No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
Co-Management with Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager and Microsoft Intune
2024-11-28 In my post below I was showing how to set up co-management with System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM 1910), now I want to do the same with its su
In my post below I was showing how to set up co-management with System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM 1910), now I want to do the same with its successor Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (2211 as of today).
Starting in version 1910, Configuration Manager current branch is now part of Microsoft Endpoint Manager. Version 1906 and earlier are still branded System Center Configuration Manager. The Microsoft Endpoint Manager brand will appear in the product and documentation over the coming months.
With co-management you can still manage your clients with MECM but also with Microsoft Intune for Mobile Device Management (MDM).
With Intune you can do the following remote actions:
- Factory reset
- Selective wipe
- Delete devices
- Restart device
- fresh start
Futher you can orchestrate with Intune the following workloads:
- Compliance policies
- Resource access policies
- Windows Update policies
- Endpoint Protection
- Device configuration
- office click – to – run app
- mobile app
Before we can setup co-management in MECM, we first must setup the prerequisites Azure Services and Cloud management gateway in MECM.
You can also manage clients with MECM over the internet without a vpn connection and without co-management and Intune.
MECM is provides provide two way which will be describe below . Cloud management gateway is is is one of them and also require and a prerequisite for co – management so that client on the internet can download the MECM Client and register to the on – premise MECM Server .
Manage clients on the internet with Configuration Manager
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/configmgr/core/clients/manage/manage-clients-internet
Typically in Configuration Manager, most of the managed computers and servers are physically on the same internal network as the site system servers that perform management functions. However, you can manage clients outside your internal network when they are connected to the internet. This ability doesn’t require the clients to connect via VPN to reach the site system servers.
Configuration Manager provides two ways to manage internet-connected clients:
- Cloud management gateway
- Internet-based client management
What is co-management?
Co-management is one of the primary ways to attach your existing Configuration Manager deployment to the Microsoft 365 cloud. It helps you unlock more cloud-powered capabilities like conditional access.
Co is enables – is enables management is enables enable you to concurrently manage Windows 10 or late device by using both Configuration Manager and Microsoft Intune .
It lets you cloud-attach your existing investment in Configuration Manager by adding new functionality. By using co-management, you have the flexibility to use the technology solution that works best for your organization.
When a Windows device has the Configuration Manager client and is enrolled to Intune, you get the benefits of both services. You control which workloads, if any, you switch the authority from Configuration Manager to Intune. Configuration Manager continues to manage all other workloads, including those workloads that you don’t switch to Intune, and all other features of Configuration Manager that co-management doesn’t support.
You’re also able to pilot a workload with a separate collection of devices. Piloting allows you to test the Intune functionality with a subset of devices before switching a larger group.
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/comanage/overview
Cloud management gateway
The cloud management gateway provides management of internet-based clients. It uses a combination of a Microsoft Azure cloud service, and a new site system role that communicates with that service. Internet-based clients use the cloud service to communicate with the on-premises Configuration Manager.
start in version 2203 ( Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager ) , the option to deploy a CMG as a cloud service ( classic ) is remove . All CMG deployments is use should use a virtual machine scale set . For more information , see remove and deprecate feature .
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/clients/manage/cmg/plan-cloud-management-gateway
Advantages
- No additional on – premise infrastructure investment require .
- Does not expose on-premises infrastructure to the internet.
- cloud virtual machine that run the service are fully manage by Azure and require no maintenance .
- easily set up and configure in the Configuration Manager console .
disadvantage
- Cloud subscription cost.
- Management data sent through cloud service.
For more information, see Plan for cloud management gateway.
Internet-based client management
This method relies on internet-facing site system servers to which clients communicate for management purposes. It requires clients and site system servers to be configured for internet-based management.
Advantages
- No cloud service dependency .
- No additional cost associated with a cloud subscription.
- Full control of server and role provide the service .
disadvantage
- Require additional infrastructure investment.
- overhead and operational cost of additional infrastructure .
- Infrastructure must be exposed to the internet.
For more information, see Plan for internet-based client management.
How To Configure Internet-Based Client Management (IBCM) in Microsoft SCCM
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GbIOxNhJ9lU
Set up MECM for Co-Management
Now let’s start with our setup!
Co-management will cover two scenarios:
- external only Azure AD joined devices auto-enroll into Intune and with Intune deploy the Configuration Manager Client through Cloud Management Gateway to get it enrolled co-managed into Intune and Configuration Manager.
- internal on – Prem only domain is joined join device manage in Configuration Manager will auto – register to Hybrid Azure ad join and auto – enroll into Intune to be co – manage with Configuration Manager and Intune .
First as mentioned we need to create the Azure Services and the Cloud Mangement Gateway.
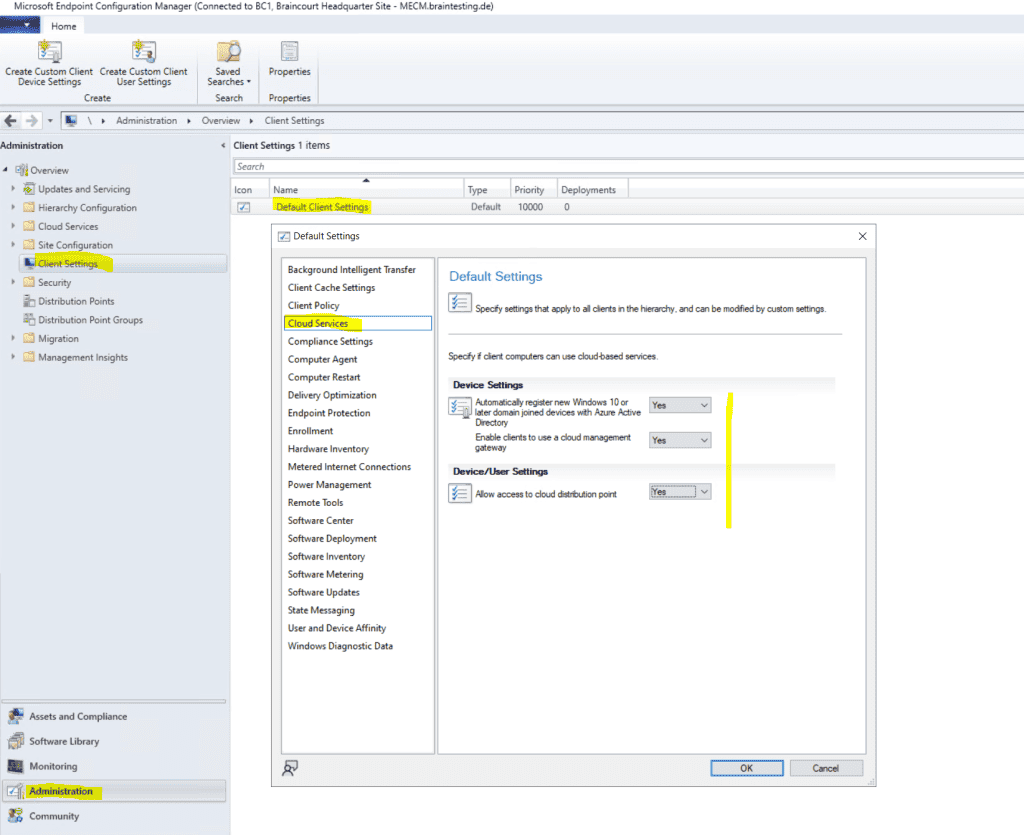
Set up Client Settings
Be sure to enable the following features in the Cloud Services section inside the Client Settings.
allow access to cloud distribution point , otherwise clients is be wo n’t be able to download content from the cloud distribution point and internet .
set enable client to use a cloud management gateway to yes . Further check is joined that automatically register new Windows 10 domain join device with Azure Active Directory and allow access to cloud distribution point is also set to yes .

Now first we need to configure the Azure Services.
Configure Azure Services
Configure Azure services for use with Configuration Manager
Use the Azure Services Wizard to simplify the process of configuring the Azure cloud services you use with Configuration Manager. This wizard provides a common configuration experience by using Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) web app registrations. These apps provide subscription and configuration details, and authenticate communications with Azure AD. The app replaces entering this same information each time you set up a new Configuration Manager component or service with Azure.
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/configmgr/core/servers/deploy/configure/azure-services-wizard
Right click on Azure Services –> Configure Azure Services
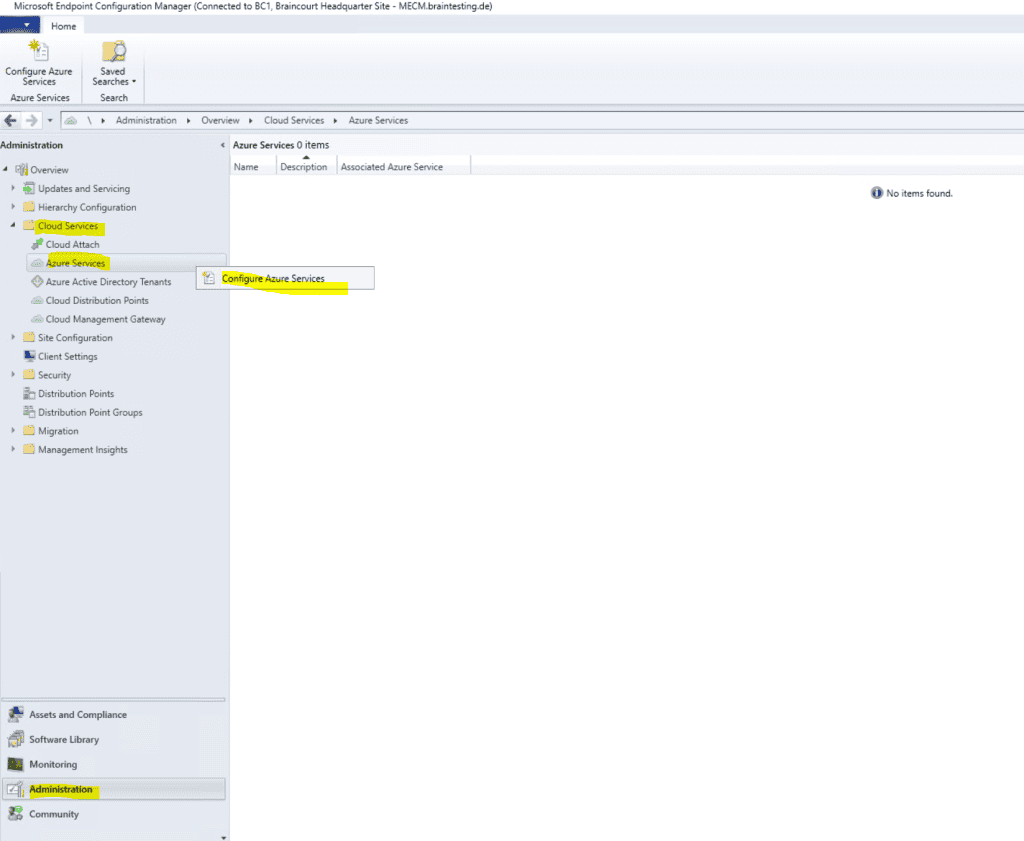
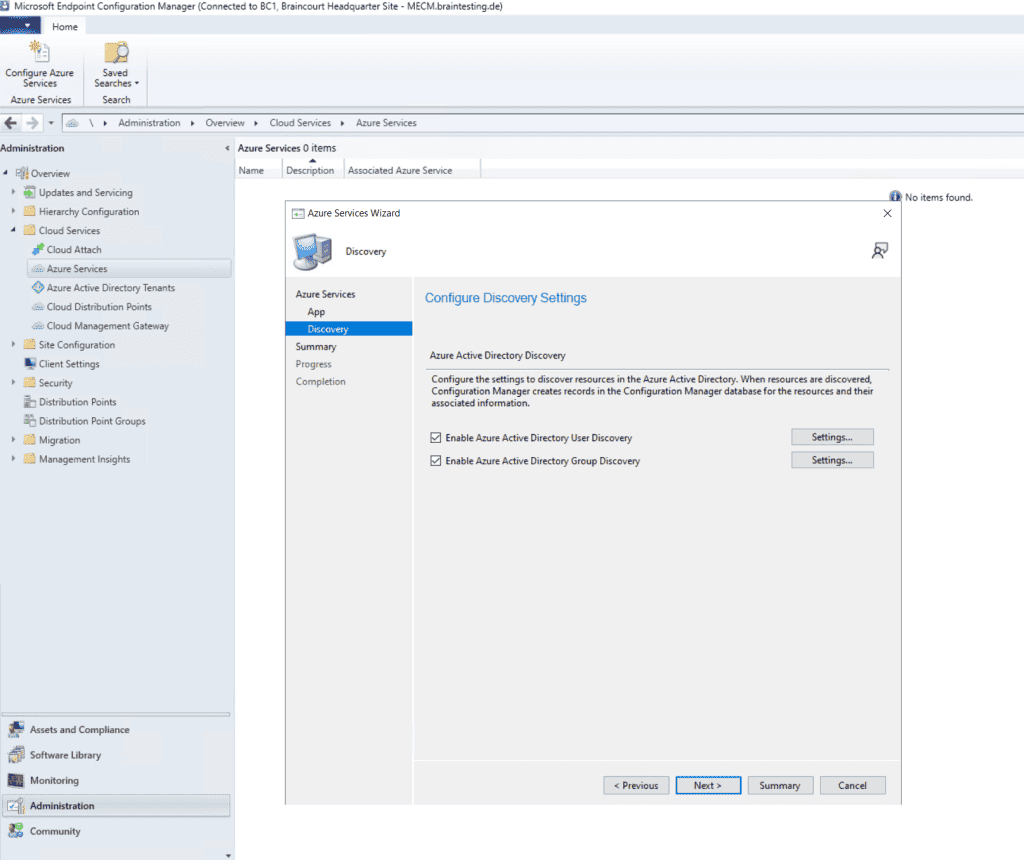
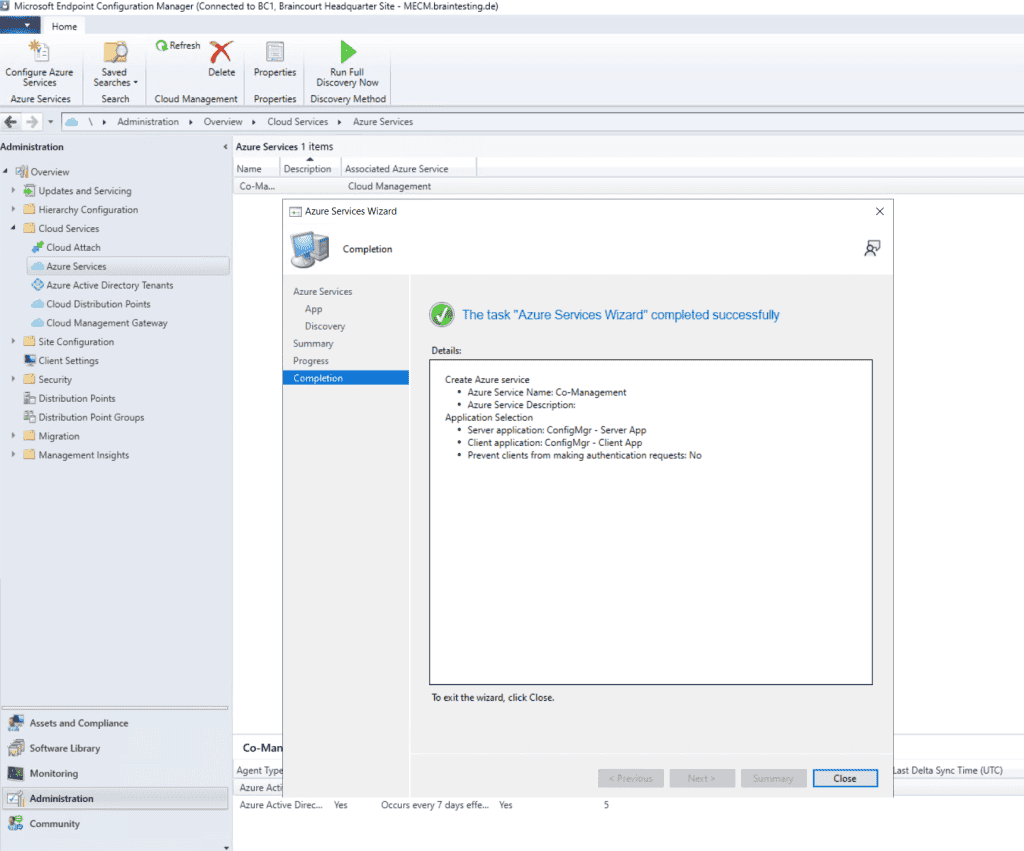
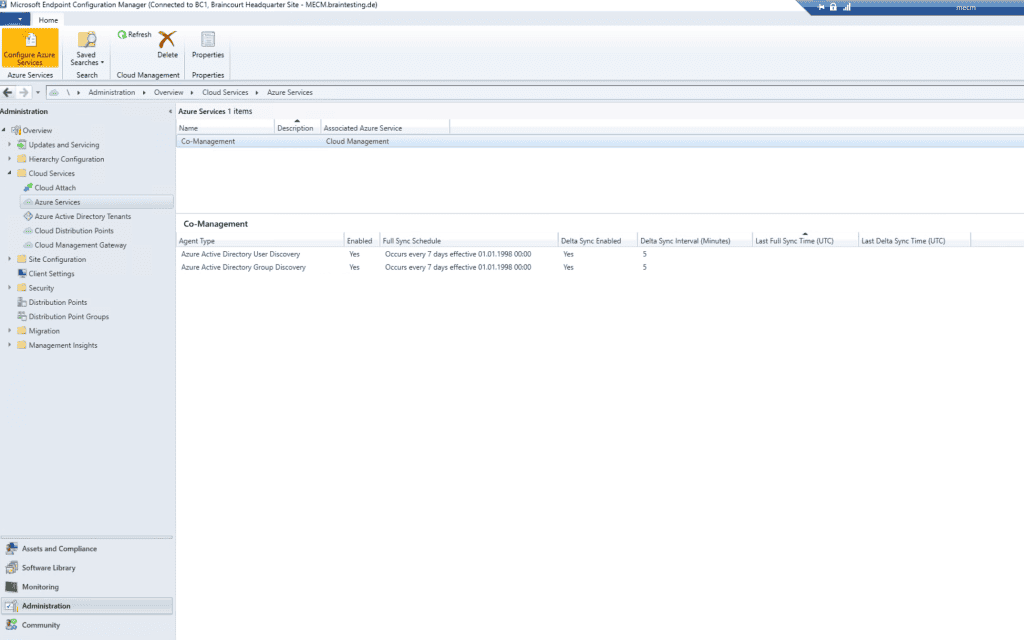
Deploying the Azure service for Cloud Management enables Configuration Manager clients to authenticate with the site using Azure Active Directory. We will also enable discovery of Azure Active Directory resources for this tenant.
Select Cloud Management.
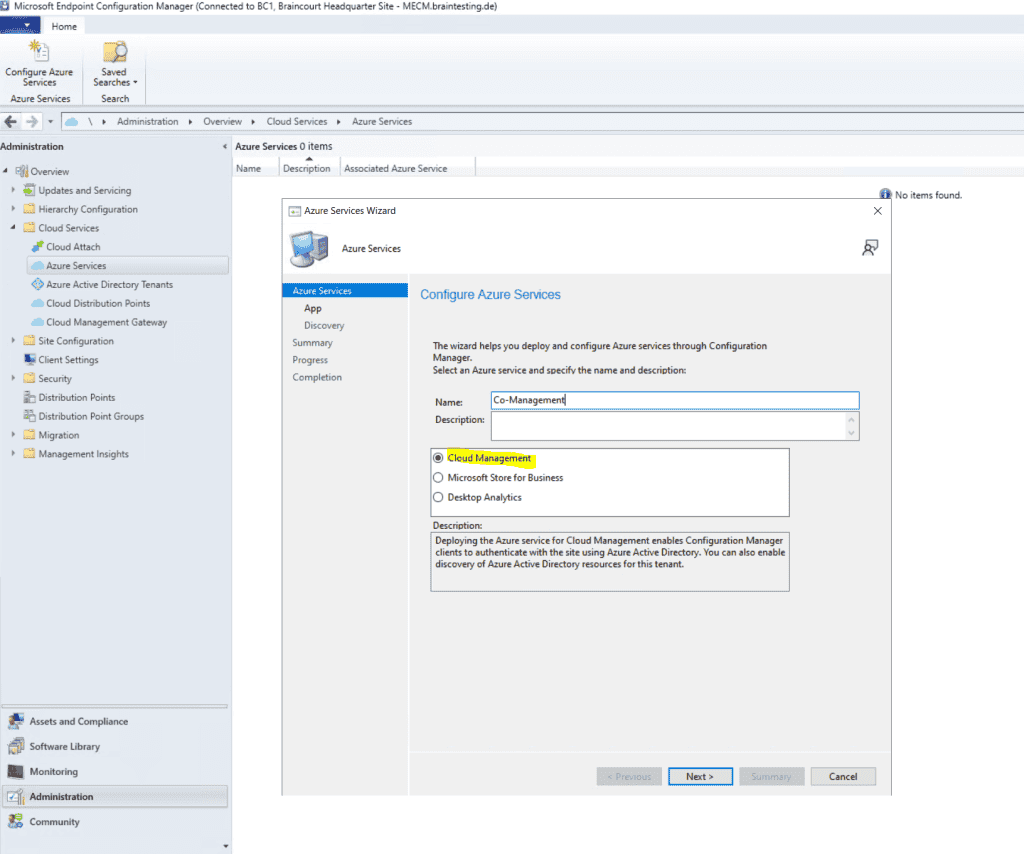
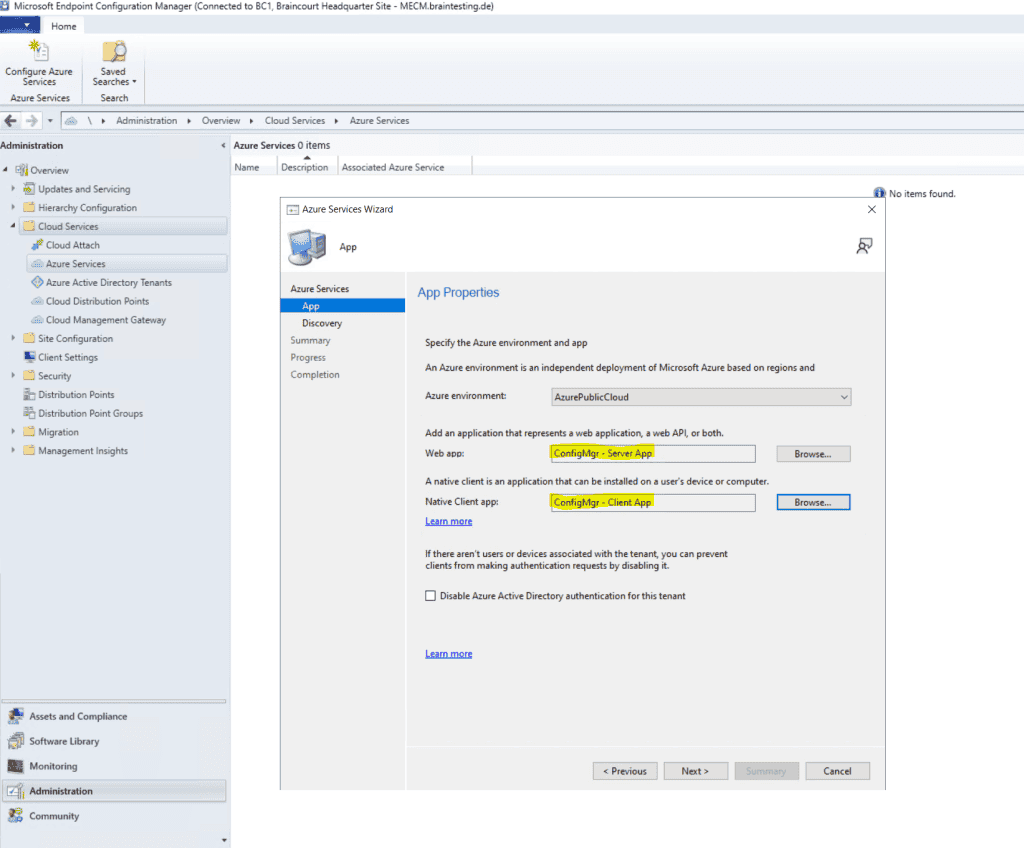
Here we need to create a web app and a client app. You must use here an Azure global admin account which also have rights on the subscription to create resources.
