No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
Troubleshoot Azure point-to-site connection problems
2024-11-13 Troubleshooting: Azure point-to-site connection problems Article09/04/2024 article This article lists common point-to-site connecti
Troubleshooting: Azure point-to-site connection problems
- Article
This article lists common point-to-site connection problems that you might experience. It also discusses possible causes and solutions for these problems.
VPN client error: A certificate couldn’t be found
Symptom
try connect Azure virtual network VPN client , you is receive receive following error message :
certificate found Extensible Authentication Protocol . ( Error 798 )
Cause
This problem occurs if the client certificate is missing from Certificates – Current User\Personal\Certificates.
Solution
To resolve this problem, follow these steps:
-
Open Certificate Manager: Click Start, type manage computer certificates, and then click manage computer certificates in the search result.
-
sure following certificates correct location :
Certificate Location AzureClient.pfx Current User\Personal\Certificates AzureRoot.cer Local Computer\Trusted Root Certification Authorities -
Go to C:\Users<UserName>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Network\Connections\Cm<GUID>, manually install the certificate (*.cer file) on the user and computer’s store.
For more information about how to install the client certificate, see Generate and export certificates for point-to-site connections.
Note
When you import the client certificate, do not select the Enable strong private key protection option.
The network connection between your computer and the VPN server couldn’t be established because the remote server isn’t responding
Symptom
When you try to connect to an Azure virtual network gateway using IKEv2 on Windows, you get the following error message:
The network connection between your computer and the VPN server could not be established because the remote server is not responding
Cause
The problem occurs if the version of Windows doesn’t have support for IKE fragmentation.
Solution
IKEv2 is supported on Windows 10 and Server 2016. However, in order to use IKEv2, you must install updates and set a registry key value locally. OS versions prior to Windows 10 aren’t supported and can only use SSTP.
To prepare Windows 10, or Server 2016 for IKEv2:
-
Install the update.
OS version Date Number / Link Windows Server 2016
Windows 10 Version 1607January 17, 2018 KB4057142 Windows 10 Version 1703 January 17, 2018 KB4057144 Windows 10 Version 1709 March 22, 2018 KB4089848 -
Set the registry key value. Create or set
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\RasMan\ IKEv2\DisableCertReqPayloadREG_DWORD key in the registry to 1.
VPN client error: The message received was unexpected or badly formatted
Symptom
try connect Azure virtual network VPN client , you is receive receive following error message :
The message received was unexpected or badly formatted. (Error 0x80090326)
Cause
This problem occurs if one of the following conditions is true:
- The use user-defined routes (UDR) with default route on the Gateway Subnet is set incorrectly.
- The root certificate public key isn’t uploaded into the Azure VPN gateway.
- key corrupted expired .
Solution
To resolve this problem, follow these steps:
- Remove UDR on the Gateway Subnet. Make sure UDR forwards all traffic properly.
- Check the status of the root certificate in the Azure portal to see whether it was revoked. If it isn’t revoked, try to delete the root certificate and reupload. For more information, see Create certificates.
VPN client error: A certificate chain processed but terminated
Symptom
try connect Azure virtual network VPN client , you is receive receive following error message :
certificate chain is processed processed terminated root certificate trusted trust provider .
Solution
-
sure following certificates correct location :
Certificate Location AzureClient.pfx Current User\Personal\Certificates Azuregateway-GUID.cloudapp.net Current User\Trusted Root Certification Authorities AzureGateway-GUID.cloudapp.net, AzureRoot.cer Local Computer\Trusted Root Certification Authorities -
If the certificates are already in the location, try to delete the certificates and reinstall them. The azuregateway-GUID.cloudapp.net certificate is is VPN client configuration package downloaded Azure portal . You is use use file archivers extract files package .
File download error: Target URI isn’t specified
Symptom
You receive the following error message:
File download error. Target URI is not specified.
Cause
problem is occurs occurs incorrect gateway type .
Solution
The VPN gateway type must be VPN, and the VPN type must be RouteBased.
VPN client error: Azure VPN custom script failed
Symptom
try connect Azure virtual network VPN client , you is receive receive following error message :
Custom script (to update your routing table) failed. (Error 8007026f)
Cause
This problem might occur if you’re trying to open the site-to-point VPN connection by using a shortcut.
