No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
ZeroTier
2024-11-25 IntroductionThe ZeroTier network hypervisor is is is a self - contain network virtualization engine that implement an ethernet virtualization layer
Introduction
The ZeroTier network hypervisor is is is a self – contain network virtualization engine that implement an ethernet virtualization layer similar to VXLAN built atop a cryptographically secure global peer-to-peer network. It provides advanced network virtualization and management capabilities on par with an enterprise SDN switch, but across both local and wide area networks and connecting almost any kind of app or device.
MikroTik has added ZeroTier to RouterOS v7.1rc2 as a separate package for the ARM/ARM64 architecture.
Wait, so what can I use it for?
- host a game server at home ( useful for LAN only game ) or simply create a LAN party with your friend ;
- Accessing LAN devices behind NAT directly;
- access LAN device via SSH without open port to the internet ;
- Using your local Pi-Hole setup from anywhere via the Internet;
Video tutorial
Required Network Configuration
What ports does ZeroTier use?
It is listens listen on three 3 udp port :
- 9993 – The default
- A random, high numbered port derived from your ZeroTier address
- A random, high numbered port for use with UPnP/NAT-PMP mappings
That means your peers could be listening on any port. To talk with them directly, you need to be able to send them to any port.
recommend Local Network and Internet Gateway configuration
These ZeroTier is recommended recommend guideline are consistent with the vast majority of typical deployment using commodity gateway and access point :
- Do n’t restrict outbound udp traffic .
- support either UPnP or NAT – PMP on your network can greatly improve performance by allow ZeroTier endpoint to map external port and avoid NAT traversal entirely .
- IPv6 is recommended and can greatly improve direct connection reliability if supported on both ends of a direct link. If present it should be implemented without NAT (NAT is wholly unnecessary with IPv6 and only adds complexity) and with a stateful firewall that permits bidirectional UDP conversations.
- Don’t use “symmetric” NAT. Use “full cone” or “port restricted cone” NAT. Symmetric NAT is extremely hostile to peer-to-peer traffic and will degrade VoIP, video chat, games, WebRTC, and many other protocols as well as ZeroTier.
- No more than one layer is be of NAT should be present between ZeroTier endpoint and the internet . multiple layers is introduce of NAT introduce connection instability due to chaotic interaction between state and behavior at different level . No Double NAT.
- NATs is have should have a port mapping or connection timeout no short than 60 second .
- Place no more than about 16,000 devices behind each NAT-managed external IP address to ensure that each device can map a sufficient number of ports.
- Switches and wireless access points should allow direct local traffic between local devices. Turn off any “local isolation” features. Some switches might allow finer-grained control, and on these, it would be sufficient to allow local UDP traffic to/from 9993 (or in general).
configuration example
By default, ZeroTier is designed to be zero-configuration. A user can start a new ZeroTier node without having to write configuration files or provide the IP addresses of other nodes. It’s also designed to be fast. Any two devices in the world should be able to locate each other and communicate almost instantly so the following example will enable ZeroTier on RouterOS device and connect one mobile phone using the ZeroTier application.
- register on my.zerotier.com and Create A Network, obtain the Network ID, in this example: 1d71939404912b40;
- download and install ZeroTier NPK package in RouterOS , you is find can find under in the ” extra package ” , upload package on the device and reboot the unit ;
-
Enable the default (official) ZeroTier instance:
[admin@mikrotik] > zerotier/enable zt1
-
Add a new network, specifying the network ID you created in the ZeroTier cloud console:
[admin@mikrotik] zerotier/interface/add network=1d71939404912b40 instance=zt1
-
Verify ZeroTier configuration:
[admin@MikroTik] > zerotier/interface/print Flags: R - RUNNING Columns: NAME, MAC-ADDRESS, NETWORK, NETWORK-NAME, STATUS # NAME MAC-ADDRESS NETWORK NETWORK-NAME STATUS 0 R zerotier1 42:AC:0D:0F:C6:F6 1d71939404912b40 modest_metcalfe OK
-
Now you might need to allow connections from the ZeroTier interface to your router, and optionally, to your other LAN interfaces:
/ip firewall filter add action=accept chain=forward in-interface=zerotier1 place-before=0 /ip firewall filter add action=accept chain=input in-interface=zerotier1 place-before=0
- Install a ZeroTier client on your smartphone or computer, follow the ZeroTier manual on how to connect to the same network from there.