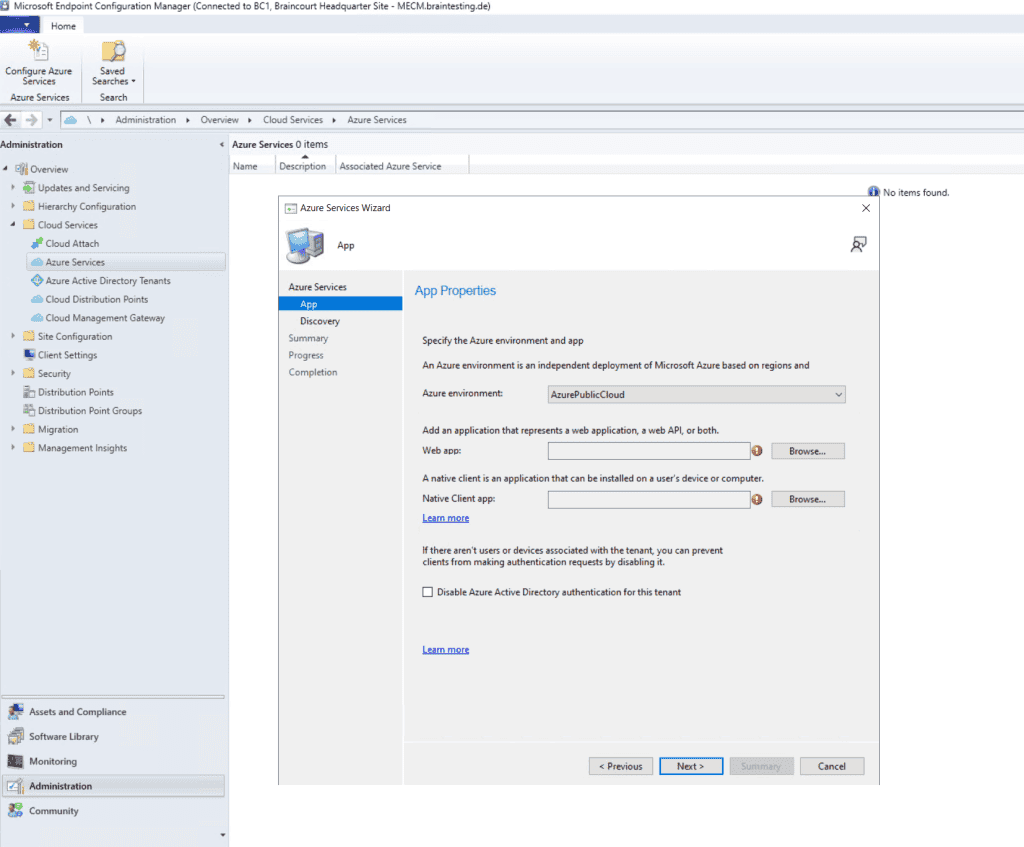
To create the web app we need to click on Browse and then on Create.
Web app: Whether the service uses an Azure AD app of type Web app / API, also referred to as a server app in Configuration Manager.
Native app: Whether the service uses an Azure AD app of type Native, also referred to as a client app in Configuration Manager.
source : https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/servers/deploy/configure/azure-services-wizard
create the server app as show below .
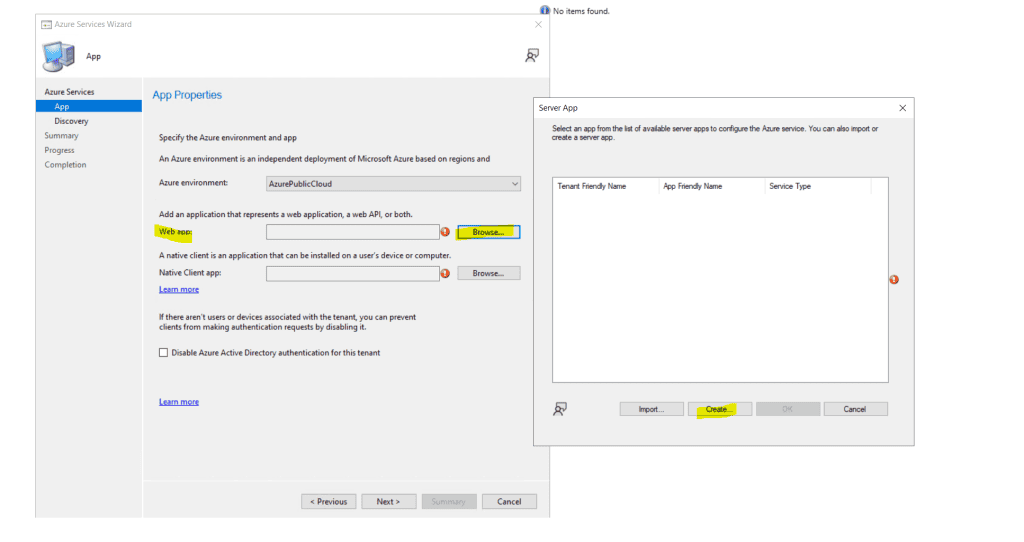
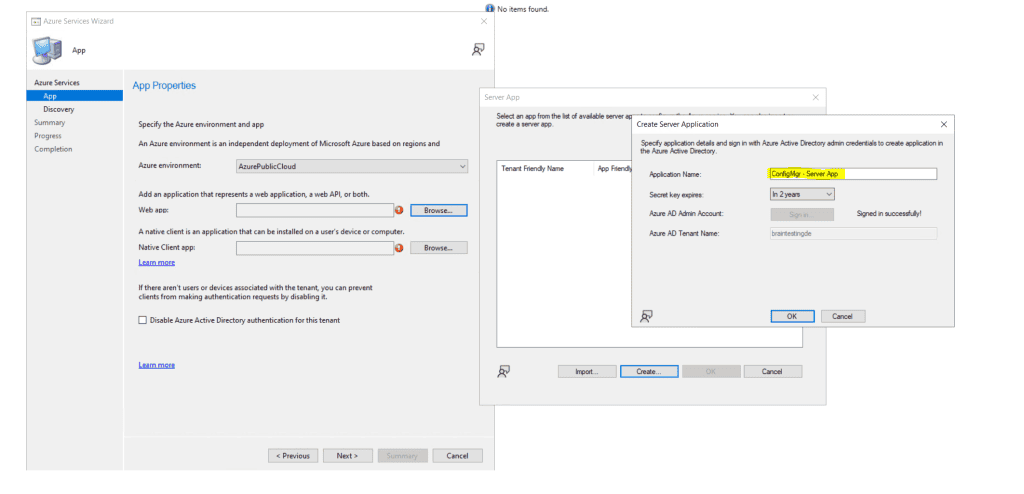
Create the client app as shown below.
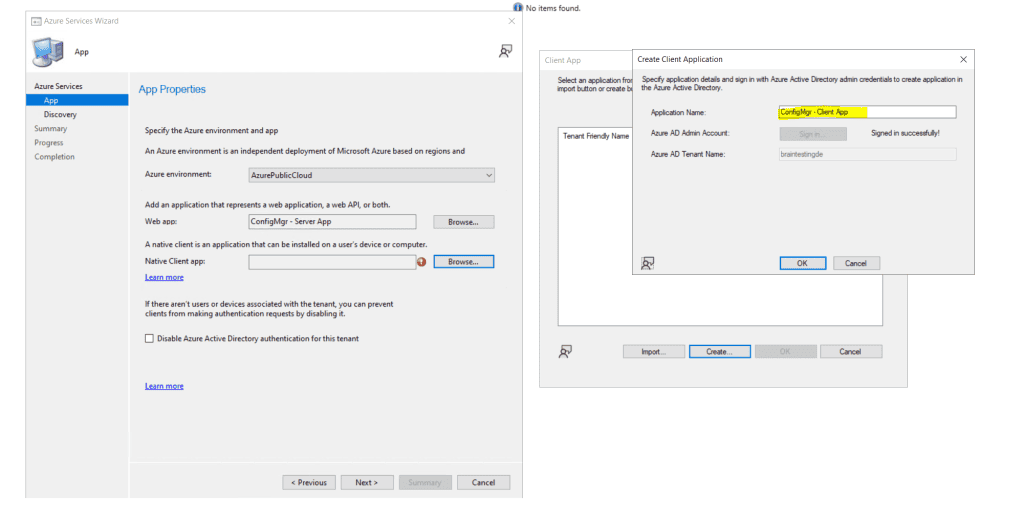
We is enable will also enable MECM to discover cloud identity .
Grant Permissions to the Server and Client App in Azure AD
In Azure Active Directory under App registrations you should now see our created applications.
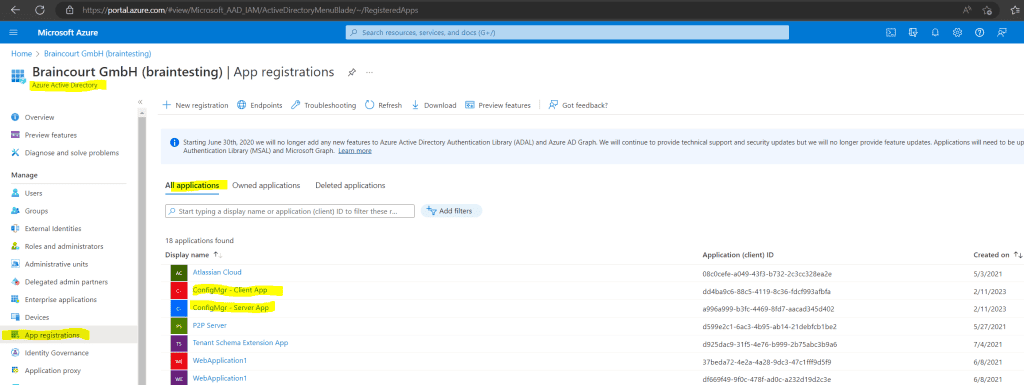
To enable the applications to access the Azure AD, we must grant permissions as shown below.
Modify Default Azure Active Directory Graph Permissions from User.Read to Directory.Read.All for the Client App.
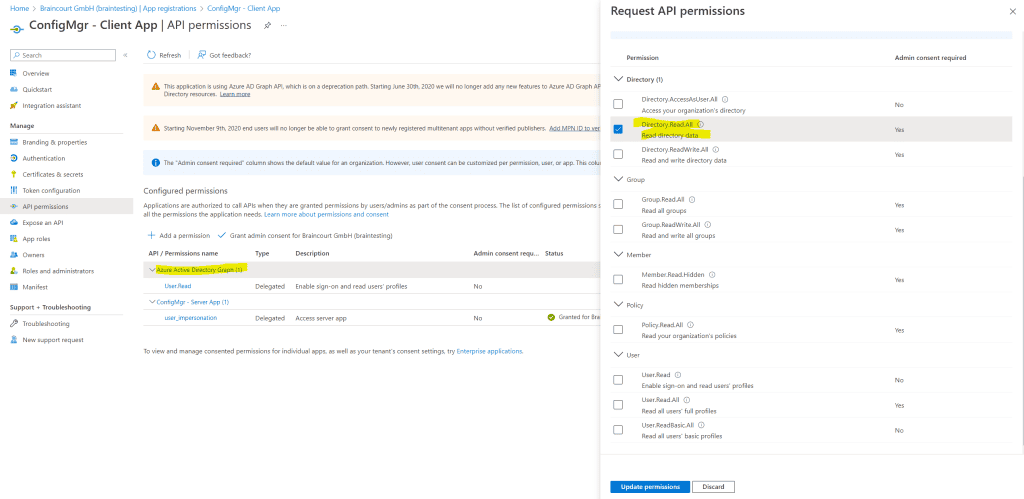
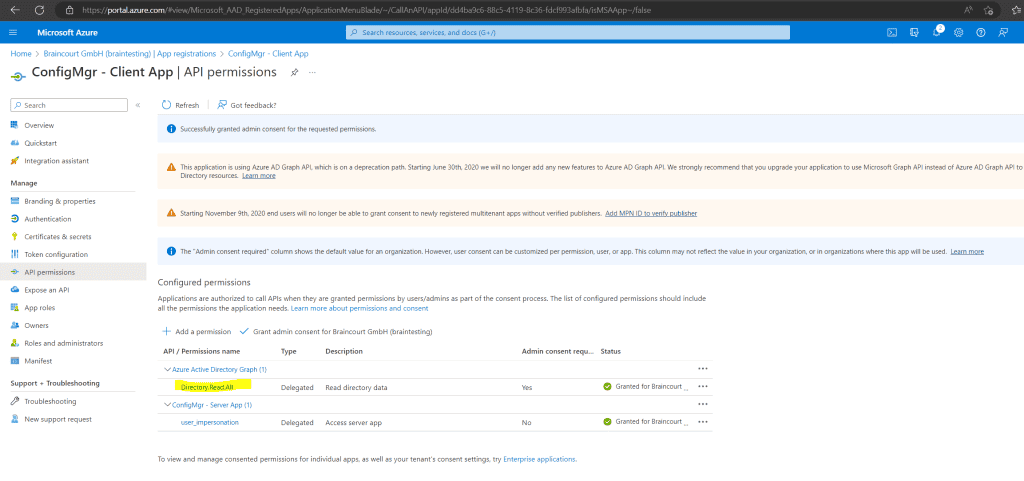
Modify Default Azure Active Directory Graph Permissions from User.Read to Directory.Read.All for the Server App if not still enabled. In my case the permissions was per default to Directory.Read.All
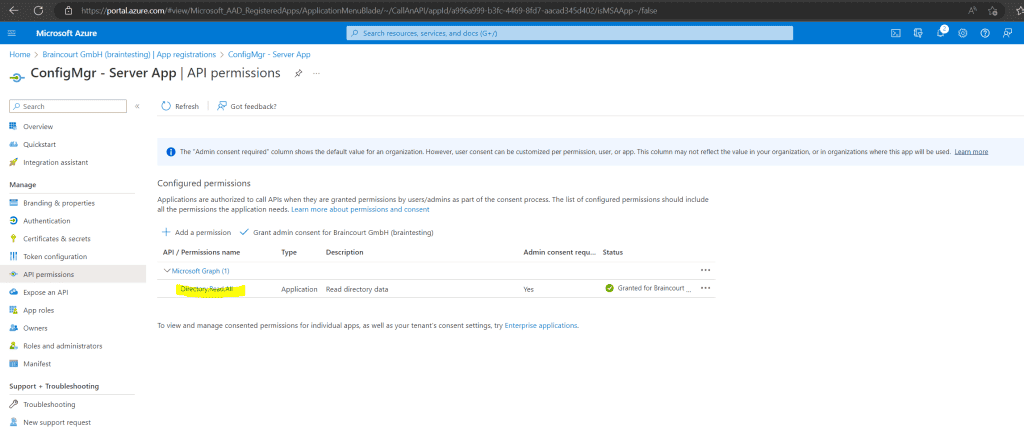
Create the Cloud Management Gateway (CMG)
Under Cloud Services right click on Cloud Management Gateway and click on Create Cloud Management Gateway .
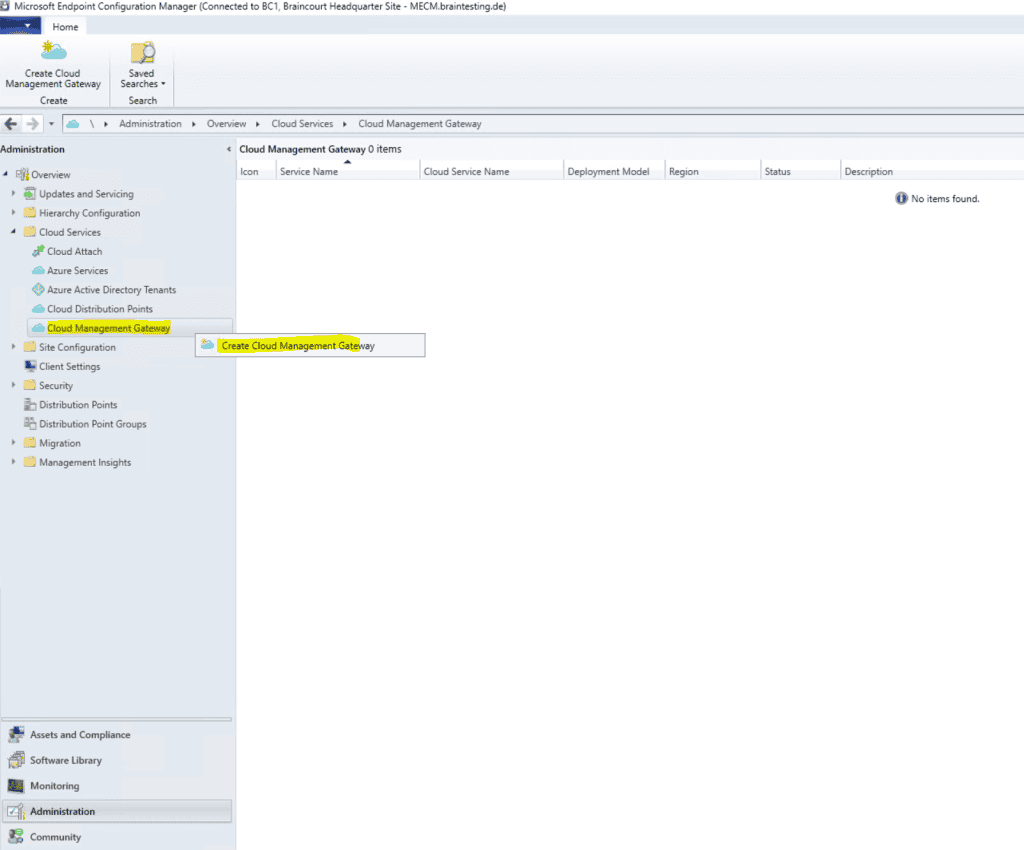
Login again with your global Azure admin account which also should have right on the subscription to create resource .
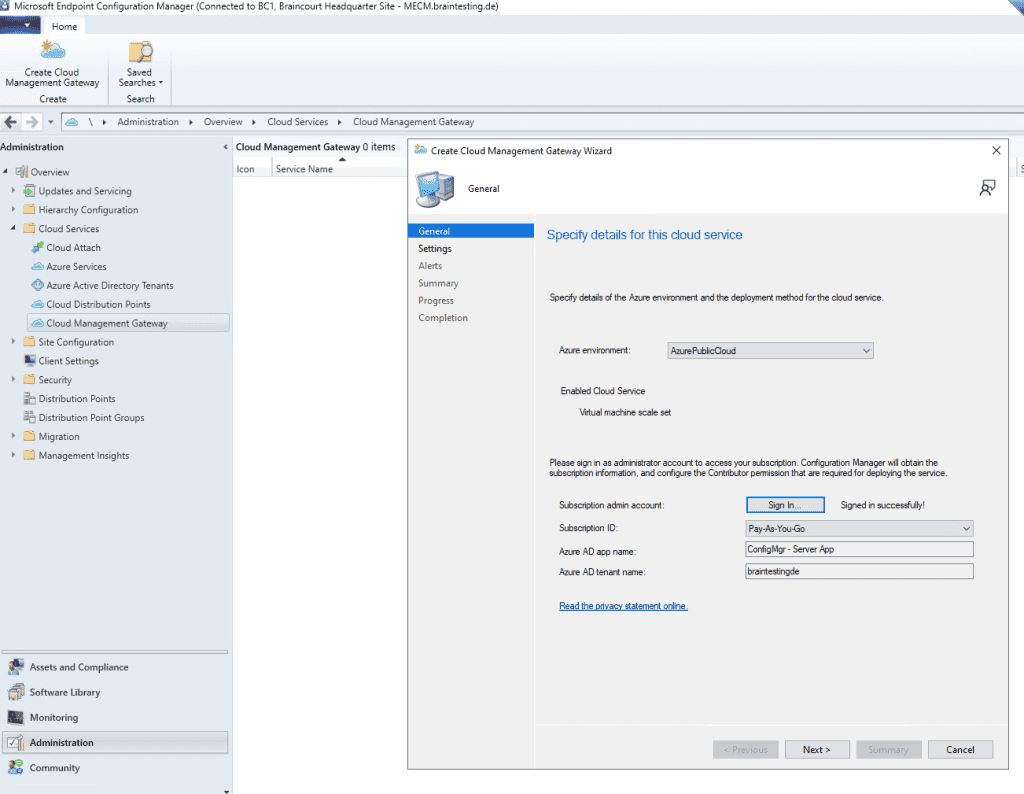
Here you is configure configure the cloud management gateway setting . The first thing is is to do here , is to upload the webserver ( IIS ) certificate for our VM Instance in Azure which represent the cloud management gateway . Therefore you is upload must upload an * .pfx file which contain not only the certificate with the public key but also the private key .