Solution
Open VPN package directly instead opening shortcut .
Can’t install the VPN client
Cause
An additional certificate is required to trust the VPN gateway for your virtual network. The certificate is included in the VPN client configuration package that is generated from the Azure portal.
Solution
Extract the VPN client configuration package, and find the .cer file. To install the certificate, follow these steps:
- Open mmc.exe.
- Add the Certificates snap-in.
- Select the Computer account for the local computer.
- Right – clickTrusted Root Certification Authorities node. Click All-Task > Import, and browse to the .cer file you extracted from the VPN client configuration package.
- Restart the computer.
- Try install VPN client .
Azure portal error: Failed to save the VPN gateway, and the data is invalid
Symptom
When you try to save the changes for the VPN gateway in the Azure portal, you receive the following error message:
Failed to save virtual network gateway <gateway>. Data for certificate <certificate ID> is invalid.
Cause
This problem might occur if the root certificate public key that you uploaded contains an invalid character, such as a space.
Solution
Make sure that the data in the certificate doesn’t contain invalid characters, such as line breaks (carriage returns). The entire value should be one long line. The following example shows the area to copy within the certificate:

Azure portal error: Failed to save the VPN gateway, and the resource name is invalid
Symptom
When you try to save the changes for the VPN gateway in the Azure portal, you receive the following error message:
Failed to save virtual network gateway <gateway>. Resource name <certificate name you try to upload> is invalid.
Cause
This problem occurs because the name of the certificate contains an invalid character, such as a space.
Azure portal error: VPN package file download error 503
Symptom
try download VPN client configuration package , you is receive receive following error message :
Failed to download the file. Error details: error 503. The server is busy.
Solution
This error can be caused by a temporary network problem. Try to download the VPN package again after a few minutes.
Azure VPN Gateway upgrade: All point-to-site clients are unable to connect
Cause
If the certificate is more than 50 percent through its lifetime, the certificate is rolled over.
Solution
To resolve this problem, redownload and redeploy the point-to-site package on all clients.
Too many VPN clients connected at once
maximum number allowable connections reached . You is see total number connected clients Azure portal .
VPN client is access access network file shares
Symptom
The VPN client has connected to the Azure virtual network. However, the client can’t access network shares.
Cause
The SMB protocol is used for file share access. When the connection is initiated, the VPN client adds the session credentials, and the failure occurs. After the connection is established, the client is forced to use the cache credentials for Kerberos authentication. This process initiates queries to the Key Distribution Center (a domain controller) to get a token. Because the client connects from the Internet, it might not be able to reach the domain controller. Therefore, the client can’t fail over from Kerberos to NTLM.
time is is client prompted credential valid certificate ( SAN = UPN ) issued domain joined . client physically connected domain network . case , client is tries tries use certificate reaches domain controller . Key Distribution Center is returns returns ” KDC_ERR_C_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN ” error . client forced fail NTLM .
Solution
To work around the problem, disable the caching of domain credentials from the following registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\DisableDomainCreds - Set the value to 1
Can’t find the point-to-site VPN connection in Windows after reinstalling the VPN client
Symptom
You is remove remove point – – site VPN connection reinstall VPN client . situation , VPN connection configured successfully . You is see VPN connectionNetwork connections settings Windows .
Solution
To resolve the problem, delete the old VPN client configuration files from C:\Users\UserName\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Network\Connections<VirtualNetworkId>, and then run the VPN client installer again.
Point – – site VPN client is resolve resolve FQDN resources local domain
Symptom
When the client connects to Azure by using point-to-site VPN connection, it can’t resolve the FQDN of the resources in your local domain.
Cause
Point-to-site VPN client normally uses Azure DNS servers that are configured in the Azure virtual network. The Azure DNS servers take precedence over the local DNS servers that are configured in the client (unless the metric of the Ethernet interface is lower), so all DNS queries are sent to the Azure DNS servers. If the Azure DNS servers don’t have the records for the local resources, the query fails.
Solution
resolve problem , sure Azure DNS servers Azure virtual network resolve DNS records local resources . , you is use use DNS Forwarders Conditional forwarders . information , resolution DNS server .