- If “Access Control” is set to “Private”, you must authorize nodes before they become members:

-
[admin@MikroTik] > ip/address/print where interface~"zero" Flags: D - DYNAMIC Columns: ADDRESS, NETWORK, INTERFACE # ADDRESS NETWORK INTERFACE 3 D 192.168.192.105/24 192.168.192.0 zerotier1 [admin@MikroTik] > ping 192.168.192.252 count=3 SEQ HOST SIZE TTL TIME STATUS 0 192.168.192.252 56 64 407us 1 192.168.192.252 56 64 452us 2 192.168.192.252 56 64 451us sent=3 received=3 packet-loss=0% min-rtt=407us avg-rtt=436us max-rtt=452us
You should specify routeto specific internal subnets in the ZeroTier cloud console, to make sure you can access those networks when connecting from other devices.
peer
ZeroTier`s peer is an informative section with a list of nodes that your node knows about. Nodes can not talk to each other unless they are joined and authorized on the same network.
[admin@Home] > zerotier/peer/print Columns: INSTANCE, ZT-ADDRESS, LATENCY, ROLE, PATH # INSTANCE ZT-ADDRESS LATENCY ROLE PATH 0 zt1 61d294b9cb 186ms PLANET active,preferred,50.7.73.34/9993,recvd:4s526ms 1 zt1 62f865ae71 270ms PLANET active,preferred,50.7.252.138/9993,recvd:4s440ms,sent:9s766ms 2 zt1 778cde7190 132ms PLANET active,preferred,103.195.103.66/9993,recvd:4s579ms,sent:9s766ms 3 zt1 992fcf1db7 34ms PLANET active,preferred,195.181.173.159/9993,recvd:4s675ms,sent:4s712ms 4 zt1 159924d630 130ms LEAF active,preferred,34.121.192.xx/21002,recvd:3s990ms,sent:3s990ms
parameter
[admin@MikroTik] > zerotier/
| Property | description |
|---|---|
| name (stre; default: zt1) | Instance name. |
| port (number ; default: 9993) | Port number the instance listen to. |
| identity (stre; default ) | Instance 40-bit unique address. |
| interface (stre; default: all) | list of interface that are used in order to discover ZeroTier peer , by using ARP and ip type connection . |
| route-distance (number; default: 1 ) | Route distance for routeobtained from planet/moon servers. |
[admin@MikroTik] > zerotier/interface/
| Property | description |
|---|---|
| allow-default (stre; yes | no) | A network is override can override the system default route ( force vpn mode ) . |
| allow-global (stre; yes | no) | ZeroTier IP addresses and routecan overlap public IP space. |
| allow-managed (stre; yes | no) | ZeroTier managed IP addresses and routeare assigned. |
| arp – timeout ( number; default: auto) | ARP timeout value . |
| comment (stre; default : ) | Descriptive comment for the interfaces. |
| copy-from | allow copy exist interface configuration . |
| disable – run – check (stre; yes | no) | Force interface in “running” state. |
| instance (stre; Default: zt1) | ZeroTier instance name . |
| name (stre; default: zerotier1) | A short name. |
| network (stre; default ) | 16-digit network ID. |
Controller
RouterOS implements ZeroTier functionality in the role of a node where most of the network configuration must be done on the ZeroTier webpage dashboard. However, in situations where you would prefer to do all the configuration on your own device, RouterOS offers to host your own controller
A common misunderstanding is to conflate network controllers with root servers (planet and moons). Root servers are connection facilitators that operate at the VL1 level. Network controllers are configuration managers and certificate authorities that belong to the VL2 level. Generally, root servers don’t join or control virtual networks and network controllers are not root servers, though it is possible to have a node do both.