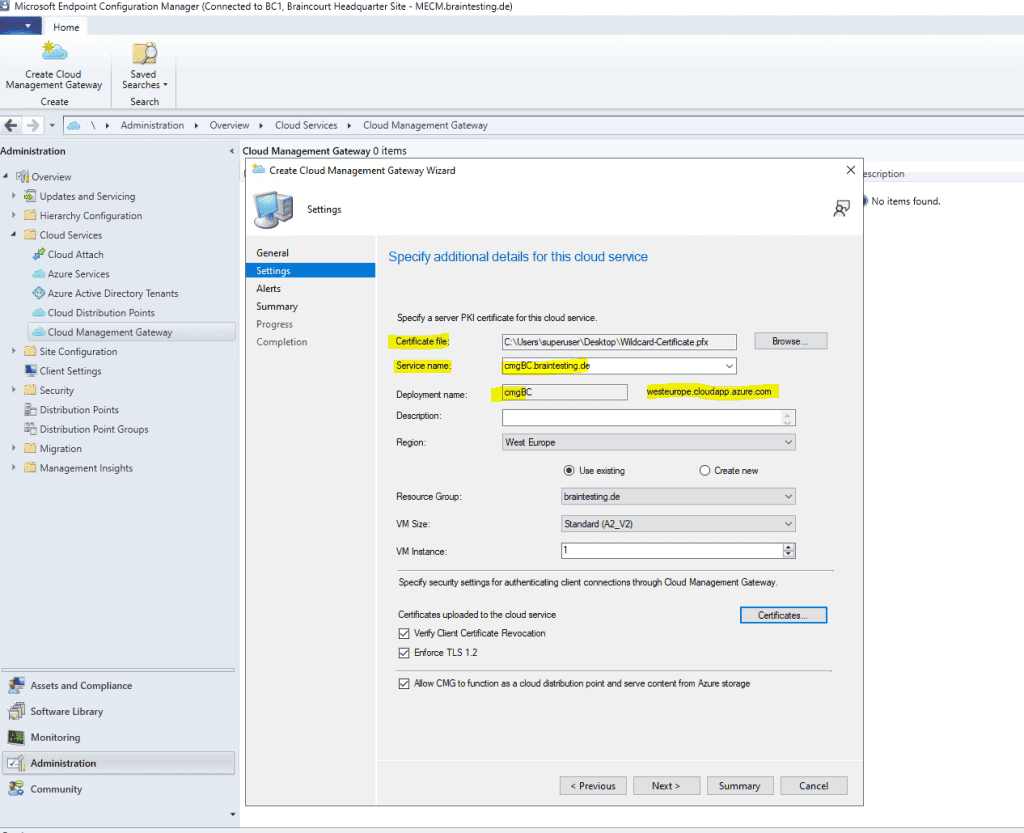
In my case I use a wildcard certificate, so I must also specify the sudomain (hostname) of the service name, in my case cmgBC.
Please be aware that the subdomain must be unique as you get a domain in the public cloudapp.net domain space. The setup assistant will unfortunately not verify this. Also the local logs on the MECM will not warn you about this. The only way to see if the deployment fails because of a subdomain which is in use by someone else is at the Activity log in Azure for the ressource group or cloud service. I will show you this logs later at troubleshooting.
Update: They changed the public domain name by changing the domain to azure and adding a subdomain which is the name from the region you deploy the cloud management gateway . As I am using the region West Europe, now the public domain name is westeurope.cloudapp.azure.com.
The deployment FQDN is is from my cloud management gateway therefore is cmgBC.westeurope.cloudapp.azure.com .
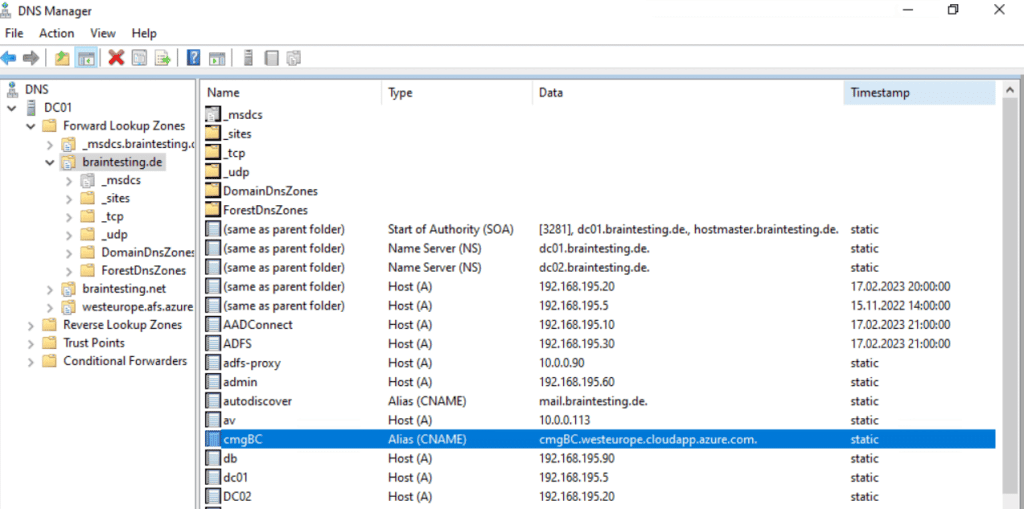
We is have also have to create a cname record in our organization ’s public DNS . The CMG service is need in Azure and all client that use it need to resolve the service name .
In my case I is need need to create a cname record cmgbc.braintesting.de that point to cmgBC.westeurope.cloudapp.azure.com
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/clients/manage/cmg/server-auth-cert#create-a-dns-cname-alias
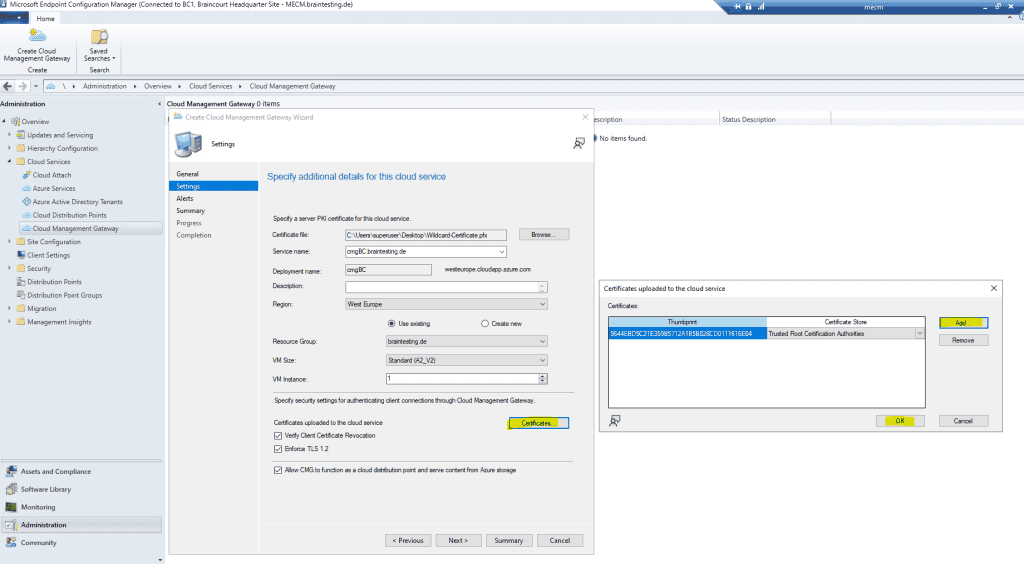
If we use a certificate from our internal PKI, we also must tell the Cloud Management Gateway (the VM Instance with IIS) that it should trust our PKI.
We can add the root certificate by clicking on the Certificates button below.
Note!!!
Below by default Verify Client Certificate Revocation is checked for the CMG, in that case you must ensure that the certificate revocation list (CRL) from your internal PKI can be downloaded from the CMG and internet, otherwise disable it.
This service certificate from CMG is used to authenticate the CMG service in Azure to Configuration Manager clients and encrypt all data transferred between them by using TLS.
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/plan-design/network/pki-certificate-requirements#cloud-management-gateway-cmg
So as we use therefore a certificate from our internal PKI, we must ensure that all clients will trust this certificate. For internal domain joined computers the root certificate from the internal PKI will be installed by default. For external Azure AD joinded devices I will use Intune. We will see later how this works.
On the next page I will use the default settings.
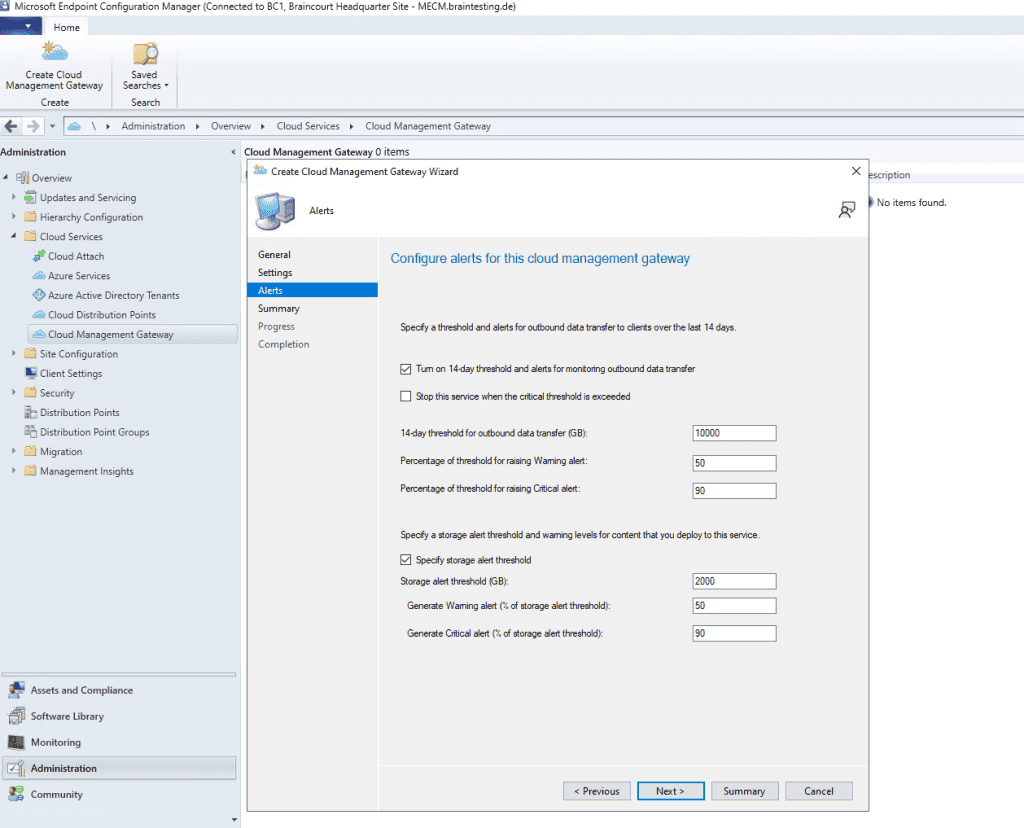
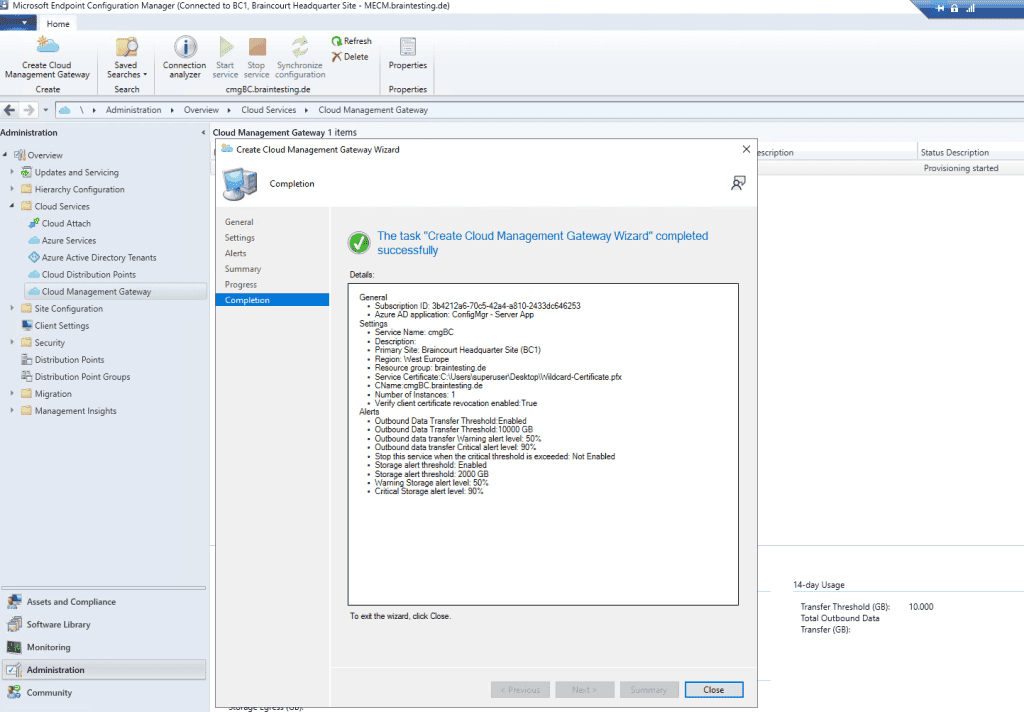
You have to wait a few minutes till the VM Instance is created.
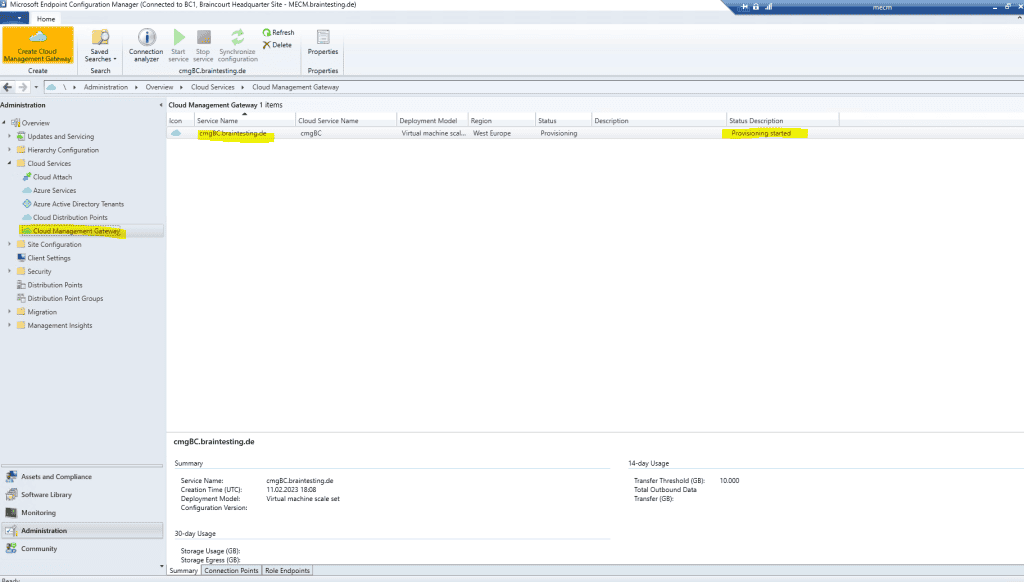
Here you can see that my provisioning failed.
More details is find about you will find in the cloudmgr.log file on the MECM server in the installation directory .
To view the logs you can use a normal text editor but better use the MECM Trace Log tool in the tools directory from MECM.
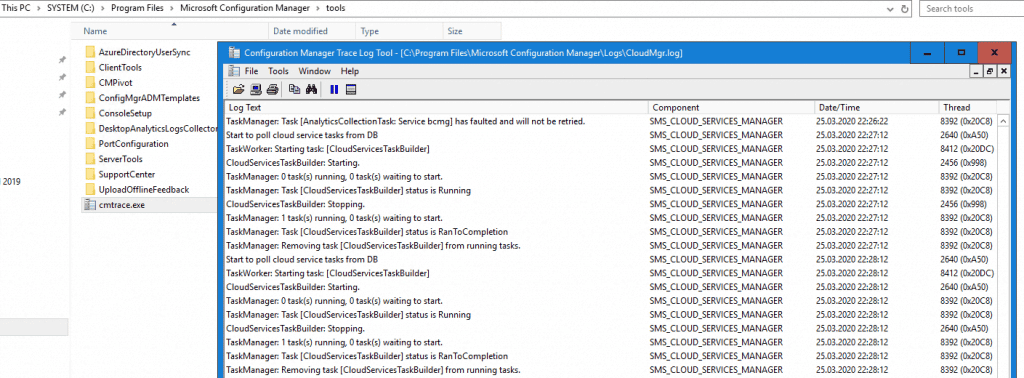
Mostly the reason why the provisioning failed you will see quickly by checking the Logs directly in Azure under the Activity log of the resource group you deployed the cloud management gateway.
The subscription is not registered to use namespace ‘Microsoft.KeyVault‘.
This error is means mean that the service Microsoft . KeyVault is not register in your Azure subscription .
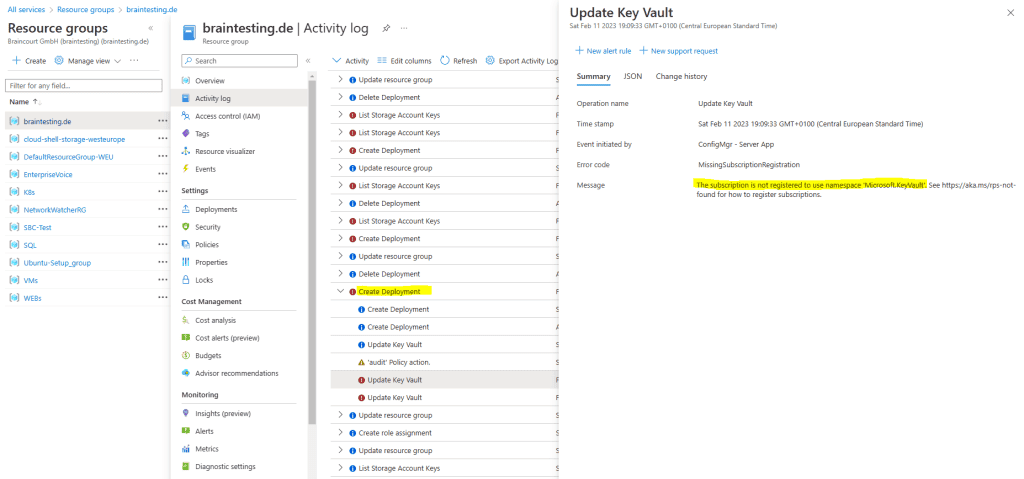
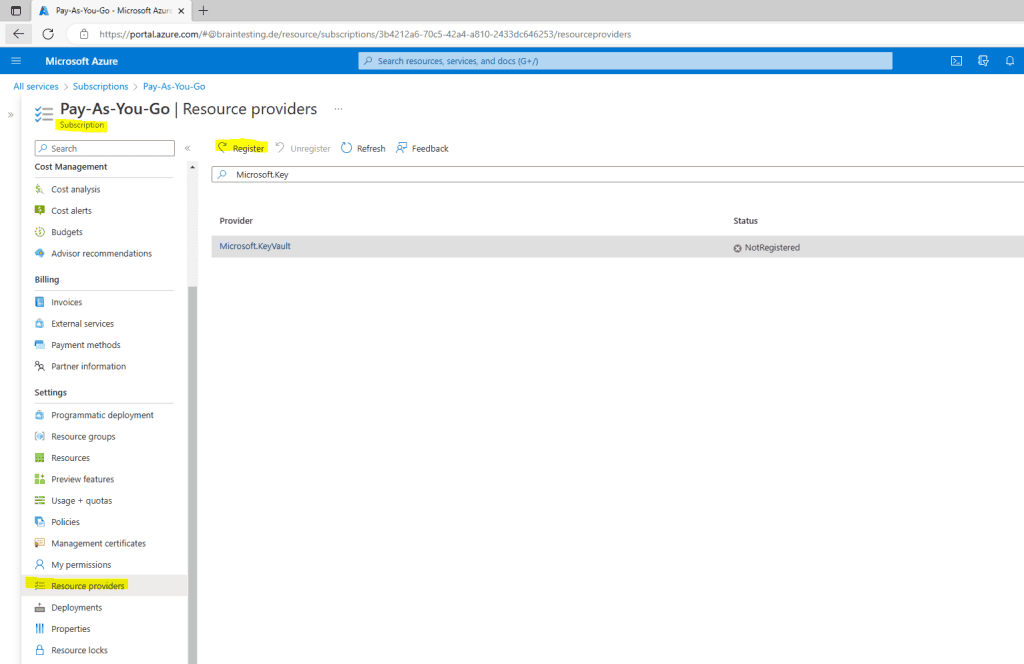
To register the Microsoft.KeyVault service to my subscription, I will go to the subscription and the Resource providers menu.
Search for the service and click on Register.
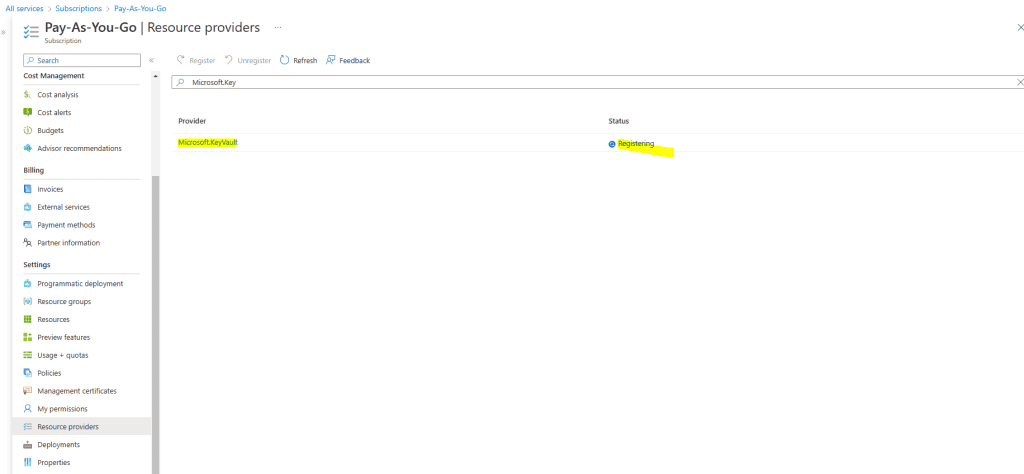
Now I have to delete the failed cloud management gateway and have to re-create it.