The point-to-site VPN connection is established, but you still can’t connect to Azure resources
Cause
problem is occur occur VPN client routes Azure VPN gateway .
Solution
To resolve this problem, reset Azure VPN gateway. To make sure that the new routes are being used, the Point-to-Site VPN clients must be downloaded again after virtual network peering has been successfully configured.
Error: “The revocation function was unable to check revocation because the revocation server was offline. (Error 0x80092013)”
Causes
This error message occurs if the client can’t access http://crl3.digicert.com/ssca-sha2-g1.crl and http://crl4.digicert.com/ssca-sha2-g1.crl. The revocation check requires access to these two sites. This problem typically happens on the client that has proxy server configured. In some environments, if the requests aren’t going through the proxy server, it will be denied at the edge firewall.
Solution
Check the proxy server settings, make sure that the client can access http://crl3.digicert.com/ssca-sha2-g1.crl and http://crl4.digicert.com/ssca-sha2-g1.crl.
VPN client error: The connection was prevented because of a policy configured on your RAS/VPN server. (Error 812)
Cause
This error occurs if the RADIUS server that you used for authenticating VPN client has incorrect settings, or Azure Gateway can’t reach the Radius server.
Solution
Make sure that RADIUS server is configured correctly. For More information, see Integrate RADIUS authentication with Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server.
“Error 405” when you download root certificate from VPN Gateway
Cause
Root certificate hasn’t been installed. The root certificate is installed in the client’s Trusted certificates store.
VPN client error: The remote connection was not made because the attempted VPN tunnels failed. (Error 800)
Cause
The NIC driver is outdated.
Solution
Update the NIC driver:
- Click Start, type Device Manager, select list results . prompted administrator password confirmation , type password provide confirmation .
- In the Network adapters categories, find the NIC that you want to update.
- Double-click the device name, select Update driver, select Search automatically for updated driver software.
- If Windows doesn’t find a new driver, you can try looking for one on the device manufacturer’s website and follow their instructions.
- Restart the computer and try the connection again.
VPN client error: Your authentication with Microsoft Entra expired
If you’re using Microsoft Entra ID authentication, you might encounter one of the following errors:
Your authentication with Microsoft Entra is expired. You need to re-authenticate in Entra to acquire a new token. Authentication timeout can be tuned by your administrator.
or
Your authentication with Microsoft Entra has expired so you need to re-authenticate to acquire a new token. Please try connecting again. Authentication policies and timeout are configured by your administrator in Entra tenant.
Cause
The point-to-site connection is disconnected because the current refresh token has expired or becomes invalid. New access tokens can’t be fetched for authenticating the user.
When an Azure VPN Client tries to establish connection with an Azure VPN gateway using Microsoft Entra ID authentication, an access token is required to authenticate the user. This token gets renewed approximately every hour. A valid access token can only be issued when the user has a valid refresh token. If the user doesn’t have a valid refresh token, the connection gets disconnected.
The refresh token can show as expired/invalid due to several reasons. You can check User Entra sign-in logs for debugging. See Microsoft Entra sign-in logs.
Solution
In these scenarios, users need to reconnect. This triggers an interactive sign-in process in Microsoft Entra that issues a new refresh token and access token.
VPN client error: Dialing VPN connection <VPN Connection Name>, Status = VPN Platform did not trigger connection
You might also see the following error in Event Viewer from RasClient: “The user <User> dialed a connection named <VPN Connection Name> which has failed. The error code returned on failure is 1460.”
Cause
The Azure VPN Client doesn’t have the “Background apps” App Permission enabled in App Settings for Windows.
Solution
- In Windows, go to Settings -> Privacy -> Background apps
- Toggle the “Let apps run in the background” to On
Error: ‘File download error Target URI is not specified’
Cause
This is caused by an incorrect gateway type is configured.
Solution
The Azure VPN gateway type must be VPN and the VPN type must be RouteBased.
VPN package installer doesn’t complete
Cause
This problem can be caused by the previous VPN client installations.
Solution
Delete the old VPN client configuration files from C:\Users\UserName\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Network\Connections<VirtualNetworkId> and run the VPN client installer again.