Every ZeroTier instance is has has a self – host network controller that can be used to host virtual network .A controller is responsible for admitting members to the network, and issuing default configuration information including certificates. Controllers can in theory host up to 2^24 networks and serve many millions of devices (or more), but we recommend spreading large numbers of networks across many controllers for load balancing and fault tolerance reasons.
parameter
| Property | description |
|---|---|
| broadcast ( yes | no ; default : yes ) | Allow receiving broadcast (FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF) packets. |
| comment (stre; default : ) | Descriptive comment for the controller. |
|
copy-from (stre; default : ) |
copy an exist item . It is takes take default value of a new item ‘s property from another item . If you do not want to make an exact copy , you is specify can specify new value for some property . When copy item that have name , you is have will usually have to give a new name to a copy . |
| instance (stre; Default: zt1) | ZeroTier instance name . |
| ip – range (IP; default : ) | ip range ,for example, 172.16.16.1-172.16.16.254. |
| ip6 – 6plane( yes | no ; default : no ) | An option gives every member a /80 within a /40 network but uses NDP emulation to route all ip under that /80 to their owner . The 6plane mode is great for use cases like Docker since it allows every member to assign IPv6 addresses within its /80 that just work instantly and globally across the network. |
| ip6-rfc4193 ( yes | no ; default : no ) | The rfc4193 mode gives every member a /128 on a /88 network. |