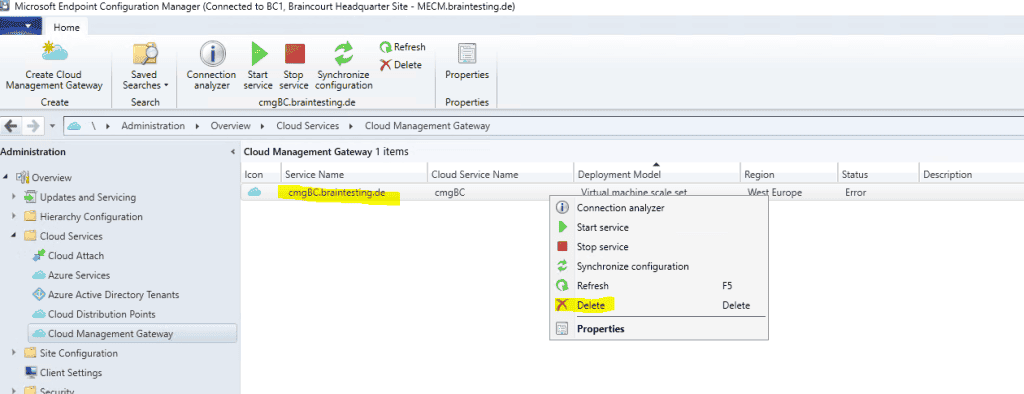
The next try was successfully deploying my cloud management gateway.
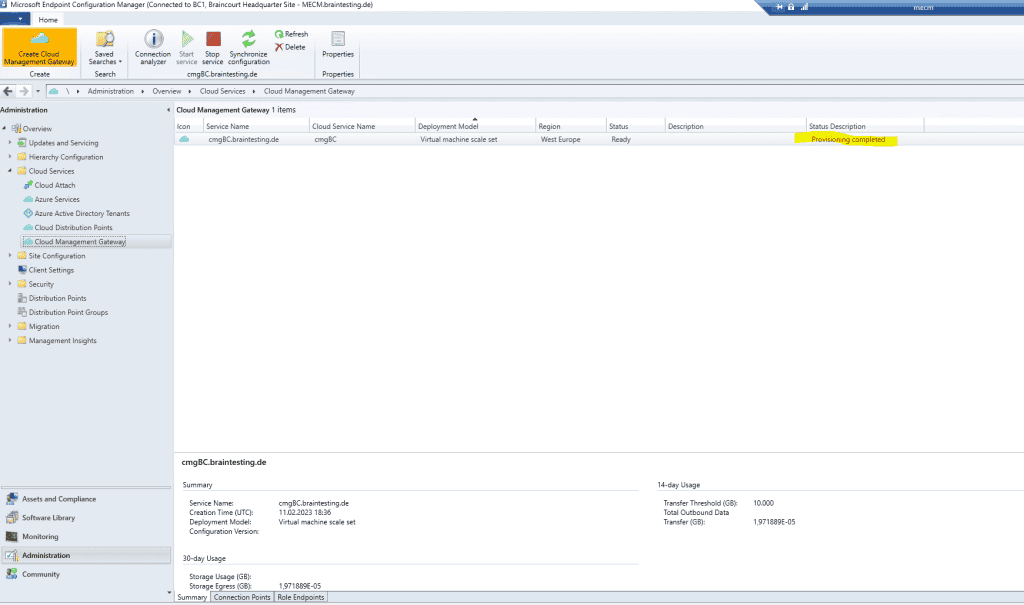
Configure Cloud Management Gateway
Now we come to the configuration of the cloud management gateway connection point. This will act as proxy between the CMG in Azure (VM) and the management point and software update point in MECM. Therefore external clients can use this channel for things like scanning and getting policies.
So go to Site Configuration – Servers and Site System Roles and add the Site System Role Cloud management gateway connection point for your primary site server .
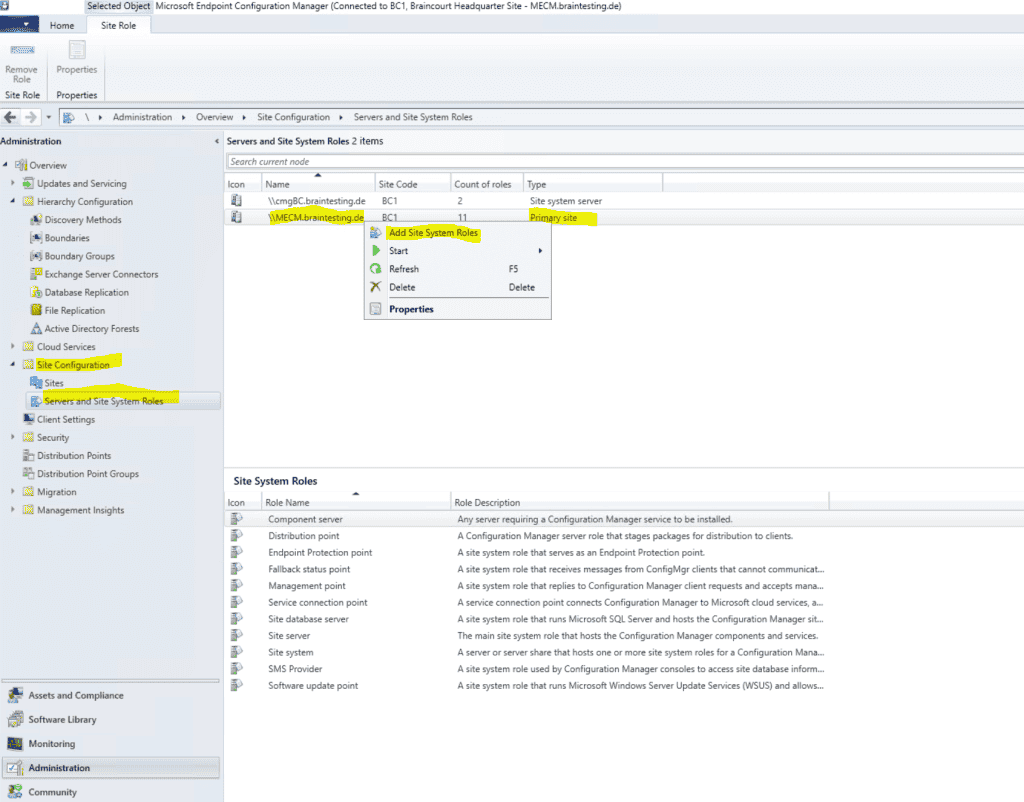
Select Cloud management gateway connection point.
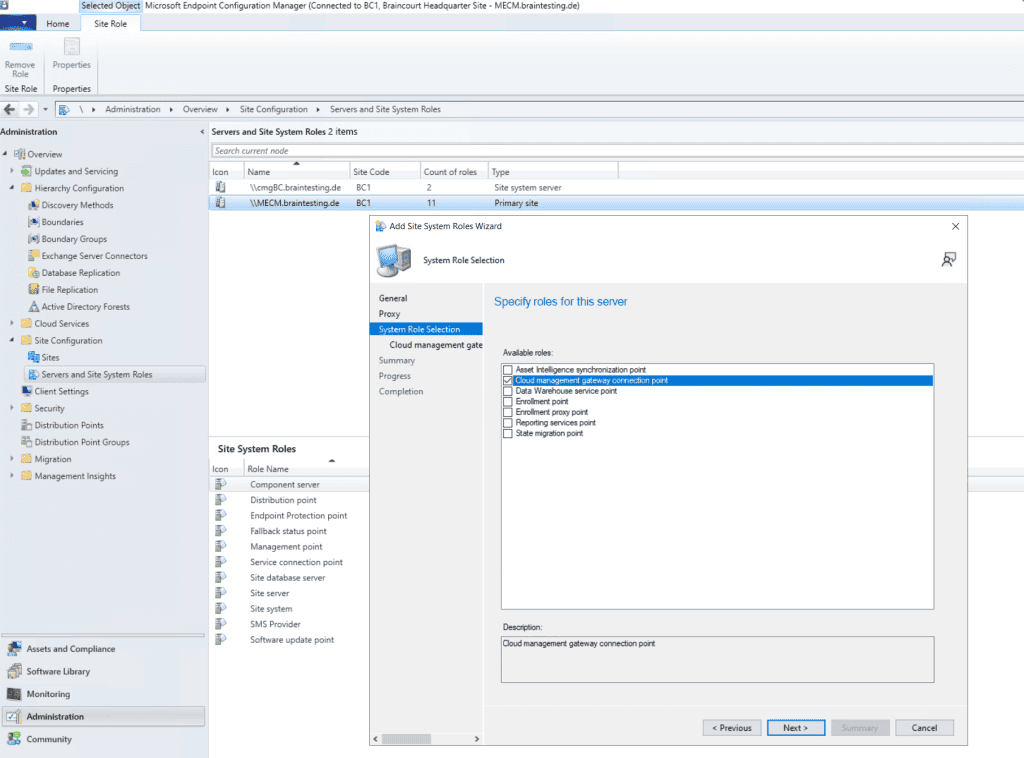
Select the CMG we created previously.
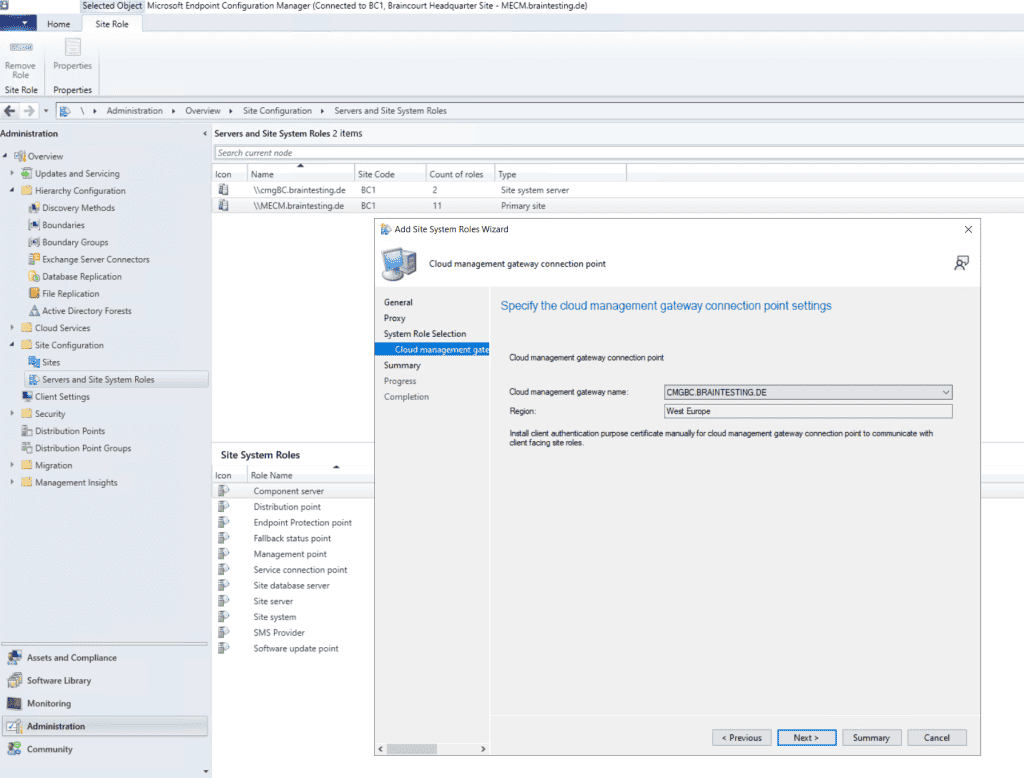
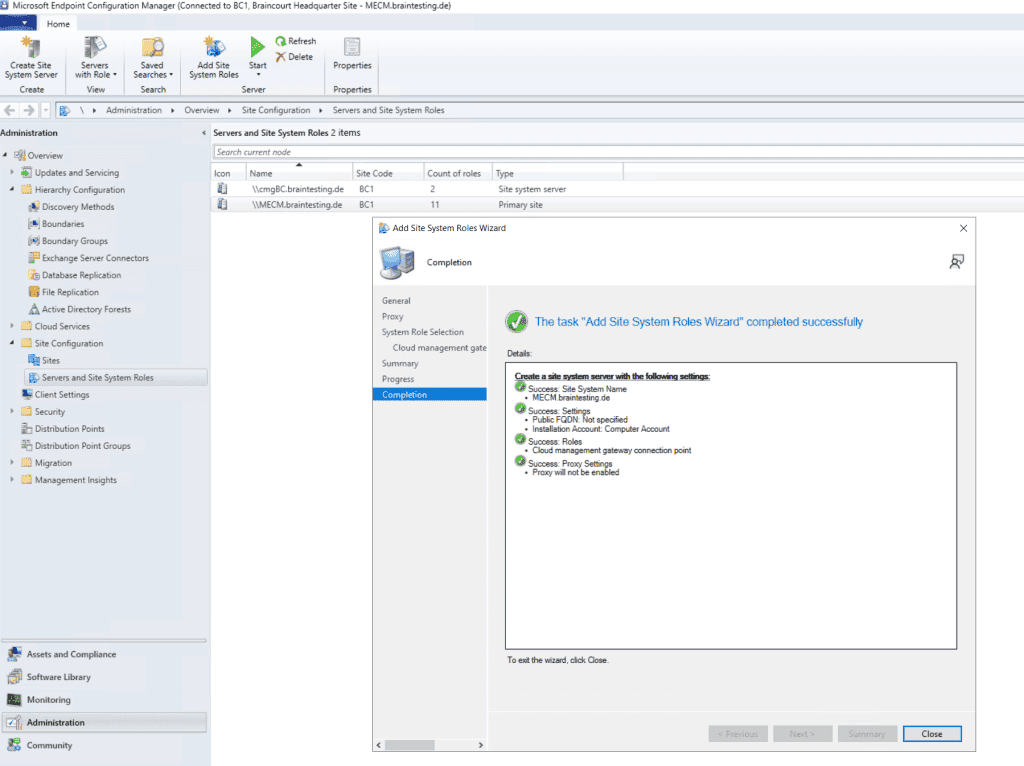
Now we must enable that our on-premise Management point and Software update point can use the cloud management gateway for external clients to establish a connection to our on-premise MECM site.
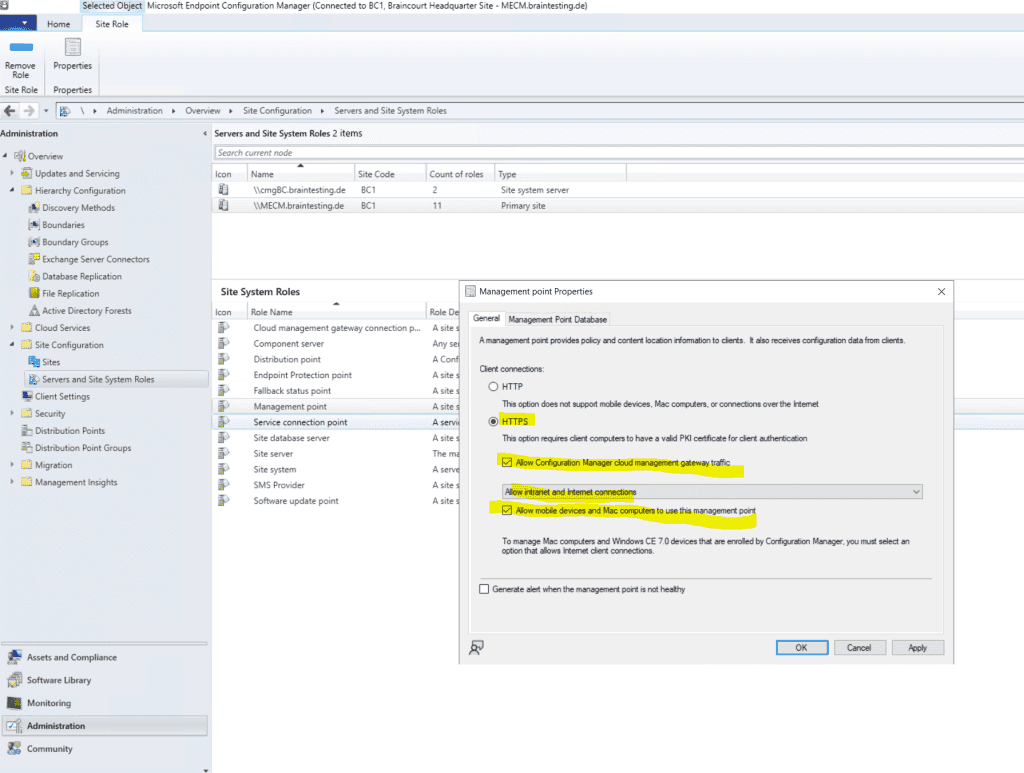
So open the properties from the Management point. Check that Client connections use HTTPS and check Allow Configuration Manager cloud management gateway traffic.
Under https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nChKKM9APAQ you will see step by step how to configure SCCM to use HTTPS/PKI.
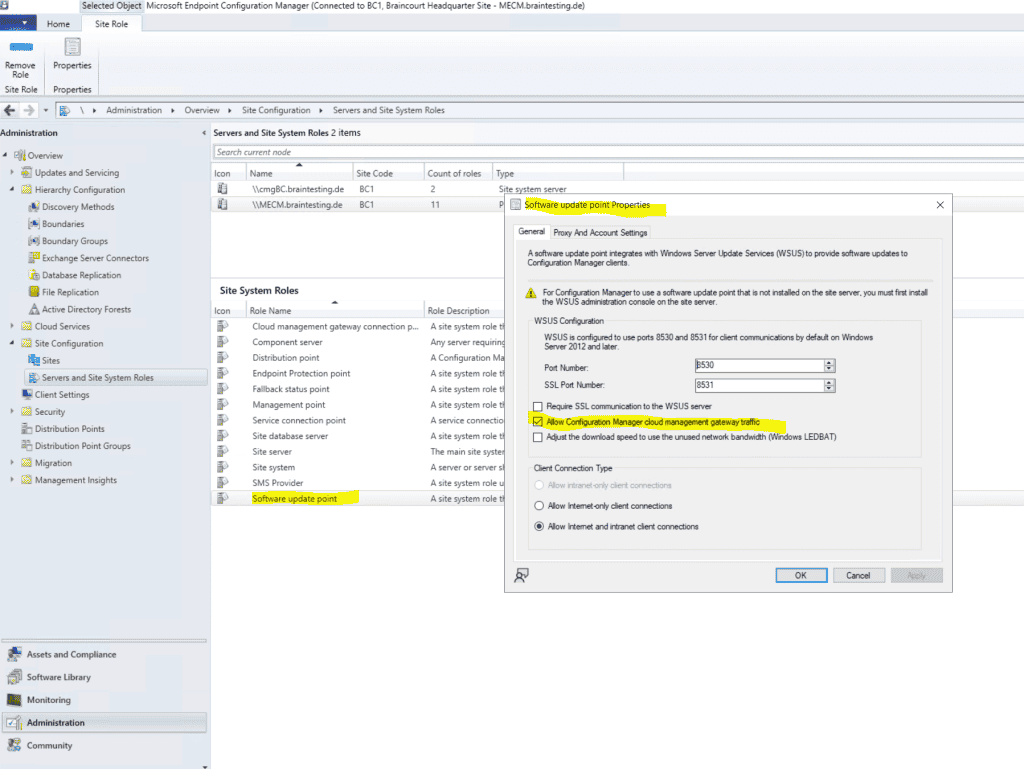
We also must define for the Software update point to allow the cloud management gateway. So be sure to check the Allow Configuration Manager cloud management gateway traffic.
After finish the setup of the cloud management gateway , you is see should see at the client the new internet – base management point ( FQDN ) in the property of the configuration manager and the Network tab .
Be aware that it can take up to 24 hour till you see this management point at the client . By default every 24 hour the client is going is go to do a content locator or a location request .
To speed thing up and this will kick in immediately you is restart can restart the SMS Agent host service on the client .
About SMS Agent Host service
Ccmexec.exe and Smsexec.exe are the processes for the agent for Microsoft Systems Management Server (SMS). The executable for the agent should not be on your computer unless you have SMS deployed. If you stop the service it will no longer report back to the SMS server. The newer versions of the Systems Management Server (SMS) are called System Center Configuration Manager ( SCCM ) and now Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (MECM).
Now after finish the setup of the Azure Services and Cloud management gateway , we is configure finally can configure and setup co – management in MECM .
How to Set Up Co-Management in Microsoft SCCM
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rTapalSHv6U
Prerequisites for Co-Management
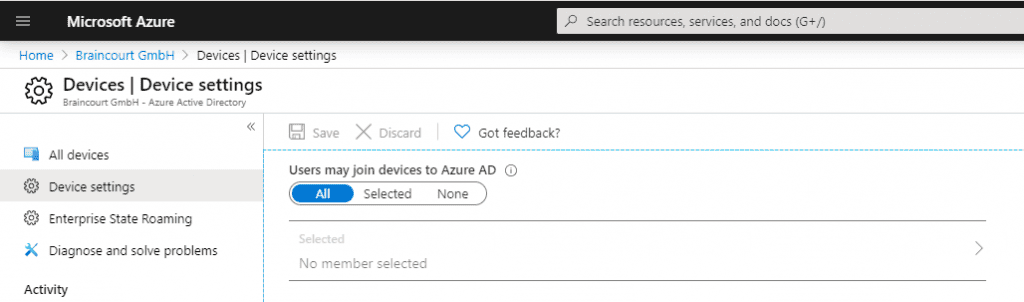
First check some prerequisites for co-management in Azure under Azure Active Directory – Devices – Device Settings.
Users is be must be able to join device to Azure AD , so switch to All or select and add the user who should be able to join .