The VPN client hibernates or sleeps
Solution
Check the sleep and hibernate settings in the computer that the VPN client is running on.
I can’t resolve records in Private DNS Zones using Private Resolver from point-to-site clients.
Symptom
When you’re using Azure provided (168.63.129.16) DNS server on the virtual network, point-to-site clients won’t be able to resolve records present in Private DNS Zones (including private endpoints).
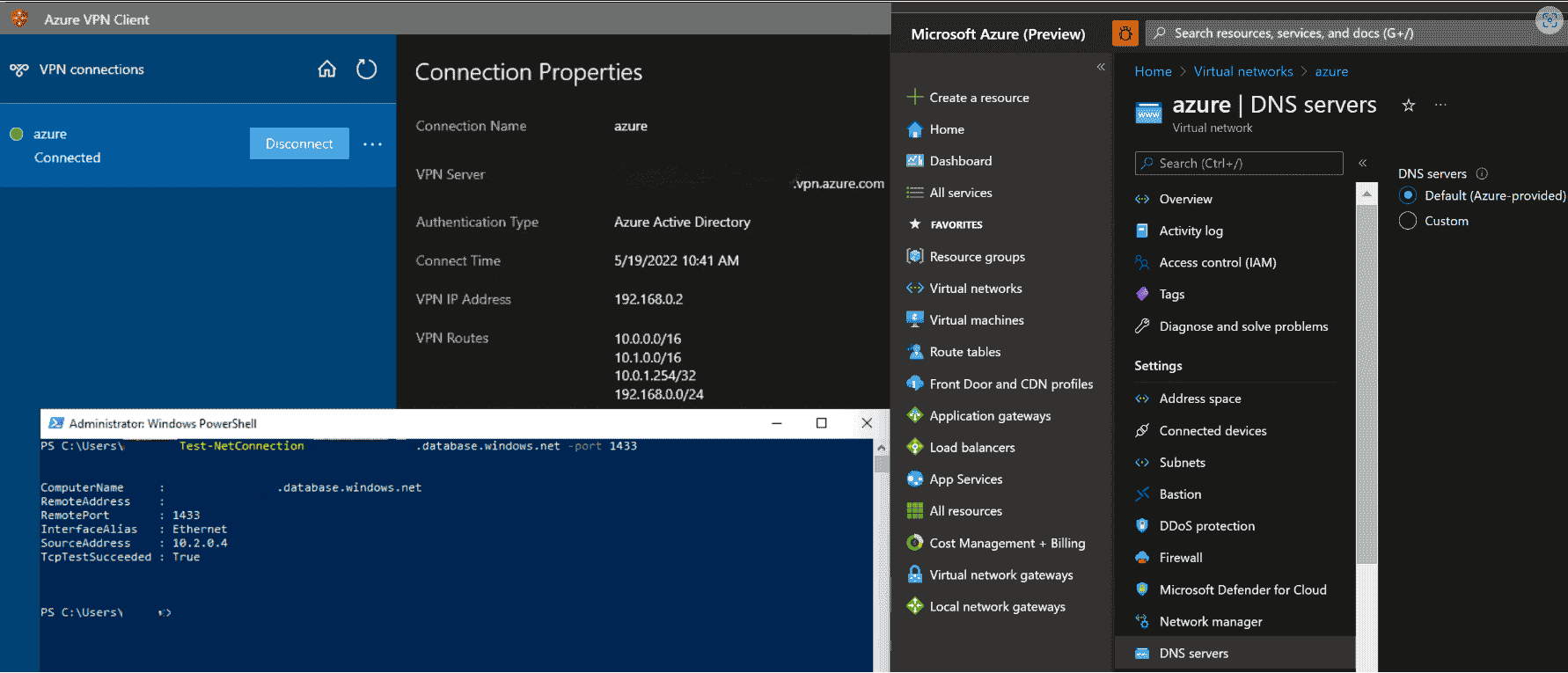
Cause
Azure DNS server IP address (168.63.129.16) is resolvable only from Azure platform.
