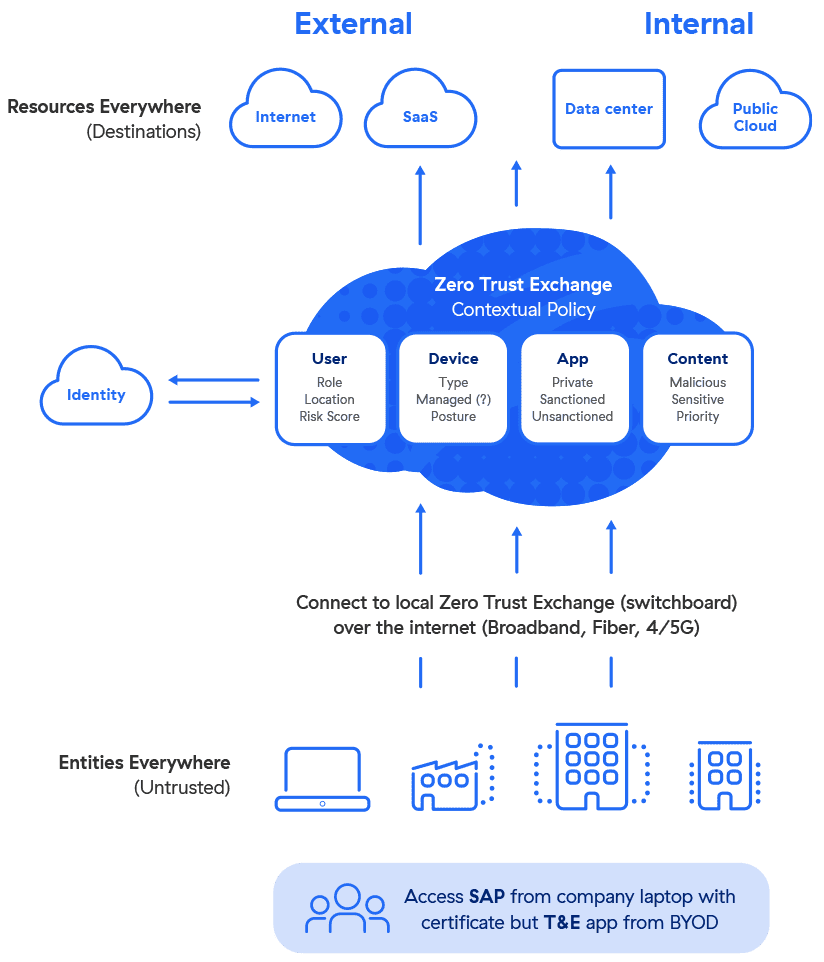
What is Zero Trust? | Benefits & Core Principles
2024-11-25 Use Cases of Zero Trust1. Reduce Business and Organizational RiskZero trust architecture reduces risk by stopping all applications and services from c
Use Cases of Zero Trust
1. Reduce Business and Organizational Risk
Zero trust architecture reduces risk by stopping all applications and services from communicating until they are authenticated in line with predefined trust principles. A zero trust strategy helps you understand how assets in your environment are communicating and, as baselines are established, enables you to eliminate overprovisioned software and services to further mitigate risk.
2. Gain Access Control over Cloud and Container Environments
Zero trust security policy are apply base on workload identity , unaffected by IP address , port , and protocol . protection is tie directly to the workload themselves and remain constant even as the environment change , significantly ease the access management , visibility , and general workload security challenge associate with cloud service provider and container .
3 . reduce the risk of a Data Breach
Zero trust architecture inspects every request, authenticates every user and device, and assesses all permissions before granting access, and then continually reassesses trust as context changes. Additionally, zero trust models create one-to-one secure connections, with no means of lateral movement. Thus, even if an attacker gains entry to your environment, they can’t access or steal data if they can’t establish trust.
4 . Support Compliance Initiatives
Zero trust renders all user and workload connections invisible from the open internet, simplifying compliance with PCI DSS, NIST 800-207, and more while supporting smoother audits. Zero trust microsegmentation enables you to create perimeters around certain types of sensitive data using fine-grained controls to separate regulated and non-regulated data. During audits, or in the event of a data breach, microsegmentation provides superior visibility and control compared to flat network architectures.


![35 Best Free Movie Websites in 2024 [Newest Update]](/img/20241112/AyREz4.jpg)