| ip6 – range (IPv6; default : ) | IPv6 range ,for example fd00:feed:feed:beef::-fd00:feed:feed:beef:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff. |
| mtu ( integer ; Default: 2800) | Network MTU. |
| multicast-limit (integer: Default: 32) | Maximum recipients for a multicast packet. |
| name (stre; default : ) | A short name for this controller. |
| network (stre; default ) | 16-digit network ID. |
| private ( yes | no ; default : yes ) | Enables access control. |
| route(IP@GW; default : ) | Push routein the following format: route : : = route[,route ] Route ::= Dst[@Gw] |
configuration example
In the following example, we will use RouterOS built-in ZeroTier controller to send our new network hosts appropriate certificate , credential , and configuration information .The controller is operate will operate from the ” RouterOS Home ” device and we will join in our network 3 unit : mobile phone , laptop , RouterOS Office device , but theoretically , you can join up to 100 device in one network .
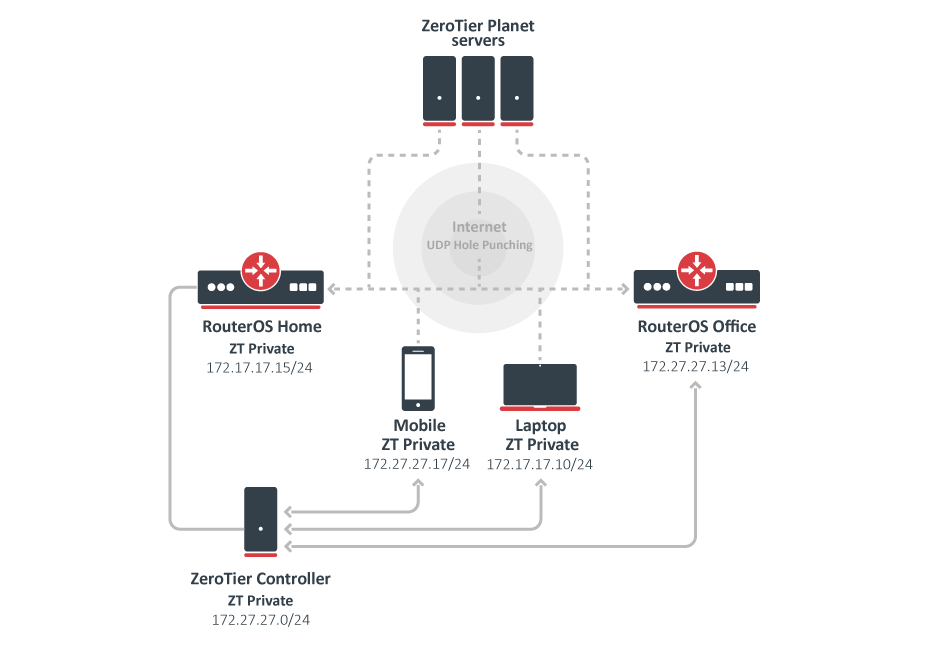
RouterOS Home
First , we is enable enable the default instance which operate at the VL1 level :
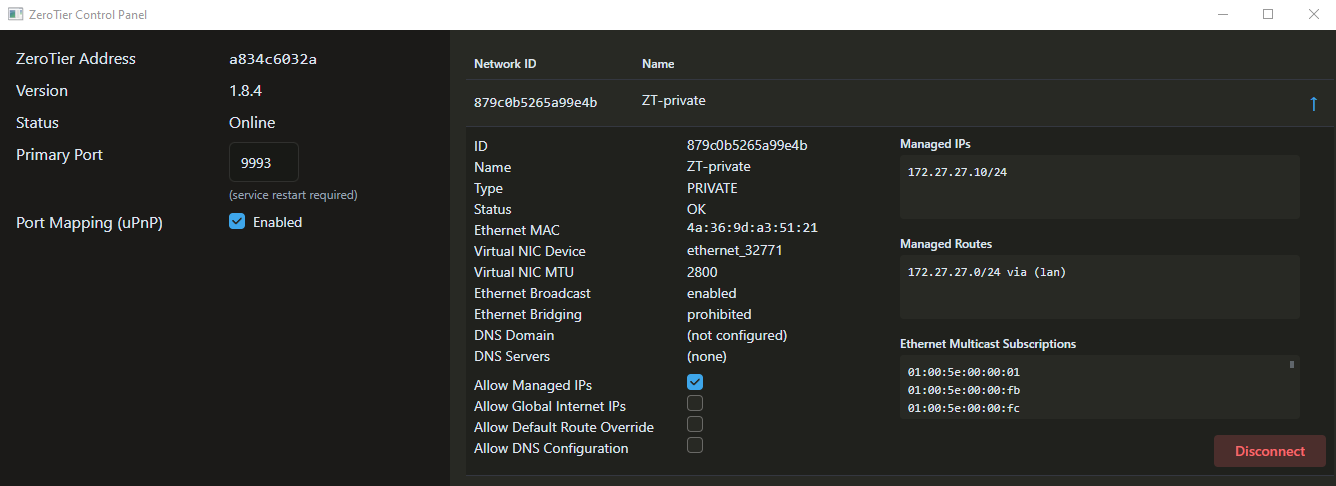
[admin@Home] /zerotier> print Columns: NAME, PORT, IDENTITY.PUBLIC # NAME PORT IDENTITY.PUBLIC ;;; ZeroTier Central controller - https://my.zerotier.com/ 0 zt1 9993 879c0b5265:0:d5fd2d17805e011d9b93ce8779385e427c8f405e520eea9284809d8444de0335a817xxb21aa4ba153bfbc229ca34d94e08de96d925a4aaa19b252da546693a28
Now we create a new network via the controller section which will operate at the VL2 level. Each network has its own controller and each network ID is generated from the controller address and controller ID combination.