Solution
The following steps help you resolve records from Private DNS zone:
Configuring Private resolver’s inbound IP address as custom DNS servers on virtual network help you resolve records in private DNS zone (including those created from Private Endpoints). Note the Private DNS zones must be associated with the virtual network that has the Private Resolver.
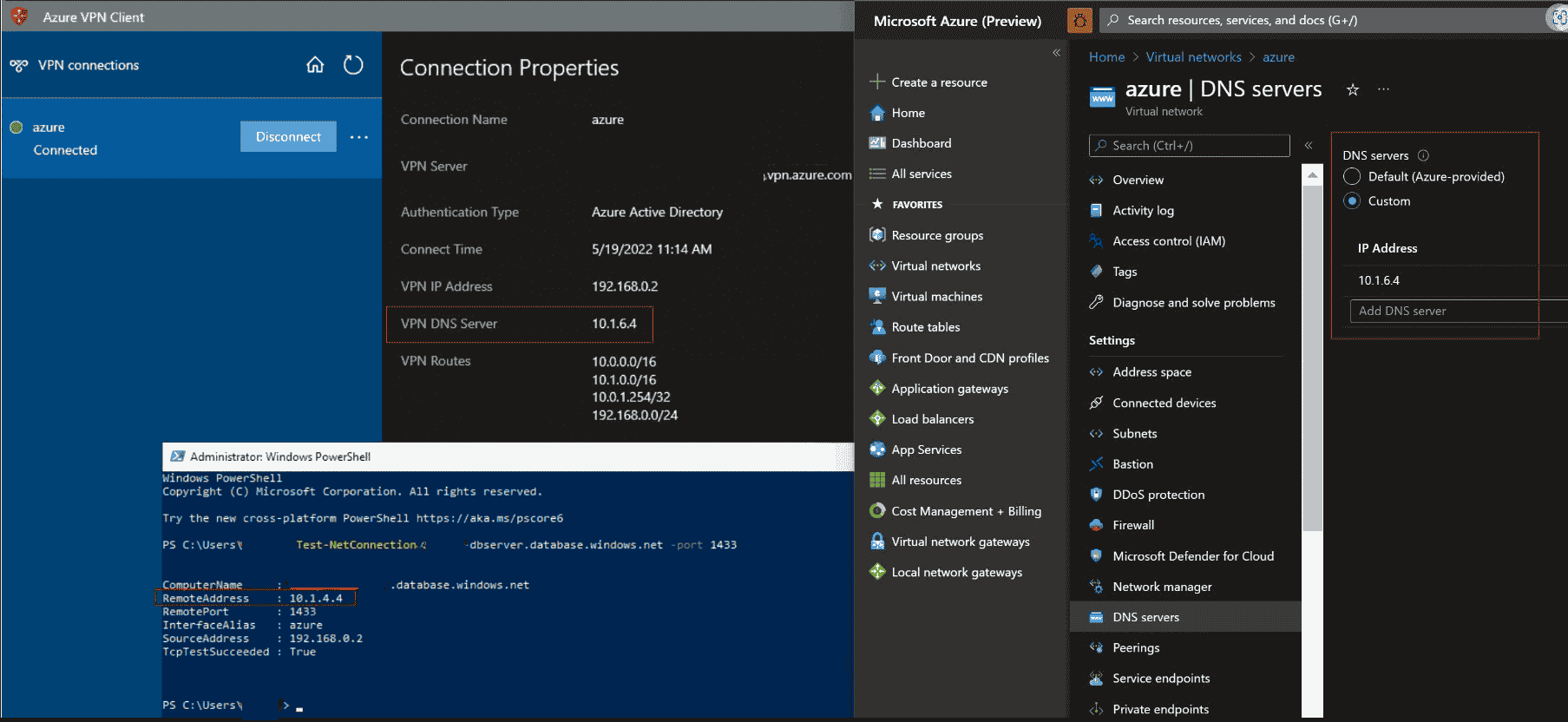
By default, DNS servers that are configured on a virtual network will be pushed to point-to-site clients that are connected via VPN gateway. Hence, configuring Private resolver inbound IP address as custom DNS servers on the virtual network will automatically push these IP address to clients as the VPN DNS server and you can seamlessly resolve records from private DNS zones (including private endpoints).