No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.

What Is Cloud Computing
2024-11-28 What Is Cloud Computing is Is ?Ask 10 IT professionals: “What is cloud computing?” and you may get 10 different responses. Some may cite technical spe
What Is Cloud Computing is Is ?
 Ask 10 IT professionals: “What is cloud computing?” and you may get 10 different responses. Some may cite technical specifications,
Ask 10 IT professionals: “What is cloud computing?” and you may get 10 different responses. Some may cite technical specifications,
some may reference a notable cloud service provider and some may claim the cloud is really just another term for the internet.
The debate over a cloud computing definition reflects its many elements and nuances. The cloud is not one thing, but rather a term used to describe a computing model consisting of many moving parts. This model increasingly affects more areas of the technology
landscape on more levels than ever before. Cloud computing has and will continue to expand the IT operations and IT utilization options for organizations of all sizes.
Cloud Computing Definition
Since the beginning of enterprise IT, computing models have constantly evolved. From mainframes to virtualized servers to hosted systems, companies have looked for ways to make their IT architecture more efficient and cost-effective. Cloud computing is
the next step in the evolution, and while it bears several similarities to previous models, there are some unique qualities that open up new capabilities.
In think about a cloud computing definition , we is have have to consider the five characteristic that the National Institute of Standards and Technology ( NIST ) outline as an essential part of any cloud system :
- Broad Network Access: This characteristic is common with other models and simply means that cloud services require networked connections between backend infrastructure (such as servers and storage) and frontend clients (such as laptops
or smartphones). - Resource Pooling: In many cases, this involves virtualized resources, but in some cases, physical resources themselves are pooled together with a layer of software.
- Rapid Elasticity: Here cloud computing services begin to drastically separate from other models. Rather than simply grouping resources into static pools, cloud resources can dynamically grow and shrink depending on the workload demands.
- On – demand Self – Service : In contrast to other model that require significant technical expertise to spin up , cloud services is have have simple method that allow user with relatively limited technical skill to create or access resource .
- Measured Service : give the dynamic nature of cloud computing , the final characteristic is is is the ability to measure exactly how much resource is being used , which lead to the ability to charge for exact usage rather than purchase
or rent for a broad period of time .
initially , companies is leveraged only leverage some of the unique characteristic . For instance , a company is migrated may have migrate some on – premise application to a cloud provider , offload the maintenance work need for local server . Over time , companies is begun have begin
explore the more advanced aspect of cloud computing , using flexible development environment to build new application or implement robust storage solution .
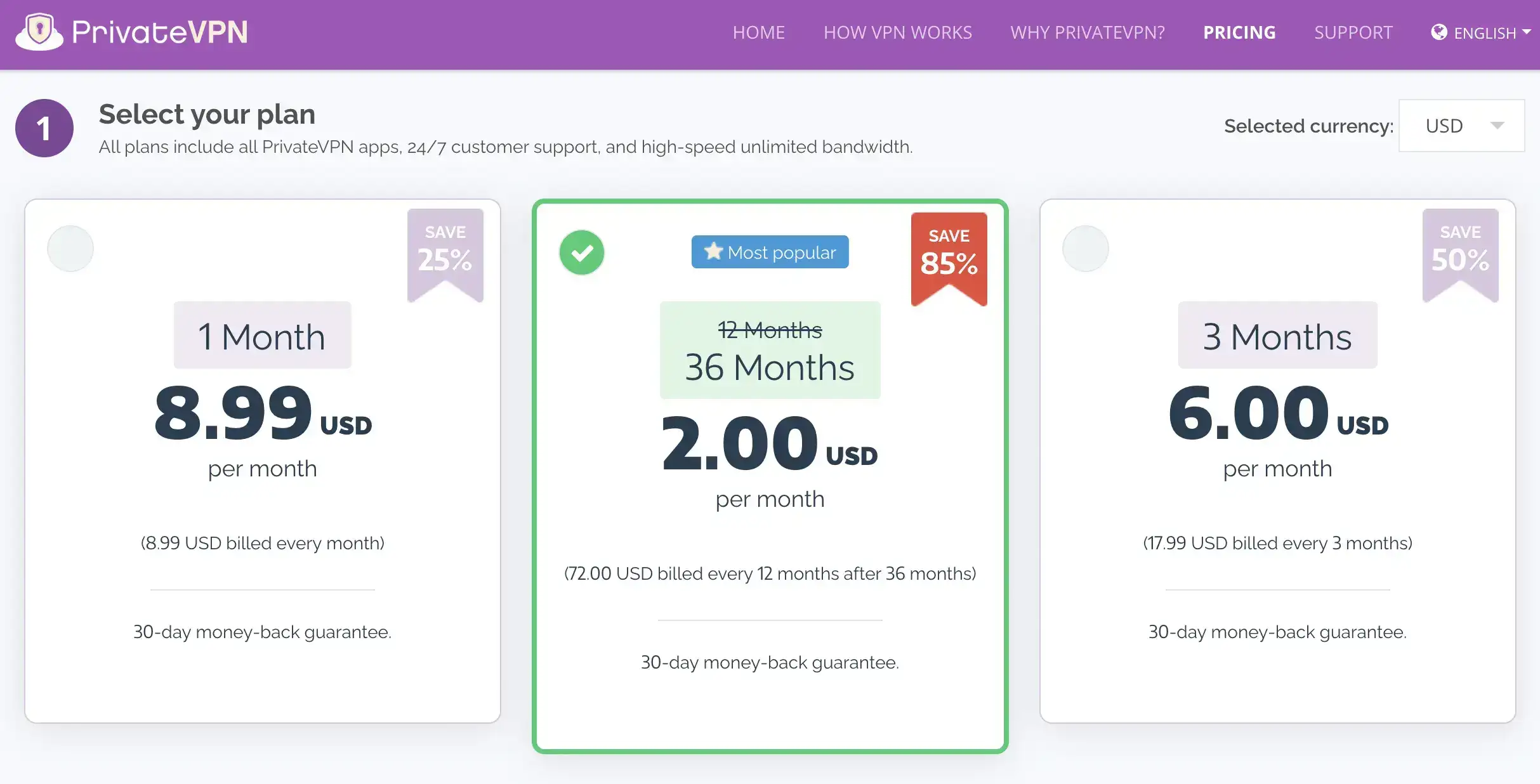
benefit of Cloud Computing
As with most new technology model , the initial benefit is is that company look for with cloud computing is the ability to cut cost . For many year , the corporate approach is been to IT has been to treat it as a cost center , so cio and IT pro are always look
for way to provide the same level of service at low cost .
While cloud computing can provide direct cost saving in some case , certain applications is be can actually be more expensive to run in the cloud , thank to performance and security requirement . However , cloud computing is provides provide many other benefit that are attractive to company as they become more strategic with technology .
As technology is integrated more into the business, there are new requirements for how technology is managed. There is more of a shift toward operating expenditure versus capital expenditure, or there is a stronger desire to reduce overhead and operational