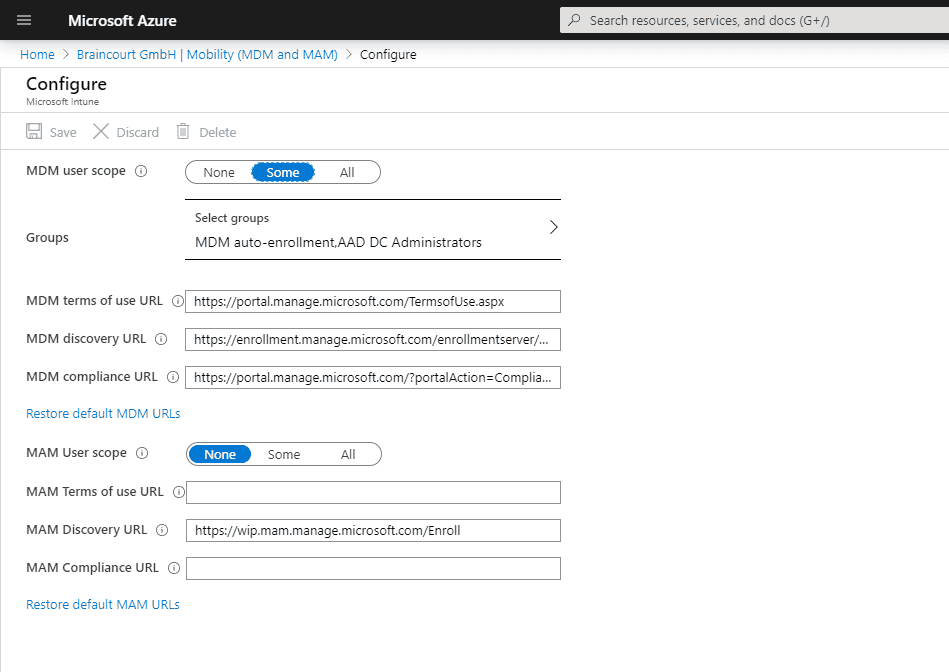
Also check under Azure Active Directory – Mobility (MDM and MAM) – Microsoft Intune, that users are able to auto-enroll into Intune.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/enrollment/windows-enroll#enable-windows-10-automatic-enrollment
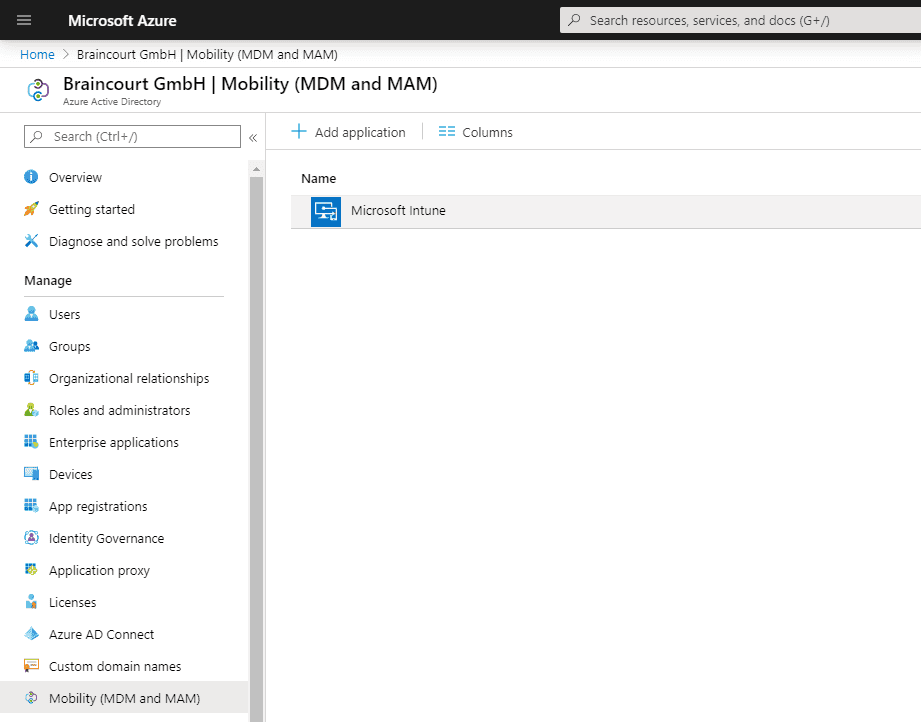
Users must be able to auto-enroll into Intune, so switch to All or Some at MDM user scope and add the users who should be able to auto-enroll into Intune.
For BYOD device , the MAM user scope is takes take precedence if both MAM user scope and MDM user scope ( automatic MDM enrollment ) are enable for all user ( or the same group of user ) . The device is use will use Windows Information Protection ( WIP ) policy ( if you configure them ) rather than being MDM enrol .
For corporate devices, the MDM user scope takes precedence if both scopes are enabled. The devices get MDM enrolled.
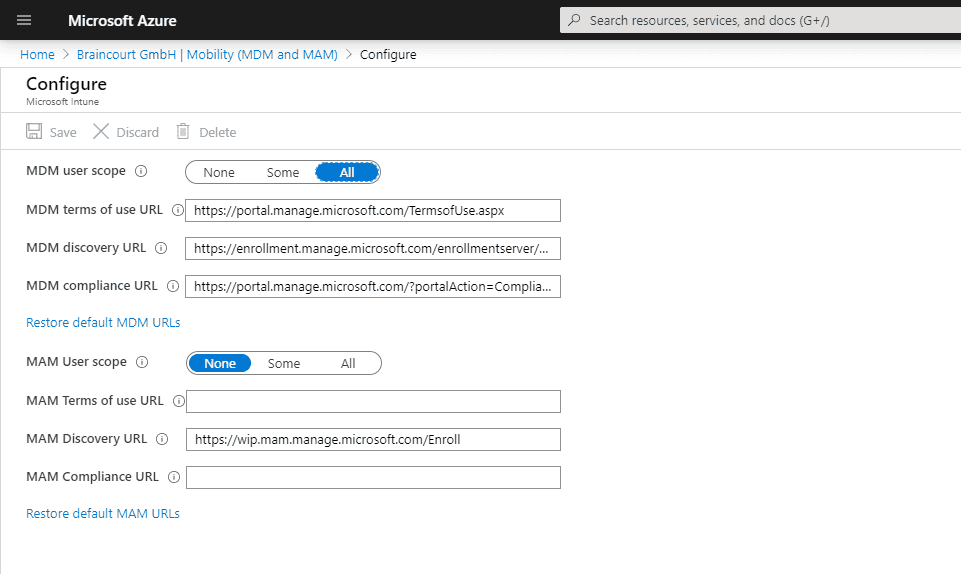
To get device auto – enroll into Intune , the user is needs also need an enabled license . In my case you is see see the Enterprise Mobility + Security E3 license which also include Intune and a separate Intune license .
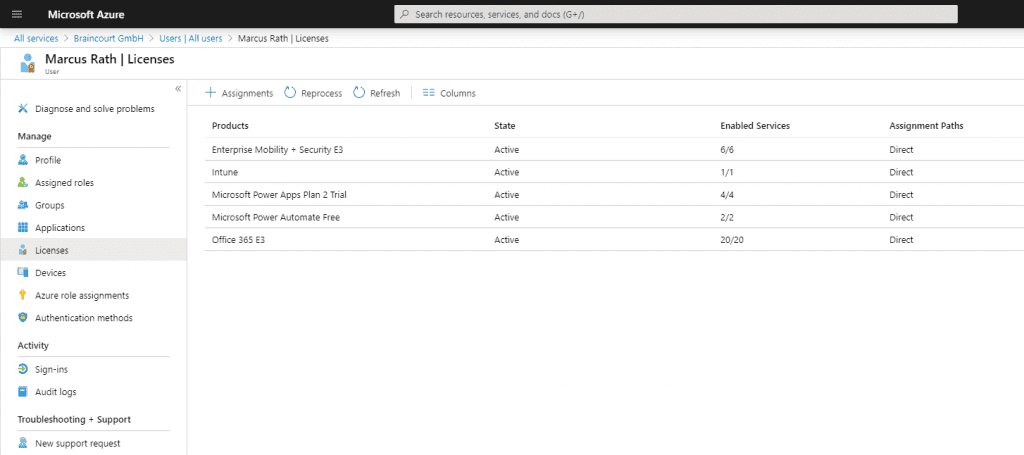
Set up Co-Management
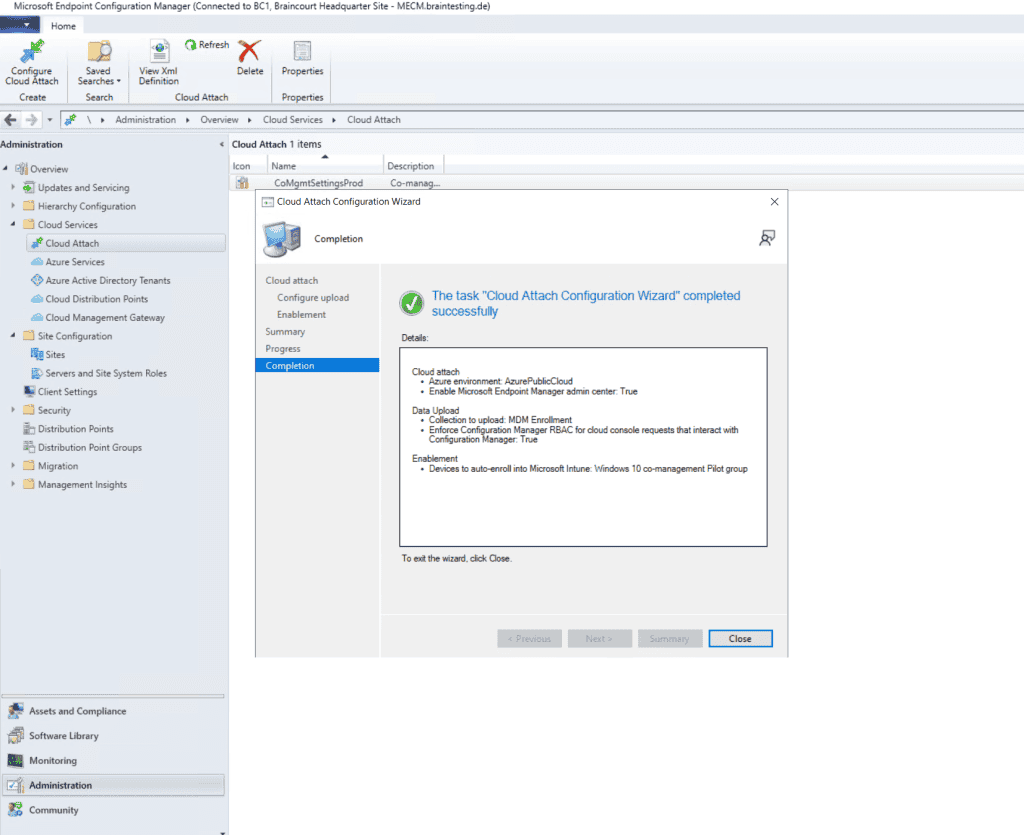
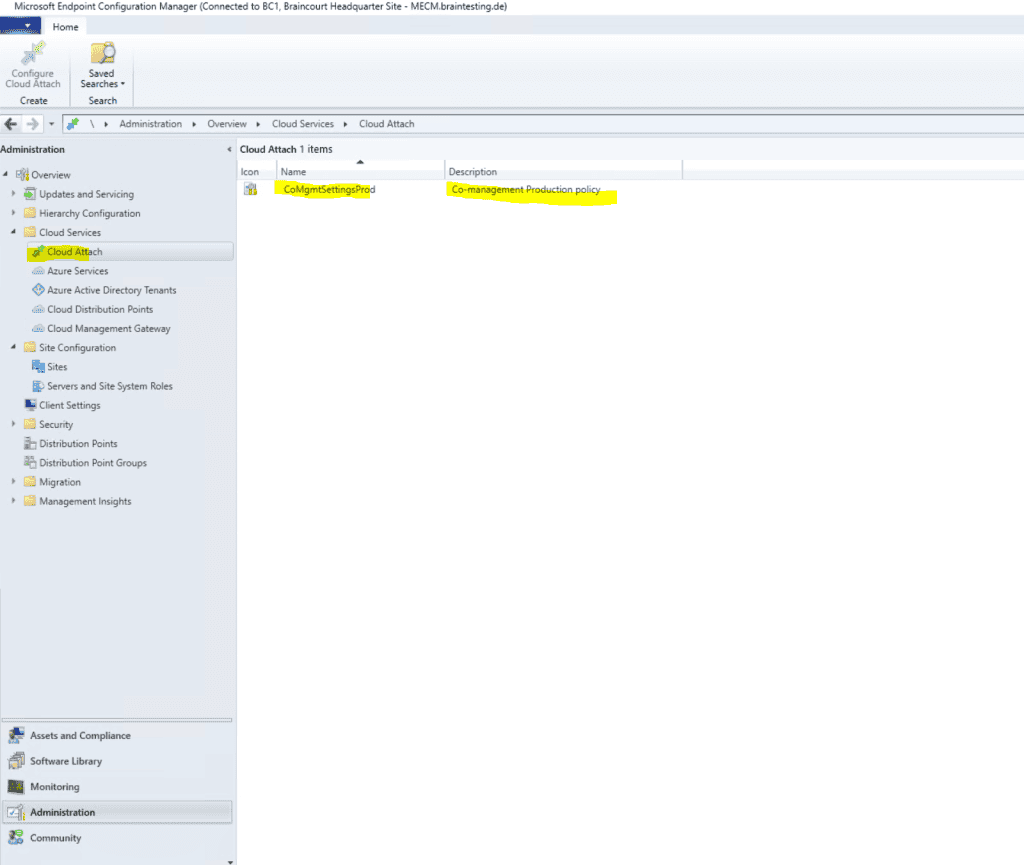
After checking all prerequisites we can start setup co-management in MECM. So go to Administration – Cloud Services – Cloud Attach.
Starting in version 2111, it’s simpler to cloud attach your Configuration Manager environment. You can choose a streamlined set of recommended defaults, or customize your cloud attach features. If you’re not running version 2111 yet, use the Tenant attach, Endpoint analytics, and Co-management articles to enable cloud attach features.
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/cloud-attach/enable
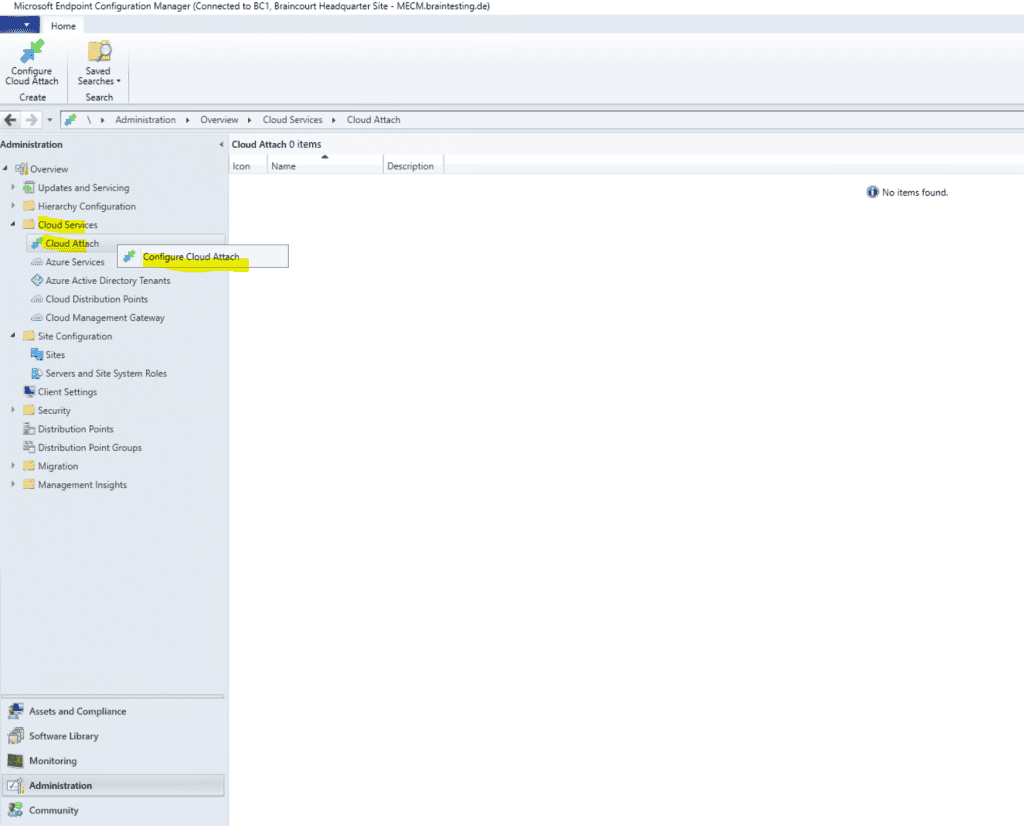
In order to first test co-management on a few devices, I will select Customize settings here to limit the devices which will get managed also by Intune.
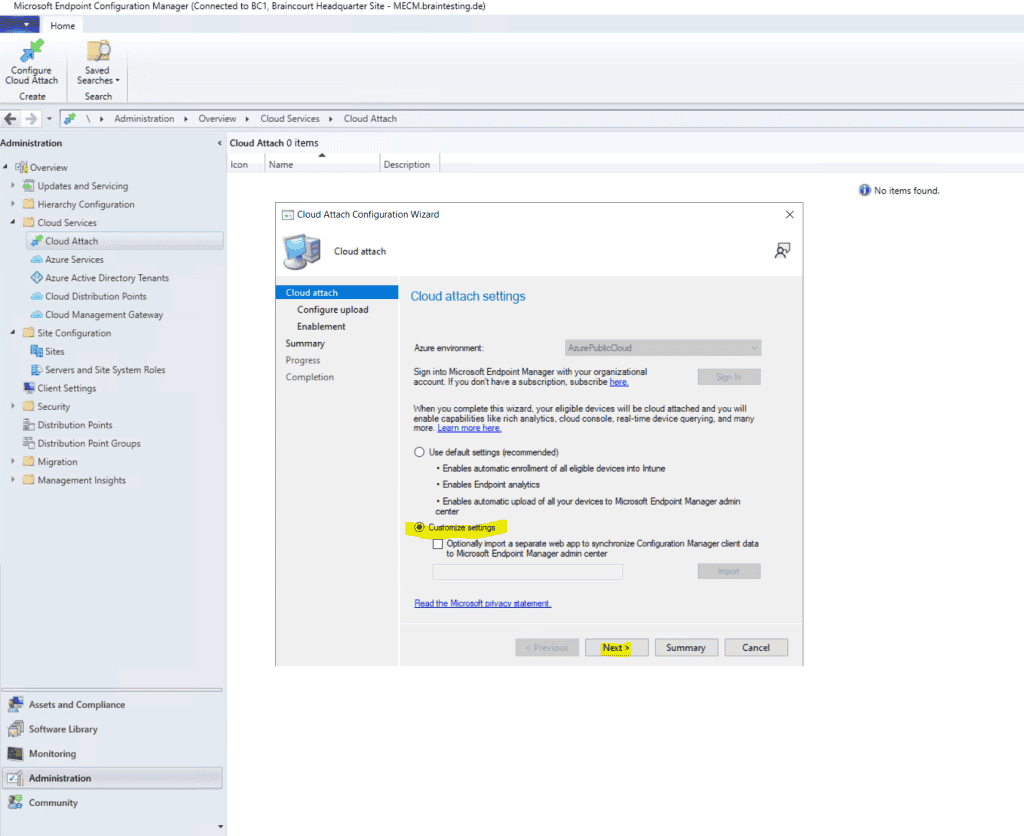
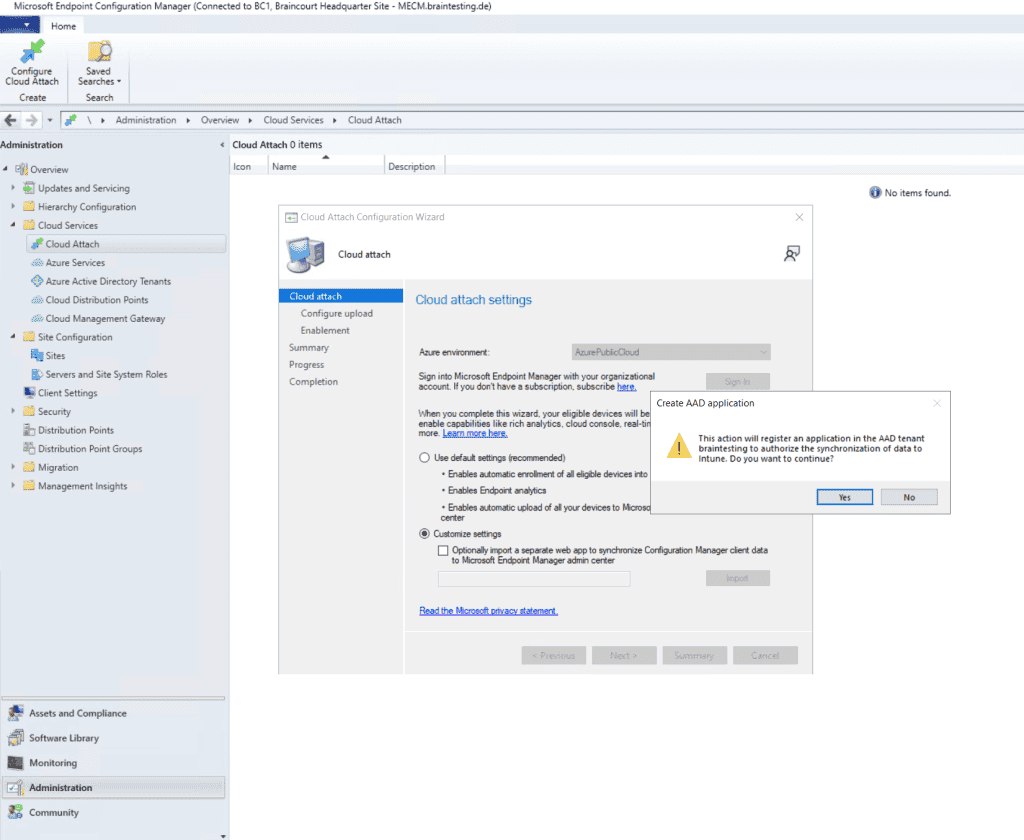
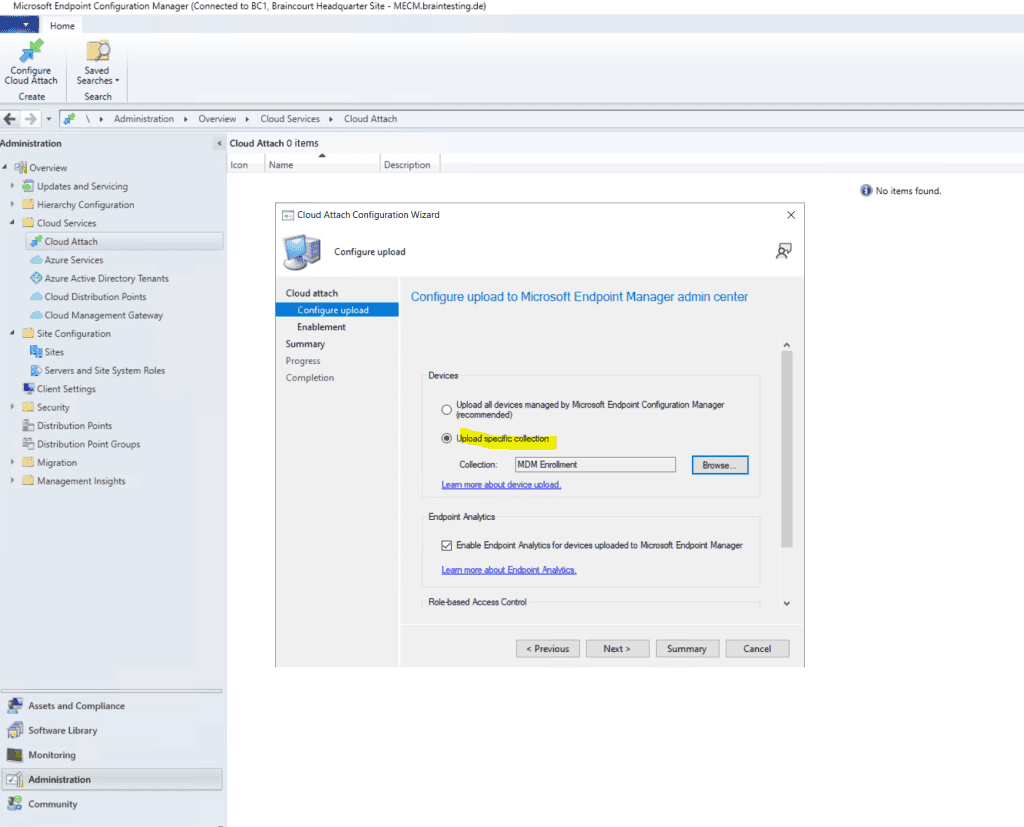
Here I will limit the devices which should be co-managed with Intune by specifying a dedicated device collection.