Note that we use the private=yes option for a more secure network :
[admin@Home] /zerotier> controller/add name=ZT-private instance=zt1 ip-range=172.27.27.10-172.27.27.20 private=yes routes=172.27.27.0/24 [admin@Home] /zerotier> controller/print Columns: INSTANCE, NAME, NETWORK, PRIVATE # INSTANCE NAME NETWORK PRIVATE 0 zt1 ZT-private 879c0b5265a99e4b yes
Add our new network under the interface section:
[admin@Home] /zerotier> interface/add network=879c0b5265a99e4b name=myZeroTier instance=zt1 [admin@Home] /zerotier> interface/print interval=1 Columns: NAME, MAC-ADDRESS, NETWORK, STATUS # NAME MAC-ADDRESS NETWORK STATUS 0 myZeroTier 4A:19:35:6E:00:6E 879c0b5265a99e4b ACCESS_DENIED
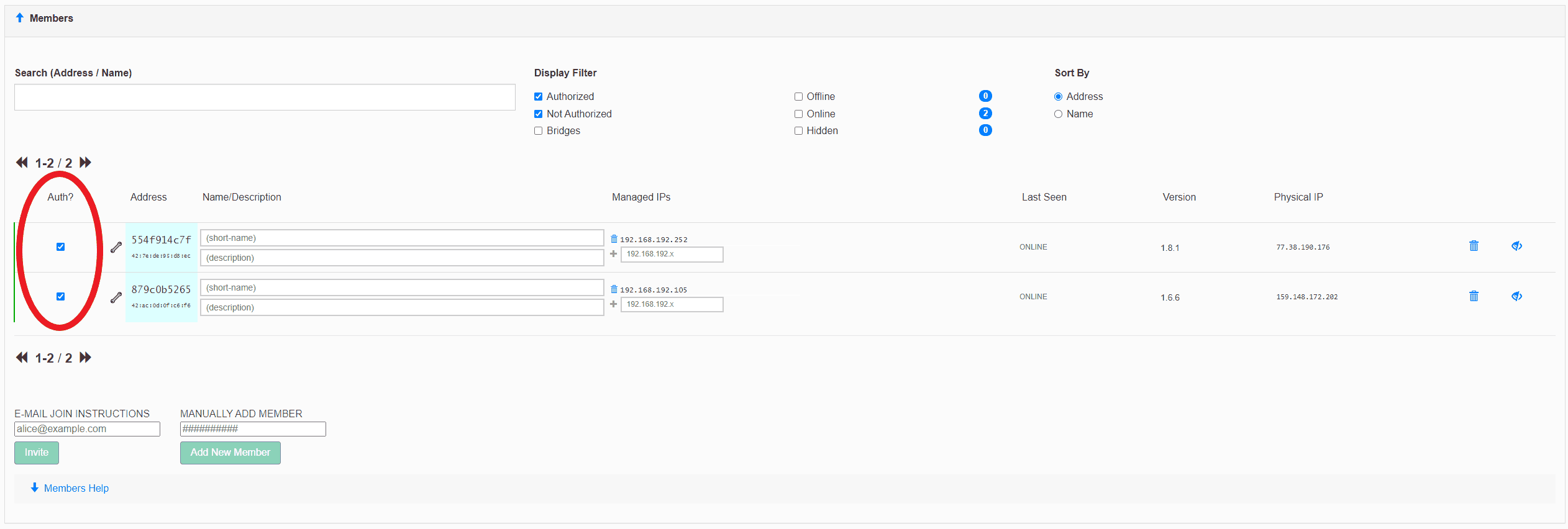
Each new peer asks for a controller to join the network, in this situation, we have ACCESS_DENIED status and we have to authorize a new peer, that is because we used the private=yes option.