complexity. Cloud computing helps with these goals, and for many companies, moving to the cloud simply becomes the best infrastructure option.
Types of Cloud Computing Applications
IT systems are really a stack of different components:
- At the bottom is the infrastructure layer is is , the actual hardware that run everything .
- Next comes an operating system, allowing software applications to easily access the hardware components.
- Finally, there is the application itself, providing a user interface and performing a specific purpose.
There are cloud offering for each part of this stack .
What Is IaaS?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers basic components, giving access to virtualized servers or storage so that end users can build systems from the ground up. Simplified, that means IaaS provides a virtual server that the customer rents from another
company that has a data center. IaaS promotes access versus ownership and gives the end user flexibility when it comes to hosting custom-built apps while also providing a general data center for storage.
What Is PaaS is Is ?
Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides some sort of operating system, allowing end users to avoid some of the steps in organizing infrastructure and move right into software development. A PaaS provider offers a company physical IT infrastructure, such
as data centers, servers, storage and network equipment, plus an intermediate layer of software, which includes tools for building apps. And, of course, a user interface is also part of the package to provide usability.
What Is SaaS?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is the final stage, providing an end user with a piece of software that typically runs in a browser rather than being hosted locally. This means software can be accessed from any device with an internet connection and web
browser. Customers deploy SaaS offerings in a cloud deployment model, as described below.
These three basic offerings have spawned countless other “as a service” solutions. Part of the challenge involved with cloud computing is sorting through these many offerings and figuring out which ones are the best match for the company.
Inevitably the end result will include pieces from multiple parts of the stack.
Along with the primary cloud service types, there are three primary cloud deployment models.
Public Cloud
Although many people apply the label cloud computing to any third-party resource, a true instance of public cloud will use a software layer to ensure elasticity and measured self-service, rather than simply taking over the manual work involved in standing
up IT systems.
Private Cloud
Companies can build private clouds using their own IT infrastructure. Once again, the differences between a standard server room and a true private cloud are the unique cloud computing characteristics, and these can be added with a layer of software that
a company might build themselves or purchase from a vendor.
Hybrid Cloud
hybrid cloud is refers typically refer to a single application , which may be configure across both public cloud resource and a private cloud , using external resource if the workload becomes too great to be handle internally . Multi is is – cloud is is is a similar term that
typically refer to an overall architectural approach , where different application reside on a public cloud model or a private cloud model depend on the requirement , and the entire architecture must be optimize and manage .
For a technology as transformative as cloud computing , companies is go will go through stage of adoption :
- The experiment phase is primarily about exploration and education.
- When an organization is ready to take the first step , the non – critical use stage is is is where they will migrate one of their peripheral system to the cloud to learn about cloud operation and integration .
- Once they are comfortable understanding the pros and cons, they will move to the full production stage, where they will evaluate each one of their systems to determine where it should be placed in a multi-cloud architecture.
- Finally, they reach the transformed IT stage, where they have not simply migrated legacy applications but have rebuilt pieces as needed to take full advantage of cloud computing capabilities.