There’s also a new built-in device collection for Co-management Eligible Devices to help you identify clients.
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/comanage/how-to-enable
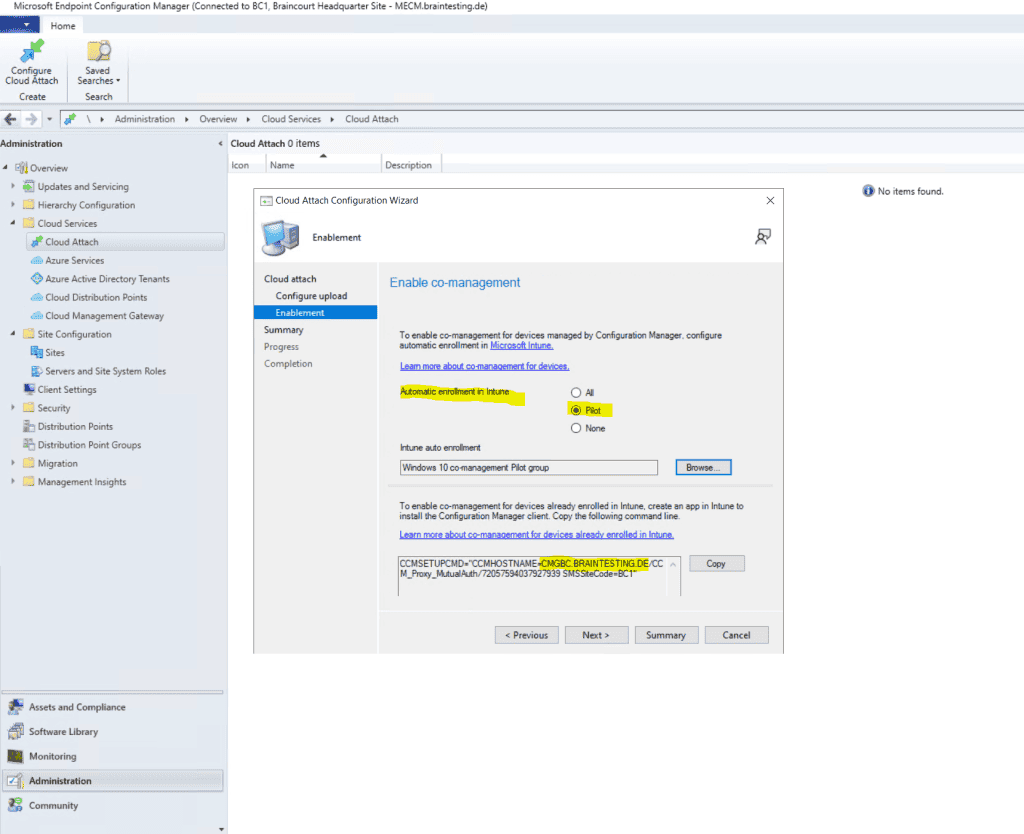
Before enrol Intune to all client you can first use a Pilot Group with a few client to do some testing .
You can see here the previously created Cloud management gateway in the command line. To enable co-management for devices already enrolled in Intune, we create further down an app in Intune to install the Configuration Manager client on them. The MDM Agent on the external devices then knows how to enroll back to our site through the cloud management gateway over the internet.
So copy the following command line.
For Intune auto-enrollment the clients must be windows 10 1709 or later.
Internal only on-prem domain joined devices first needs to auto-register to Hybrid Azure AD joined.
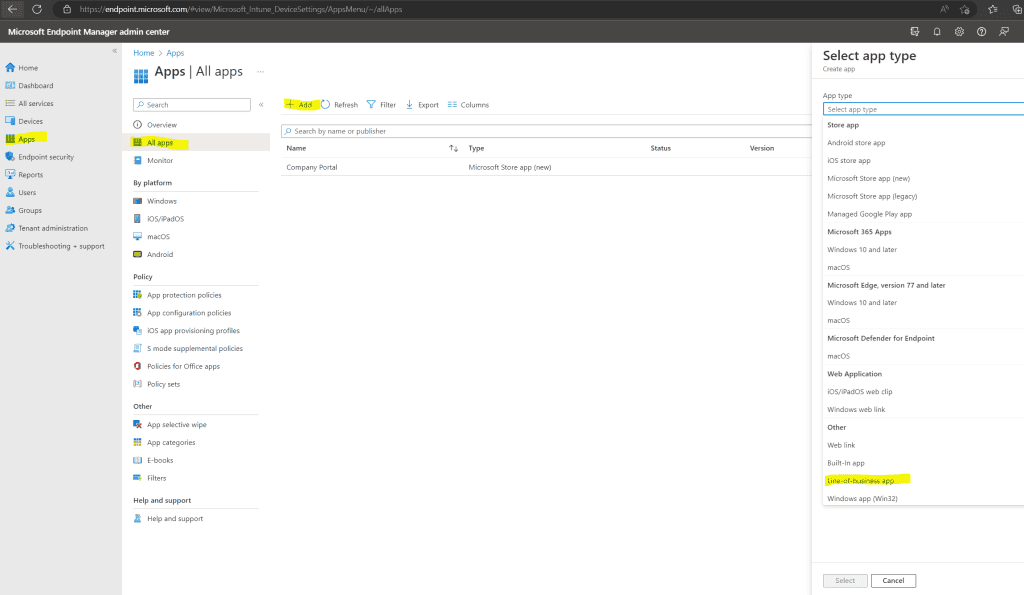
Deploy Configuration Manager by creating a new Intune App
Now we must create the Microsoft Intune App as mentioned above so that the clients on the internet can enroll and register through the cloud management gateway. Therefore the app will deploy the Configuration Manger client to the external internet clients.
In Microsoft Endpoint Manger create a line – of – business app .
https://endpoint.microsoft.com/
Upload the Configuration Manager MSI File located on the MECM Server in the installation directory under bini386ccmsetup.msi
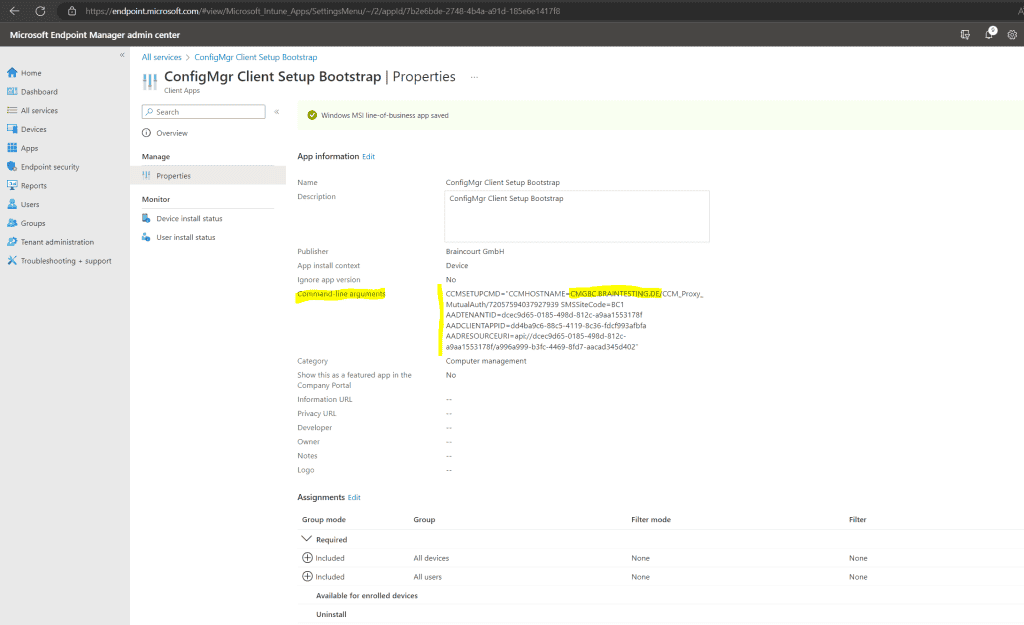
Also insert the CMG command line arguments as shown below. Therefore we need to enter the previously copied CCMHOSTNAME and SMSSiteCode.
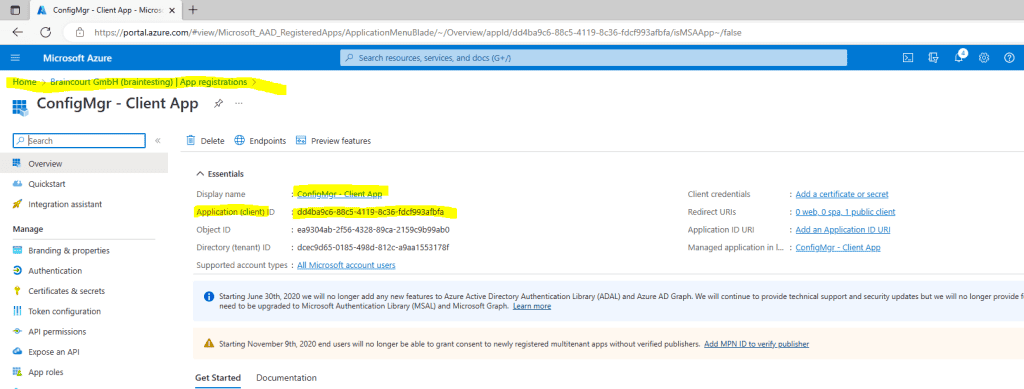
Because I also want to enroll external Azure ad join device which are pure internet client without a PKI client certificate from my internal PKI , I is need also need to include the follow two installation property to support Azure ad client authentication for the CMG :
AADCLIENTAPPID
Specifies the Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) client app identifier. You create or import the client app when you configure Azure services for Cloud Management. An Azure administrator can get the value for this property from the Azure portal. For more information, see get application ID.AADRESOURCEURI
Specifies the Azure AD server app identifier. You create or import the server app when you configure Azure services for Cloud Management. When you create the server app, in the Create Server Application window, this property is the App ID URI.An Azure administrator is get can get the value for this property from the Azure portal . In Azure Active Directory , find the server app under App registration . look for application type web app / API . open the app , select setting , and then select Properties . use the App ID URI value for this aadresourceuri client installation property .
Source: https://github.com/MicrosoftDocs/memdocs/blob/main/memdocs/configmgr/core/clients/deploy/about-client-installation-properties.md#-ccmsetupmsi-properties
AADCLIENTAPPID
AADRESOURCEURI
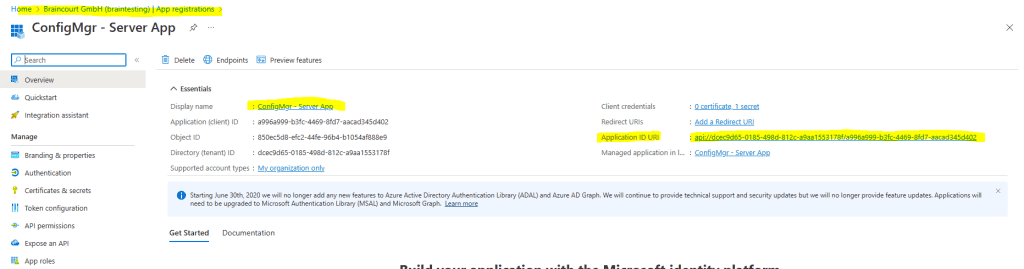
So in my case the CMG command line arguments looks like this:
ccmsetup.exe CCMHOSTNAME = CMGBC.BRAINTESTING.DE / CCM_Proxy_MutualAuth/72057594037927939 SMSSiteCode = BC1 AADTENANTID = dcec9d65 – 0185 – 498d-812c – a9aa1553178f AADCLIENTAPPID = dd4ba9c6 – 88c5 – 4119 – 8c36 – fdcf993afbfa aadresourceuri = api://dcec9d65 – 0185 – 498d-812c – a9aa1553178f / a996a999 – b3fc-4469 – 8fd7 – aacad345d402
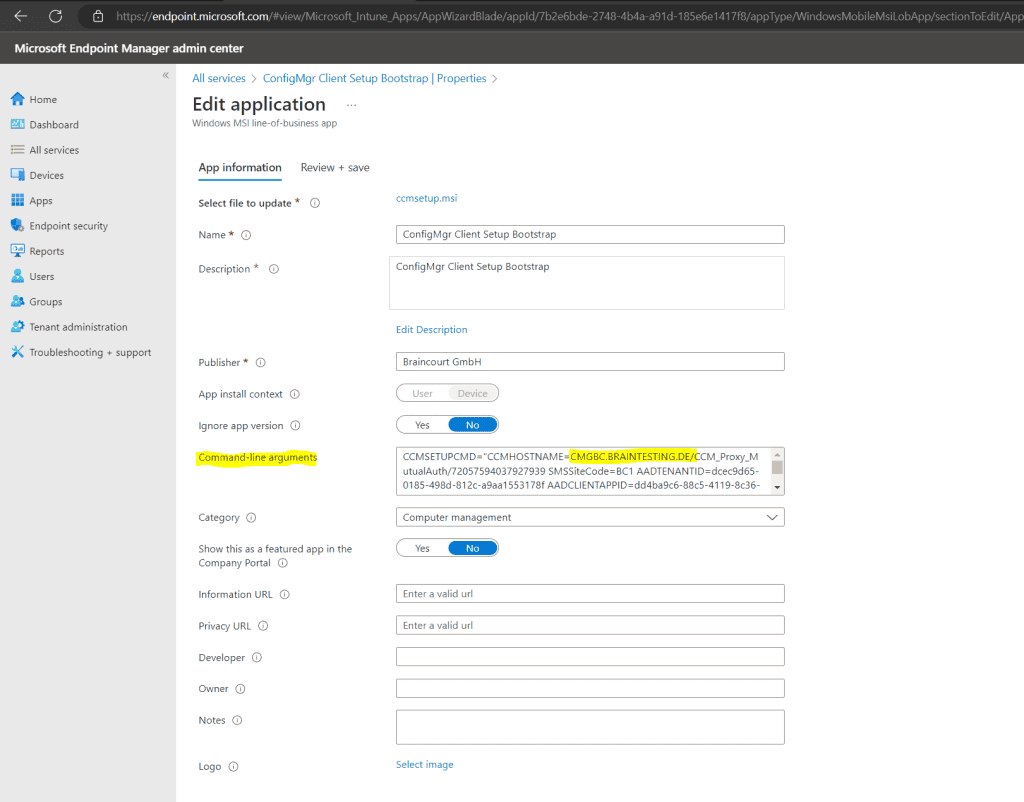
You also have to assign a group or users to which the app should be deployed.
finally click on Create .
deploy Root Certificate for Azure ad join external Devices
As mention further above , we is need also need to deploy the root certificate from our internal PKI to external Azure ad join device , without they would n’t trust the server certificate from our cloud management gateway ( VM / IIS webserver ) .
Therefore we configure in the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center a new configuration profile for our Windows devices.
https://endpoint.microsoft.com/
Home –> Devices –> Windows –> Configuration profiles –> Create profile
Select the Trusted certificate profile.
Enter a name for the app.
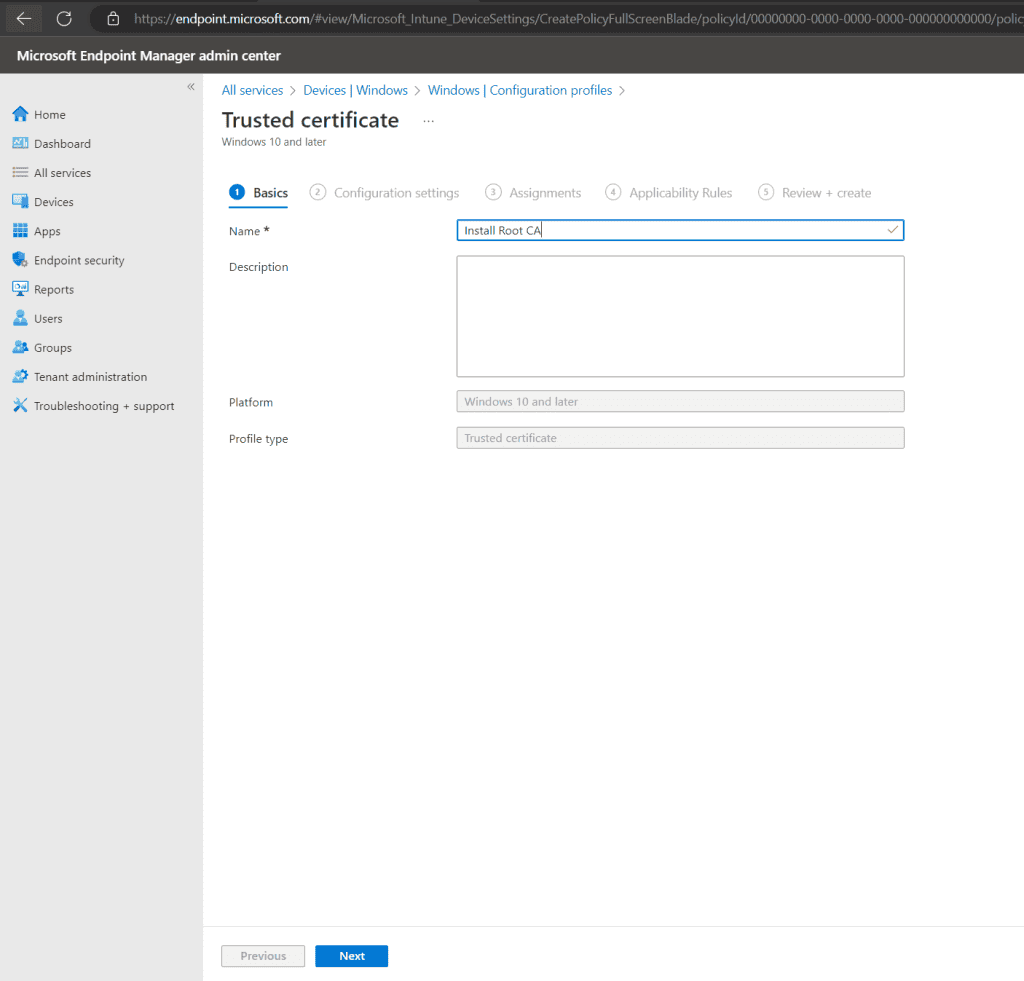
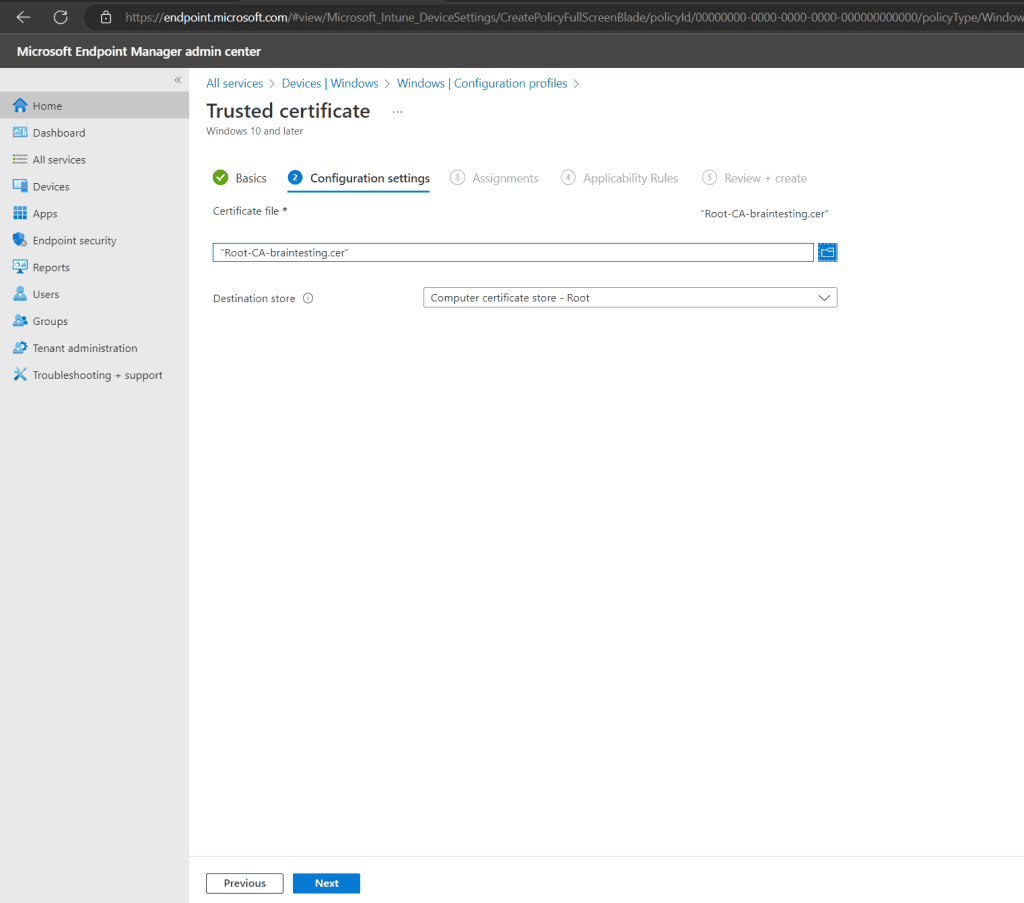
select your Root CA .