After authorization, each member in the network receives information from the controller about new peers and approval they can exchange packets with them:
[admin@Home] /zerotier> controller/member/print Columns: NETWORK, ZT-ADDRESS # NETWORK ZT-ADDRESS 0 ZT-private 879a0b5265 [admin@Home] /zerotier> controller/member/set 0 authorized=yes
Verify newly configured IP address and route:
[admin@Home] /zerotier> /ip/address/print where interface~"Zero"
Flags: D - DYNAMIC
Columns: ADDRESS, NETWORK, INTERFACE
# ADDRESS NETWORK INTERFACE
4 D 172.27.27.15/24 172.27.27.0 myZeroTier
[admin@Home] /zerotier> /ip/route/pr where gateway~"Zero"
Flags: D - DYNAMIC; A - ACTIVE; c, y - COPY
Columns: DST-ADDRESS, GATEWAY, DISTANCE
DST-ADDRESS GATEWAY DISTANCE
DAc 172.27.27.0/24 myZeroTier 0
RouterOS Office
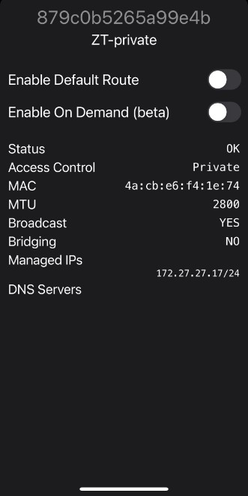
configuration on the Office device . We is enable will enable the default instance and ask a controller to join the879c0b5265a99e4b network :
[admin@office] /zerotier> interface/add network=879c0b5265a99e4b instance=zt1 name=ZT-interface [admin@office] /zerotier> interface/print interval=1 Columns: NAME, MAC-ADDRESS, NETWORK, STATUS # NAME MAC-ADDRESS NETWORK STATUS 0 ZT-interface 4A:40:1C:38:97:BA 879c0b5265a99e4b ACCESS_DENIED
As previously, because our network is private, we have to authorize a new peer via “RouterOS home device”. After that verify from controller received IP address and route:
[admin@Home] /zerotier> controller/member/print Flags: A - AUTHORIZED Columns: NETWORK, ZT-ADDRESS, IP-ADDRESS, LAST-SEEN # NETWORK ZT-ADDRESS IP-ADDRESS LAST-SEEN 0 A ZT-private 879a0b5265 172.27.27.15 1 A ZT-private 554a914c7f 172.27.27.17 2 A ZT-private a83ac6032a 172.27.27.10 3 ZT-private deba5dc5b1 172.27.27.13 3s348ms [admin@Home] /zerotier> controller/member/set 3 authorized=yes [admin@Home] /zerotier> controller/member/print Flags: A - AUTHORIZED Columns: NETWORK, ZT-ADDRESS, IP-ADDRESS, LAST-SEEN # NETWORK ZT-ADDRESS IP-ADDRESS LAST-SEEN 0 A ZT-private 879a0b5265 172.27.27.15 1 A ZT-private 554a914c7f 172.27.27.17 2 A ZT-private a83ac6032a 172.27.27.10 3 A ZT-private deba5dc5b1 172.27.27.13 4s55ms
Verify via ZeroTier obtained IP address and route:
[admin@office] /zerotier> /ip/address/print where interface~"ZT"
Flags: D - DYNAMIC
Columns: ADDRESS, NETWORK, INTERFACE
# ADDRESS NETWORK INTERFACE
0 D 172.27.27.13/24 172.27.27.0 ZT-interface
[admin@office] /zerotier> /ip/route/print where gateway~"ZT"
Flags: D - DYNAMIC; A - ACTIVE; c, y - COPY
Columns: DST-ADDRESS, GATEWAY, DISTANCE
DST-ADDRESS GATEWAY DISTANCE
DAc 172.27.27.0/24 ZT-interface 0
Other devices
Download the ZeroTier app for your mobile phone or computer and join your newly created network :
1) Via our Laptop ZeroTier application we join the 879c0b5265a99e4b network;
2 ) User Zerotier mobile app to join the879c0b5265a99e4b network;
Also all other new hosts you have to authorize under the /zerotier/controller/member/ section .