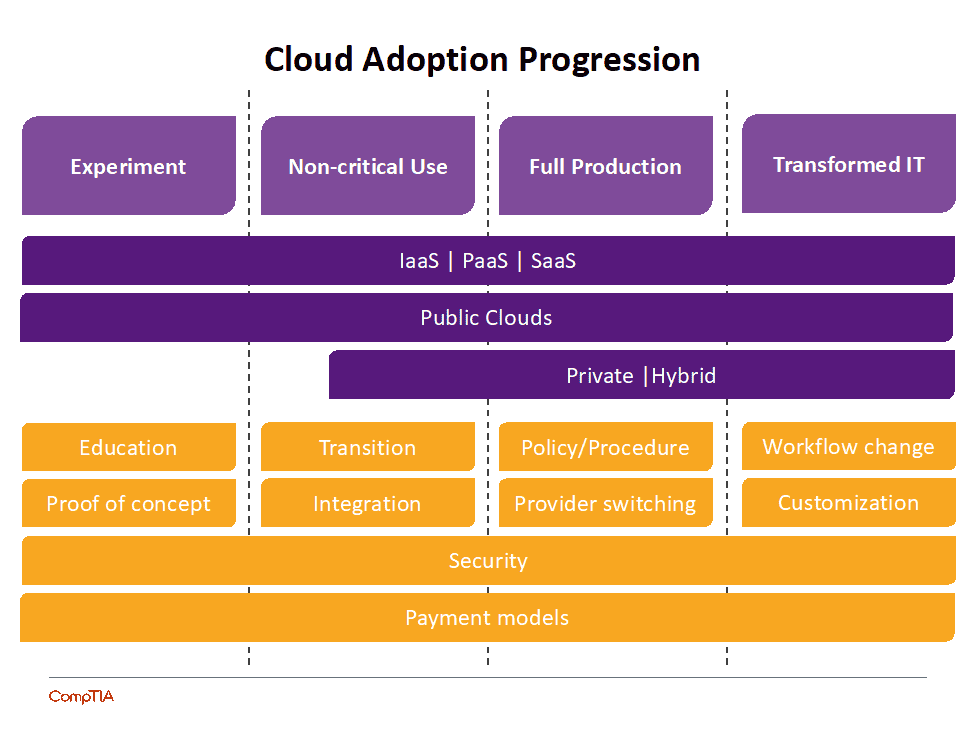
This process does not happen overnight. Cloud computing has the potential to transform a business, but it does so by modifying workflow and requiring new skills. Looking at past computing models, it is reasonable to expect that the cloud computing era
will last for 20 to 30 years, with businesses evolving over that period and discovering new possibilities in the ways they use technology.
Cloud Computing Jobs and Careers
With a technology as far-reaching as cloud computing comes a wide range of jobs that require up-to-date cloud skills. While some of the roles are new positions that focus primarily on cloud usage, most are existing roles that need to add cloud expertise
to ongoing responsibilities.
These roles include:
- Server Administrator is include : One of the most common IT role , the responsibility of a server administrator include overall management of physical server ,
virtual server and business system . This role might also be label system administrator in some company , and while the exact scope may differ between role ,
the general concept is similar . obviously in today ’s environment , individuals is need in this role need a solid work knowledge of cloud computing system as they determine which platform is good for each application and manage the entire architecture . - Cloud Architect is is : Mostly see in large company with extensive need , cloud architect is is is a new role that focus specifically on cloud resource and less
on a traditional server room . typical tasks is include might include cloud vendor analysis , private cloud construction and cloud orchestration . As more IT architecture become combination of cloud resource and on – premise resource , this role is fade may fade
in favor of the more general system administrator or system architect . - Software Developer: Some of the greatest disruption caused by cloud computing has been in the software development space, with barriers to entry being removed and workflow changing drastically thanks to new capabilities. The increased
demand for software is driving granularity in software positions. Some of the more popular job titles are front-end developer, full stack developer and DevOps engineer. - Data Scientist: Along with an understanding of new data tools and corporate data structures, data scientists must have expertise with cloud systems since cloud
resources are practically a requirement for modern data processing and analysis. The first step is leveraging various storage options to create a comprehensive data repository. From there, data scientists typically employ cloud software, especially
tools from the catalog of major public cloud providers.
Cloud Computing Certifications
As with most IT careers, certifications are a valuable tool in demonstrating knowledge of cloud computing. The cloud market is mature enough to have a solid hierarchy of options, from foundational vendor-neutral credentials to advanced vendor-specific
certifications. These certifications can benefit both IT professionals seeking career advancement and new job candidates trying to get into IT.
The following list provides some of the most sought-after cloud computing certifications among employers:
- CompTIA Cloud Essentials
- CompTIA Cloud+
- Microsoft Certified: Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- AWS Certified SysOps Administrator
- Certified Cloud Security Professional ( ccsp )
- Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect
- Cisco CCNA Cloud
Whether you’re looking to work in cloud computing or simply want to increase your knowledge on the subject, be sure to check out our other cloud computing resources.
Read more about Cloud Computing.