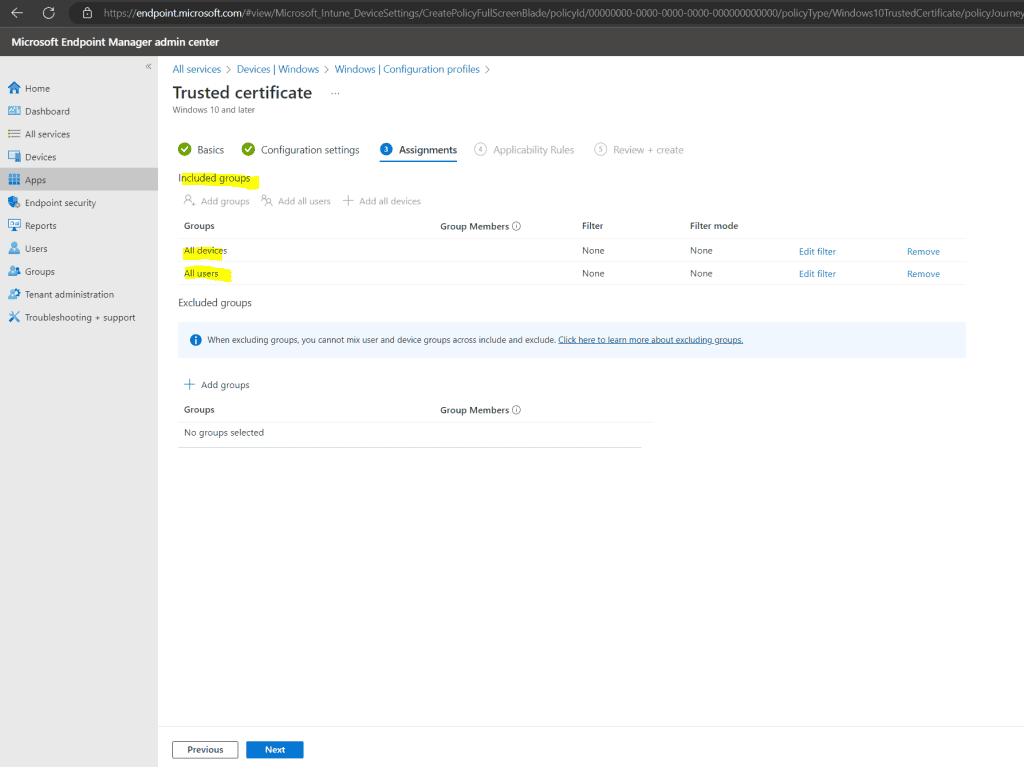
I will assign it to all users and devices.
Configuration Manager Client
As mention already at the beginning , with co – management we is have have two scenario :
- 1. external only Azure AD joined devices auto-enrolled into Intune and with Intune deployed Configuration Manager client through Cloud Management Gateway to get it enrolled co-managed into Intune and Configuration Manager.
- 2 . internal on – prem only domain is joined join device manage in Configuration Manager will auto – register to Hybrid Azure ad join and auto – enrol into Intune to be co – manage with Configuration Manager and Intune .
If you now join a new device from external to Azure AD ( scenario 1 – external client )with a user who is in the MDM user scope, the client is auto-enrolled into Intune and the Configuration Manager client will be downloaded and installed on the client by using the previously created Line-of-business app.
Below I is joined join an external Windows 10 computer with the hostname nb – John – external and the username jdoe@braintesting.de to the Azure ad from my lab environment .
John Doe had the Enterprise Mobility + Security E3 license assigned and is in the MDM scope.
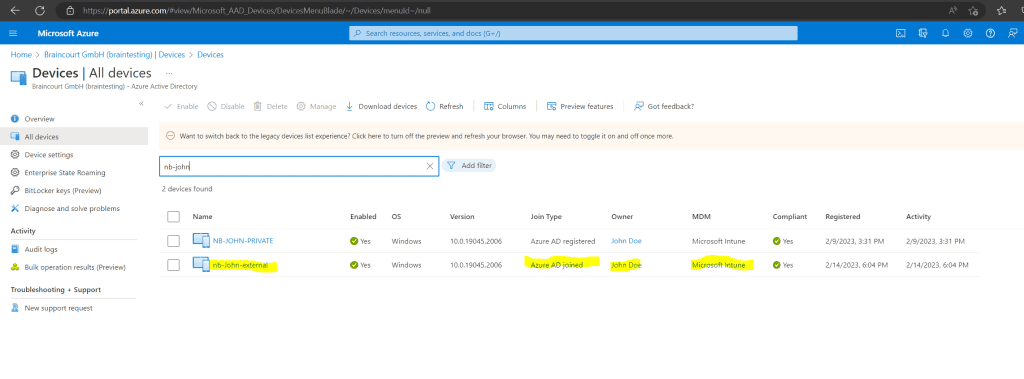
A few minutes later nb-John-external is also auto-enrolled in Intune.
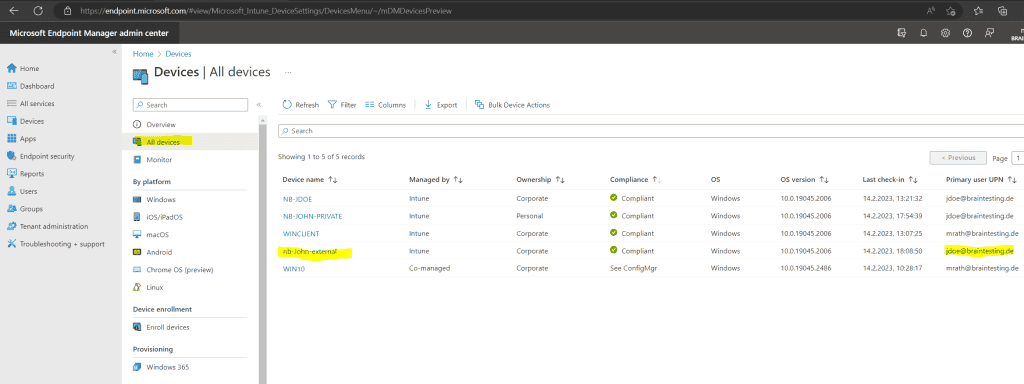
More about how to enroll Windows Computer into Microsoft Intune you is find will find in my follow post .
So far the Configuration Manager client is n’t instal on nb – John – external but will be the next minute because of our line – of – business app we configure previously .
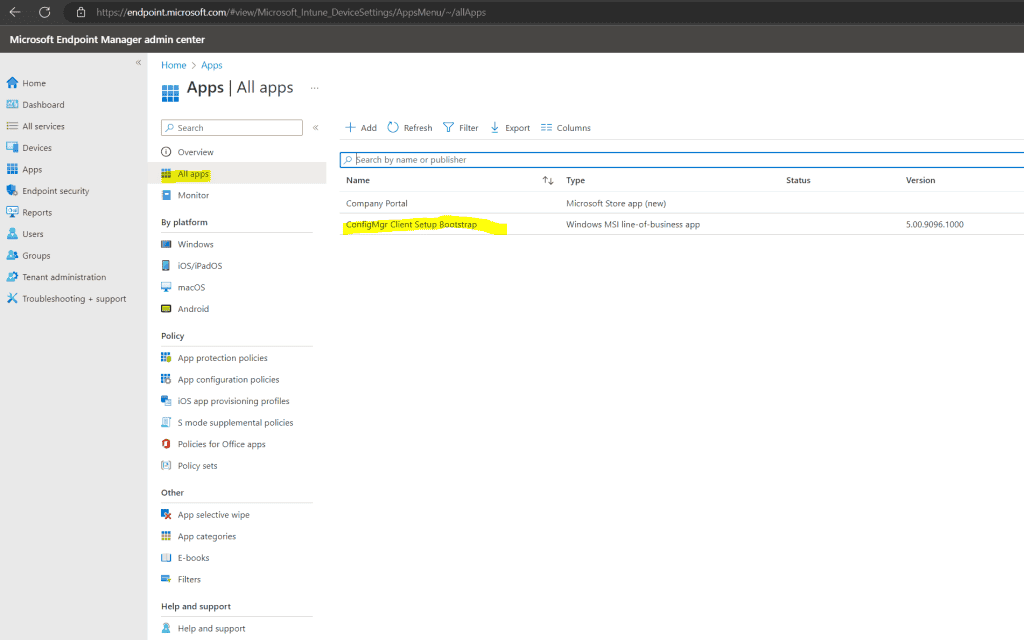
Regarding the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center the Configuration Manager client was installed.
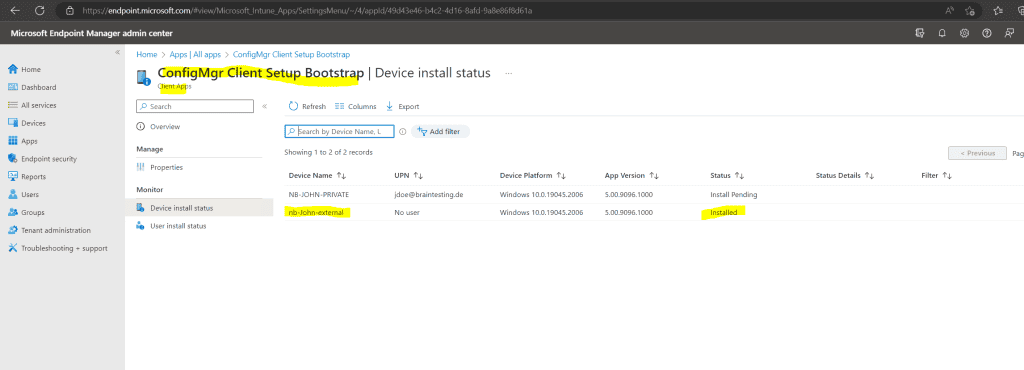
On the client you should now see the following process which will download and install the Configuration Manager client.
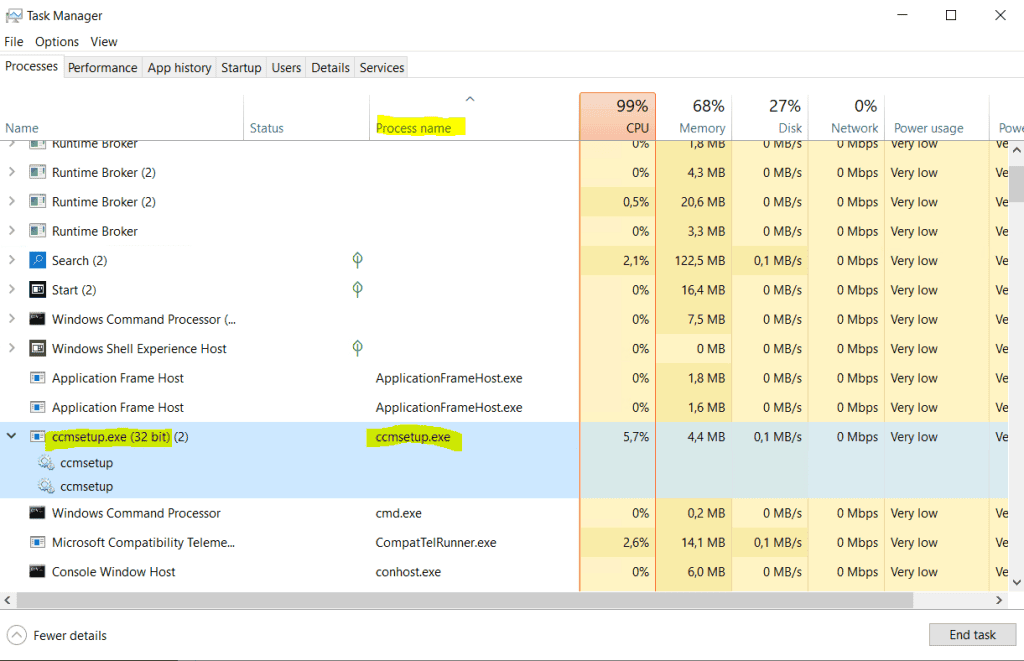
Finally the Configuration Manager client is installed.
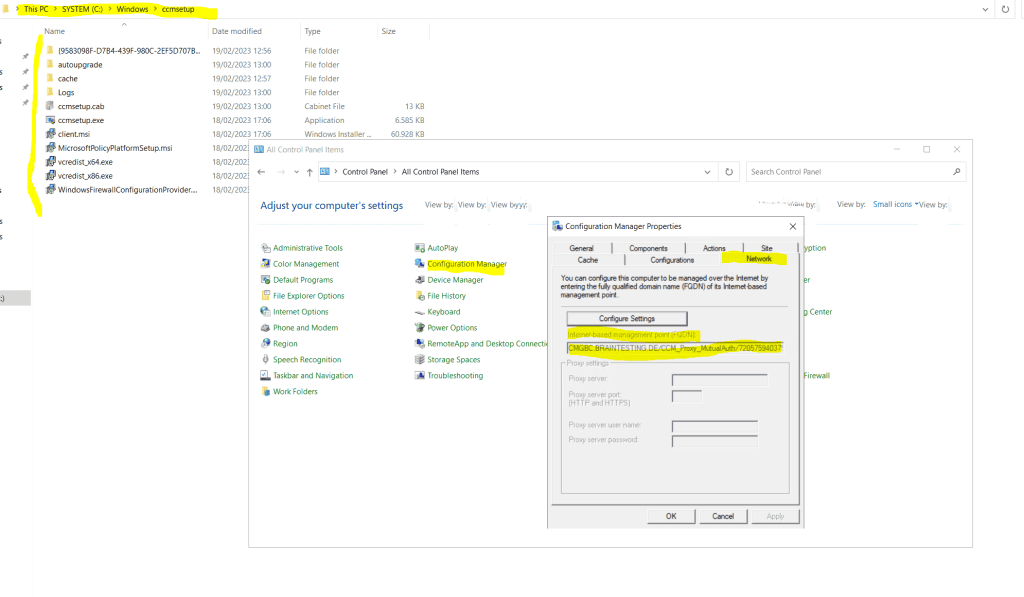
You can also check this process in the ClientIDManagerStartup.log file under C:WindowsCCMLogs
Here you can see the Configuration Manager client from an external Azure AD joined computer.
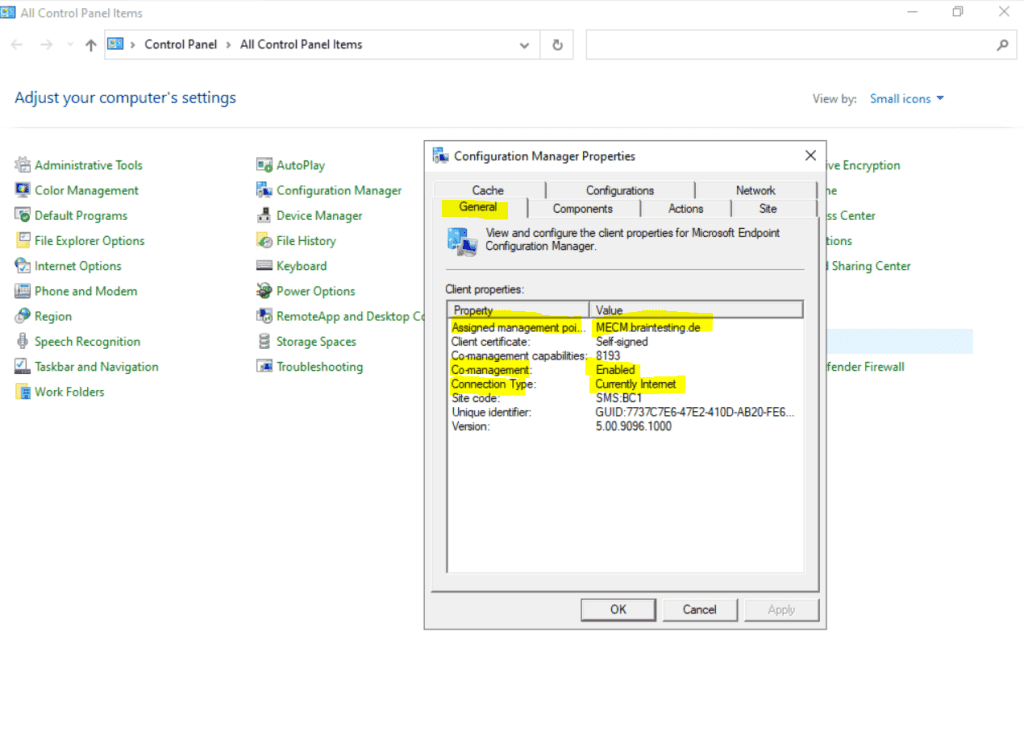
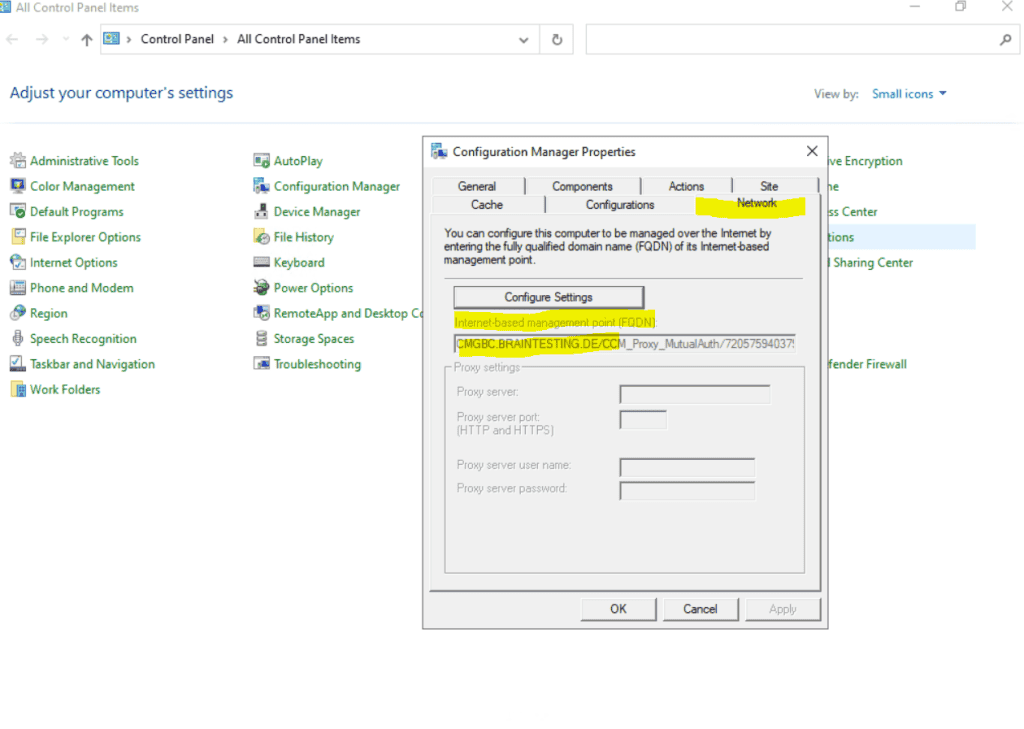
DNS CNAME records internal and public
We is need also need to publish two cname dns record , one internal in our on – premise network and one public in the internet .
The internal will be used by the MECM itself to be able to resolve the public IP address from the Cloud Management Gateway to establish a connection and secure channel with it.
The public cname dns record will be used by the external Azure ad join internet client to establish a secure connection to the Cloud Management Gateway .
Below you is see can see if the on – premise MECM is connect to the cloud management gateway .
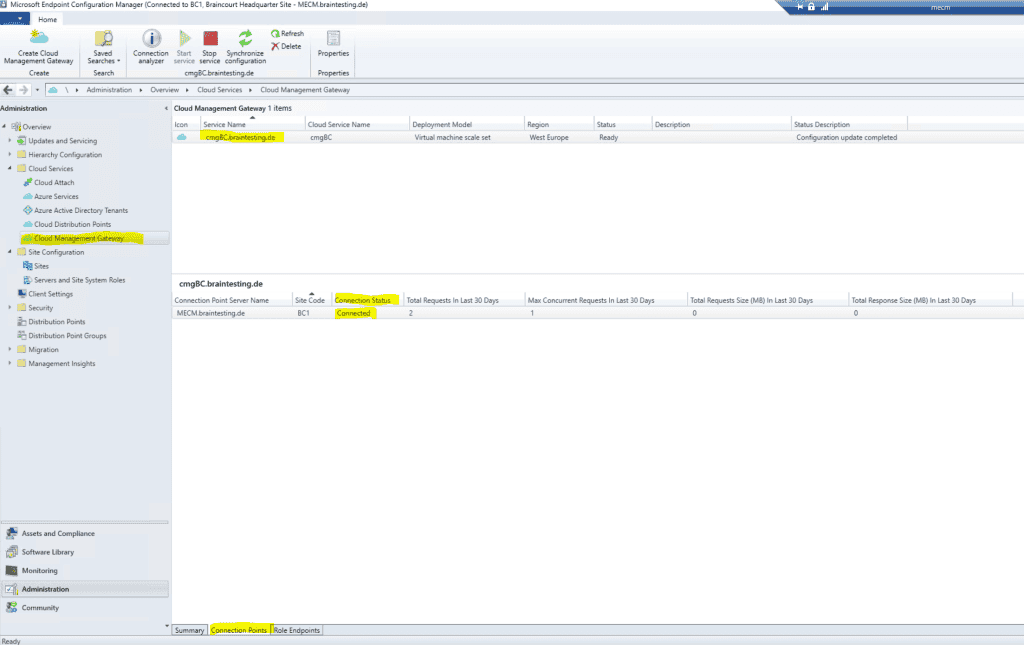
create the internal cname dns record .
You is use can also use the Connection analyzer from MECM to test the Cloud management gateway connection .
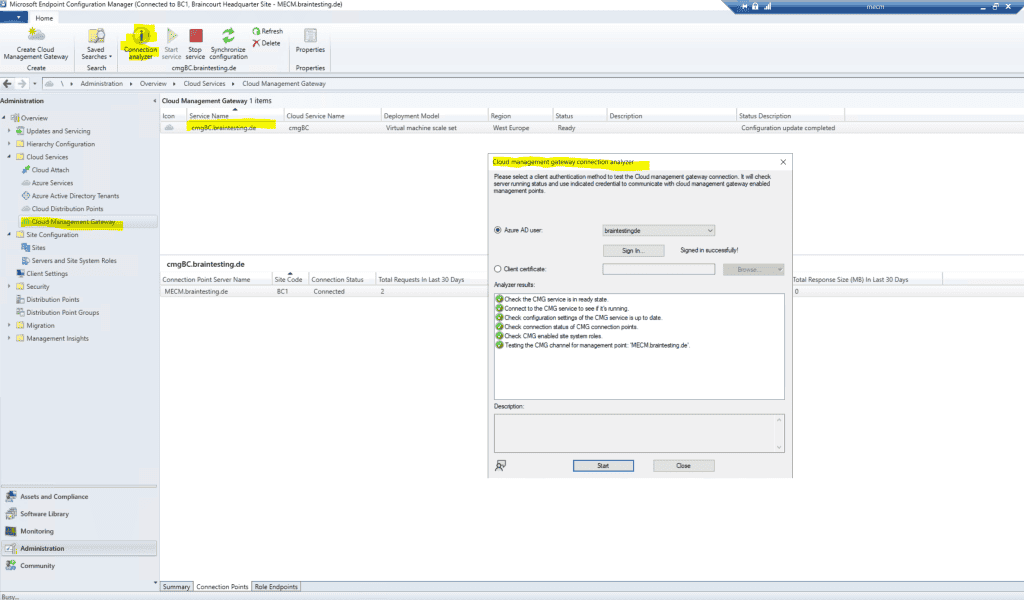
Distribute Applications through the CMG
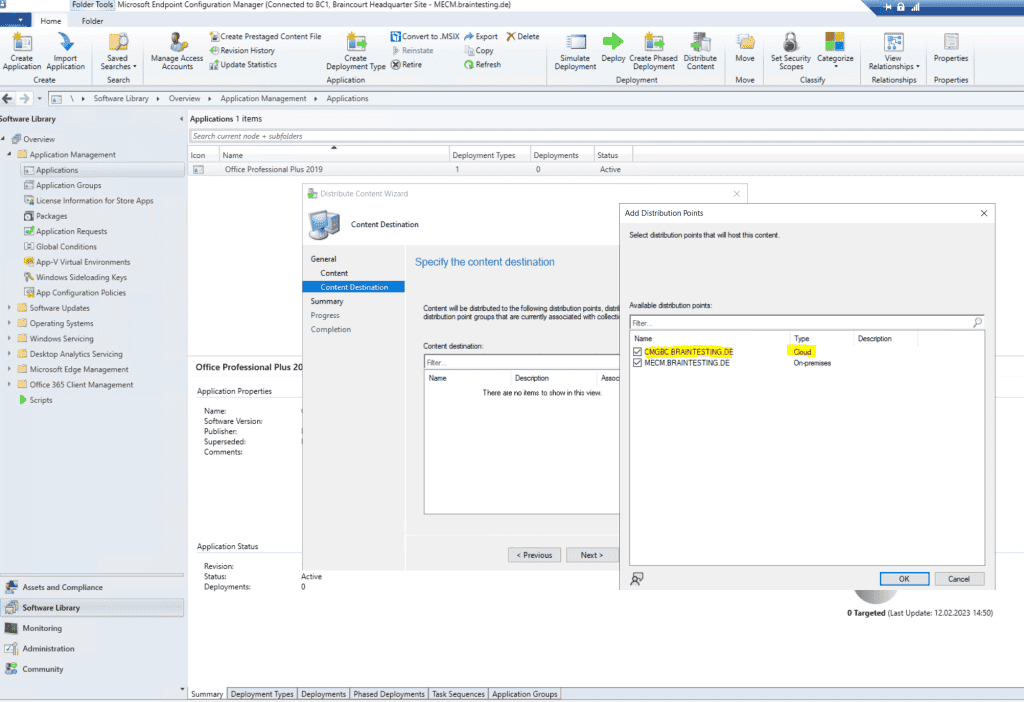
To distribute application to external client by using our new CMG , we is have have to add the new CMG as new distribution point .
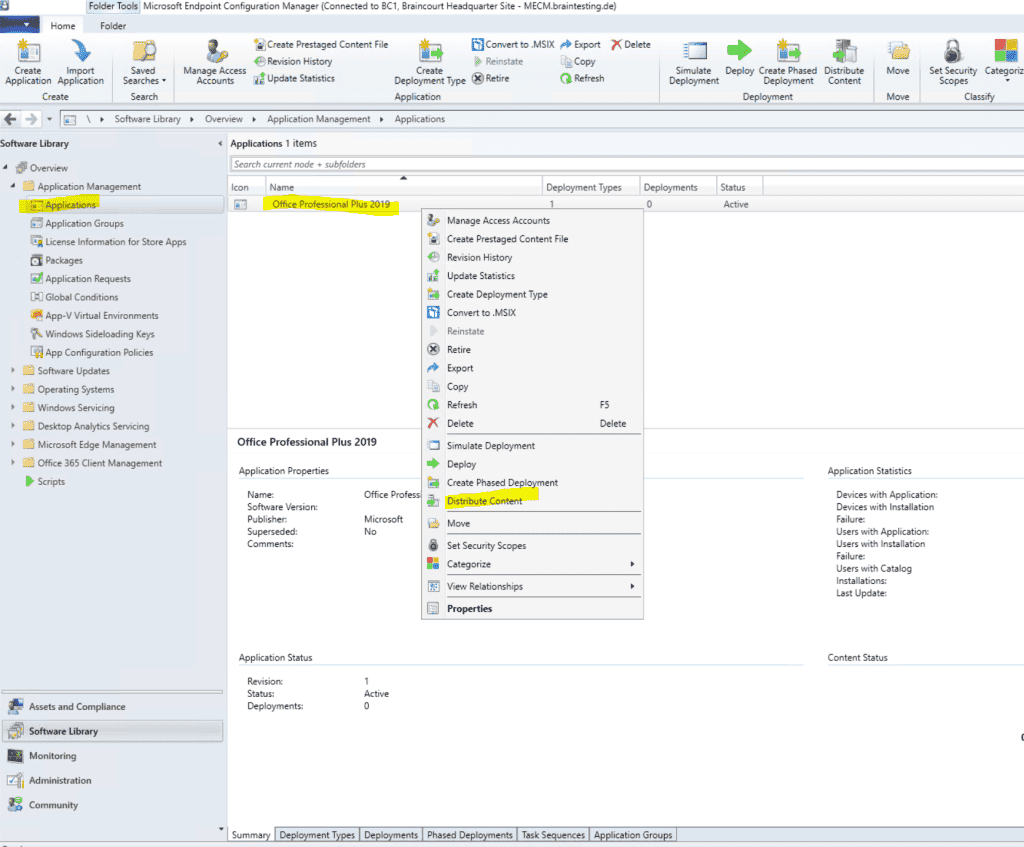
Below for testing I will distribute Office Professional 2019.
Add a distribution point.
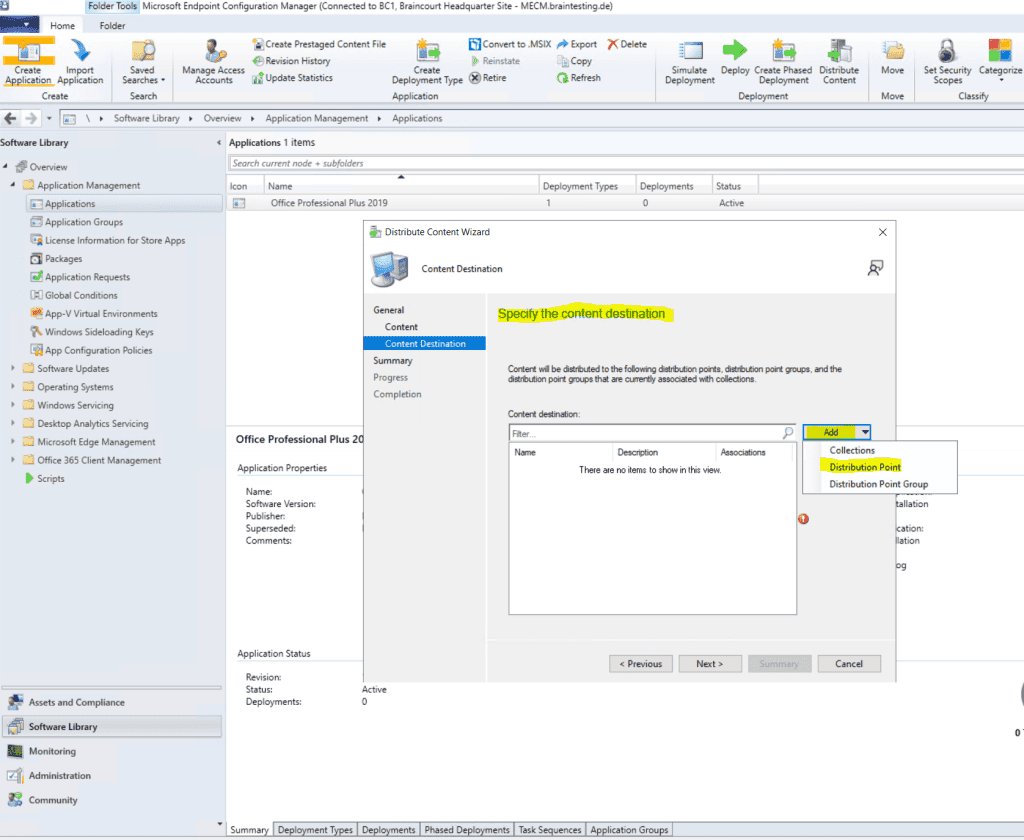
As this is a new installation in my lab environment from Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager , I is distribute will distribute the application to the cloud management gateway and on – premise .
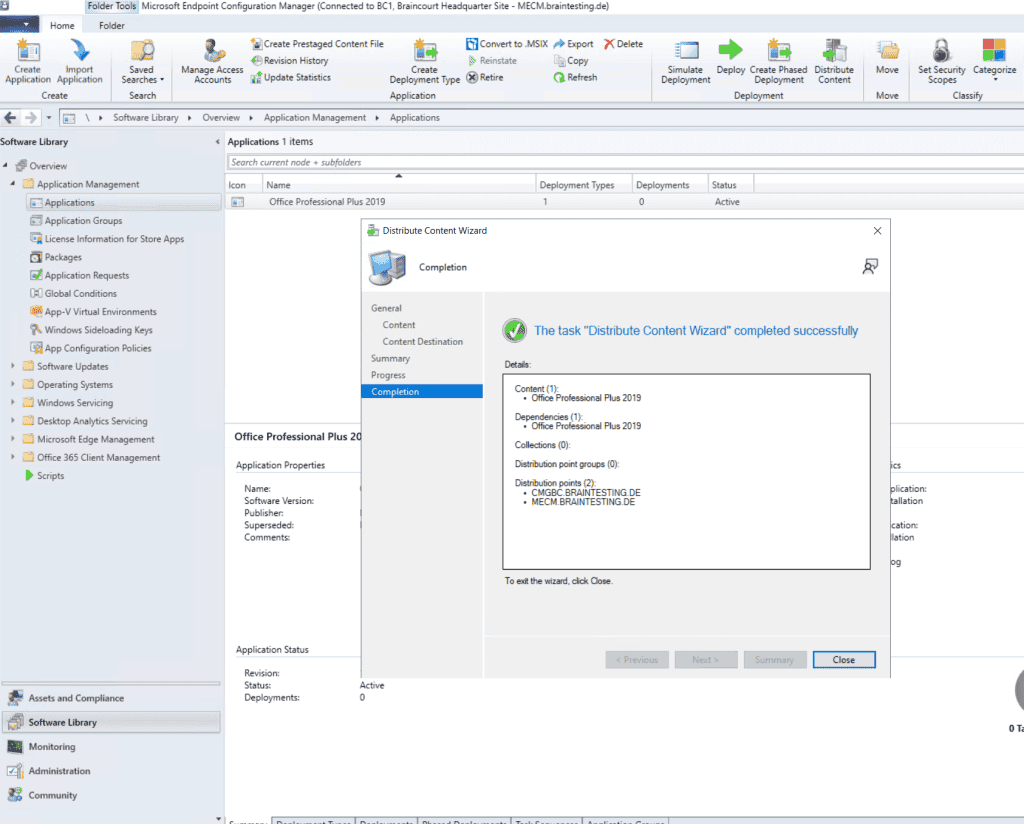
Below you can see that the distribution from Office Professional 2019 to the new Cloud Management Gateway is still in progress.
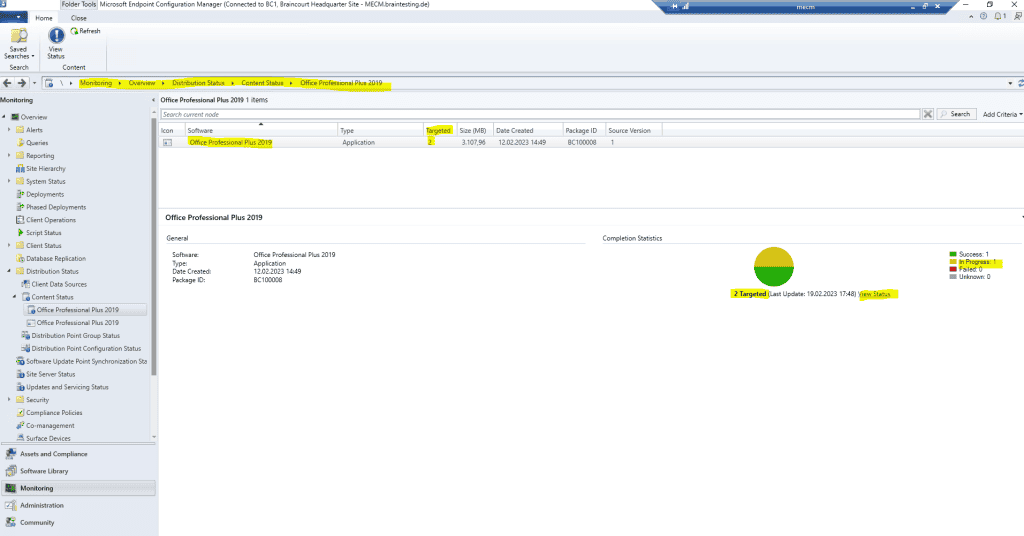
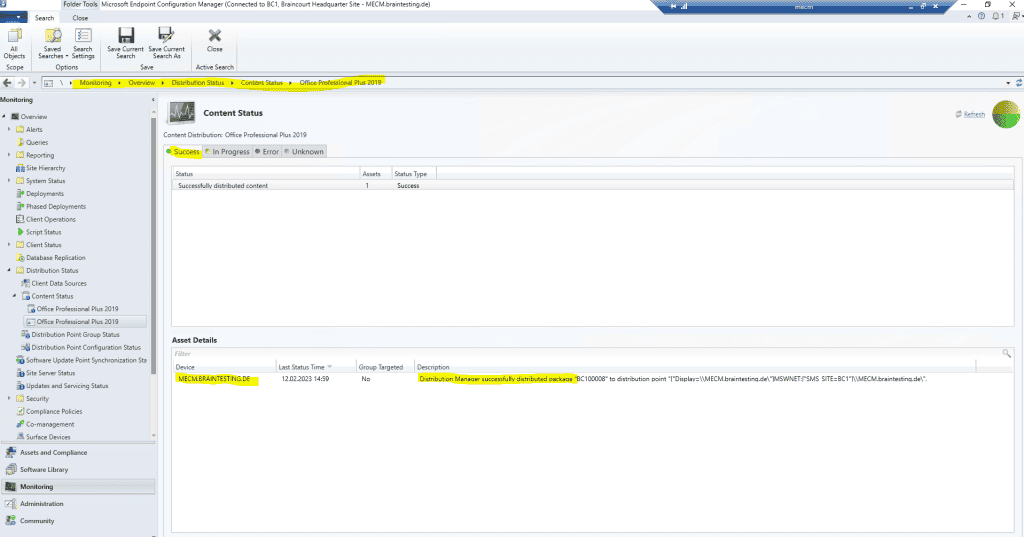
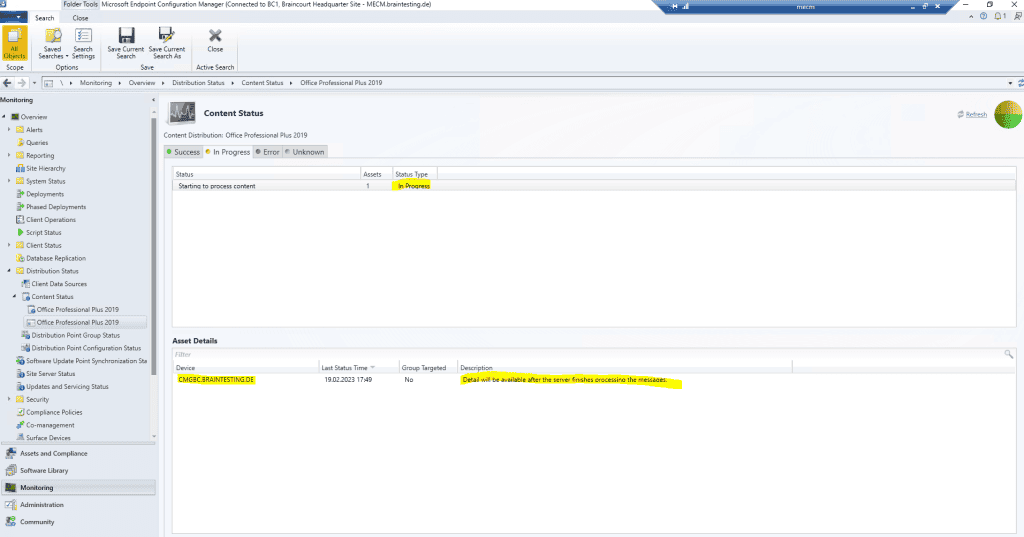
Therefore on the external internet clients so far is no application available at the Software Center.
Finally a few minutes later Office Professional 2019 was successfully distributed on the Cloud Management Gateway.
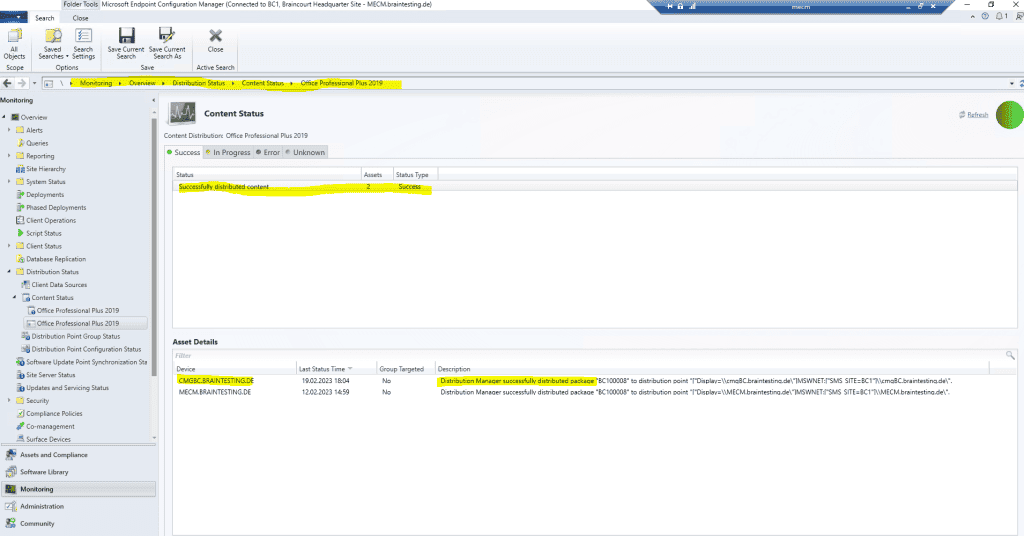
Further Office Professional 2019 is deploy to all user , therefore it is is is now also available in the Software Center for external internet client as show below .
co – management workload
You is have do n’t have to switch the workload , or you can do them individually when you ’re ready . Configuration Manager is continues continue to manage all other workload , include those workload that you do n’t switch to Intune , and all other feature of Configuration Manager that co – management does n’t support .
If you switch a workload to Intune, but later change your mind, you can switch it back to Configuration Manager, although there might be an impact. For example, Windows and Office versions will remain at a later version if installed by Intune.
Co-management supports the following workloads:
- Compliance policies
- Windows Update policies
- Resource access policies
- Endpoint Protection
- Device configuration
- office click – to – run app
- Client apps
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/comanage/workload
Switch Workloads from Configuration Manager to Intune
For Windows 10 or later devices that are in a co-management state, you can have Microsoft Intune start managing different workloads.
choose Pilot Intune to have Intune manage the workload for only client in the Pilot group .
If you are not ready to move workloads to Intune, select Configuration Manager.
The different workloads will be described in detail in the following article.
co – management workload
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/comanage/workload
When you configure a workload for Pilot Intune above, you have to select a device collection to be the pilot group in the tab Staging.
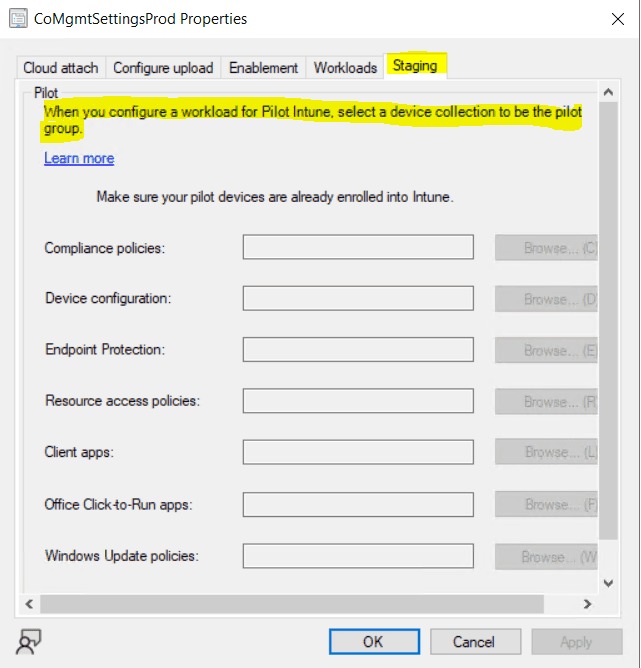
Before you switch any workload , make sure you properly configure and deploy the corresponding workload in Intune . Make sure that workload are always manage by one of the management tool for your device . When you switch a co – management workload , the co – manage devices is synchronize automatically synchronize MDM policy from Microsoft Intune .
source : https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/comanage/how-to-switch-workload
How to switch Configuration Manager workload to Intune
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/comanage/how-to-switch-workloads
link
What is co-management?
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/comanage/overviewEnable cloud attach for Configuration Manager
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/comanage/how-to-enablePlan for the CMG in Configuration Manager
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/clients/manage/cmg/plan-cloud-management-gatewayPKI certificates for clients
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/plan-design/network/pki-certificate-requirements#pki-certificates-for-clientsCloud management gateway overview
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/clients/manage/cmg/overviewCMG client authentication
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/clients/manage/cmg/plan-client-authenticationConfigure client authentication for cloud management gateway
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/clients/manage/cmg/configure-authenticationToken-based authentication for cloud management gateway
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/clients/deploy/deploy-clients-cmg-tokenHow to manage client in Configuration Manager
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/clients/manage/manage-clientHow to prepare internet-based devices for co-management
https://github.com/MicrosoftDocs/memdocs/blob/main/memdocs/configmgr/comanage/how-to-prepare-Win10.mdPKI certificate requirements for Configuration Manager
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/core/plan-design/network/pki-certificate-requirementsco – management workload
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/comanage/workloadHow to switch Configuration Manager workload to Intune
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/configmgr/comanage/how-to-switch-workloads