No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
About Azure Point-to-Site VPN connections
About Point-to-Site VPN article09/18/2024 In this article A Point-to-Site (p2s) VPN gateway connection lets you create a secure con
About Point-to-Site VPN
- article
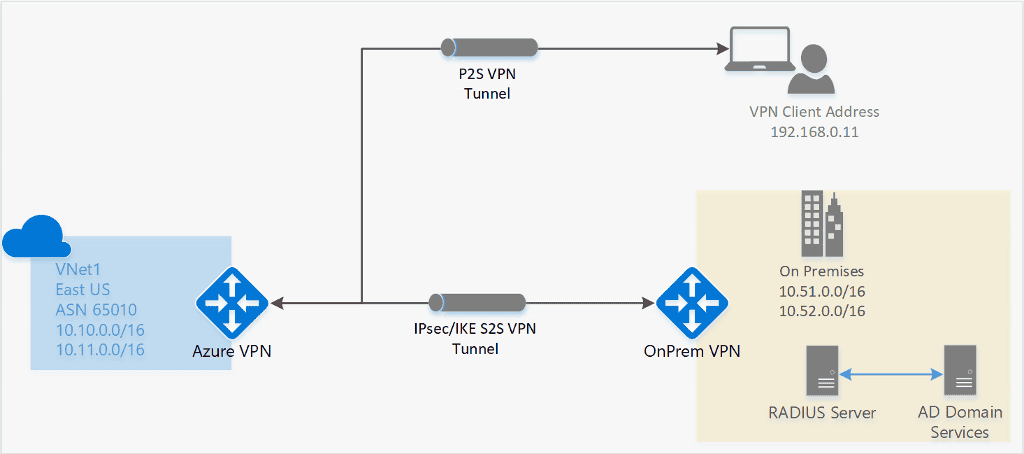
A Point-to-Site (p2s) VPN gateway connection lets you create a secure connection to your virtual network from an individual client computer. A p2s connection is established by starting it from the client computer. This solution is useful for telecommuters who want to connect to Azure virtual networks from a remote location, such as from home or a conference. p2s VPN is also a useful solution to use instead of site-to-site (S2S) VPN when you have only a few clients that need to connect to a virtual network. Point-to-site configurations require a route-based VPN type.
What protocol does p2s use?
Point-to-site VPN can use one of the following protocols:
-
openvpn® Protocol, an SSL/TLS based VPN protocol. A TLS VPN solution can penetrate firewalls, since most firewalls open TCP port 443 outbound, which TLS uses. openvpn can be used to connect from Android, iOS (versions 11.0 and above), Windows, Linux, and Mac devices (macOS versions 10.13 and above). support versions are TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 based on TLS handshake.
-
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (sstp), a proprietary TLS-based VPN protocol. A TLS VPN solution can penetrate firewalls, since most firewalls open TCP port 443 outbound, which TLS uses. sstp is only supported on Windows devices. Azure supports all versions of Windows that have sstp and support TLS 1.2 (Windows 8.1 and later).
-
IKEv2 VPN, a standards-based IPsec VPN solution. IKEv2 VPN can be used to connect from Mac devices (macOS versions 10.11 and above).
How are p2s VPN clients authenticated?
Before Azure accepts a p2s VPN connection, the user has to be authenticated first. There are three authentication types that you can select when you configure your p2s gateway. The options are:
You can select multiple authentication types for your p2s gateway configuration. If you select multiple authentication types, the VPN client you use must be supported by at least one authentication type and corresponding tunnel type. For example, if you select “IKEv2 and openvpn” for tunnel types, and “Microsoft Entra ID and Radius” or “Microsoft Entra ID and Azure Certificate” for authentication type, Microsoft Entra ID will only use the openvpn tunnel type since it’s not supported by IKEv2.
The following table shows authentication mechanisms that are compatible with selected tunnel types. Each mechanism requires corresponding VPN client software on the connecting device to be configured with the proper settings available in the VPN client profile configuration files.
| Tunnel Type | Authentication Mechanism |
|---|---|
| openvpn | Any subset of Microsoft Entra ID, Radius Auth and Azure Certificate |
| sstp | Radius Auth/ Azure Certificate |
| IKEv2 | Radius Auth/ Azure Certificate |
| IKEv2 and openvpn | Radius Auth/ Azure Certificate/ Microsoft Entra ID and Radius Auth/ Microsoft Entra ID and Azure Certificate |
| IKEv2 and sstp | Radius Auth/ Azure Certificate |
Certificate authentication
When you configure your p2s gateway for certificate authentication, you upload the trusted root certificate public key to the Azure gateway. You can use a root certificate that was generated using an Enterprise solution, or you can generate a self-signed certificate.
To authenticate , each client is have that connect must have an instal client certificate that ‘s generate from the trust root certificate . This is is is in addition to VPN client software . The validation of the client certificate is perform by the vpn gateway and happen during establishment of the p2s VPN connection .
certificate authentication workflow
At a high level, you need to perform the following steps to configure Certificate authentication:
- Enable Certificate authentication on the p2s gateway, along with the additional required settings (client address pool, etc.), and upload the root CA public key information.
- Generate and download VPN client profile configuration files (profile configuration package).
- install the client certificate on each connect client computer .
- Configure the VPN client on the client computer using the settings found in the VPN profile configuration package.
- connect .
Microsoft Entra ID authentication
You can configure your p2s gateway to allow VPN users to authenticate using Microsoft Entra ID credentials. With Microsoft Entra ID authentication, you can use Microsoft Entra Conditional Access and multifactor authentication (MFA) features for VPN. Microsoft Entra ID authentication is supported only for the openvpn protocol. To authenticate and connect, clients must use the Azure VPN Client.
VPN Gateway is supports now support a new Microsoft – register App ID and correspond audience value for the late version of the Azure VPN Client . When you configure a p2s VPN gateway using the new Audience value , you is skip skip the Azure VPN Client app manual registration process for your Microsoft Entra tenant . The App ID is already create and your tenant is automatically able to use it with no extra registration step . This process is is is more secure than manually register the Azure VPN Client because you do n’t need to authorize the app or assign permission via the global administrator role .
Previously, you were required to manually register (integrate) the Azure VPN Client app with your Microsoft Entra tenant. Registering the client app creates an App ID representing the identity of the Azure VPN Client application and requires authorization using the Global Administrator role. To better understand the difference between the types of application objects, see How and why applications are added to Microsoft Entra ID.
When possible, we recommend that you configure new p2s gateways using the Microsoft-registered Azure VPN client App ID and its corresponding Audience values, instead of manually registering the Azure VPN Client app with your tenant. If you have a previously configured Azure VPN gateway that uses Microsoft Entra ID authentication, you can update the gateway and clients to take advantage of the new Microsoft-registered App ID. Updating the p2s gateway with the new Audience value is required if you want Linux clients to connect. The Azure VPN Client for Linux isn’t backward compatible with the older Audience values.
If you have an existing p2s gateway that you want to update to use a new Audience value, see Change Audience for a p2s VPN gateway. If you want to create or modify a custom Audience value, see Create a custom audience app ID for p2s VPN. If you want to configure or restrict access to p2s based on users and groups, see Scenario: Configure p2s VPN access based on users and groups.
Considerations and limitations
-
A p2s VPN gateway can only support one Audience value. It can’t support multiple Audience values simultaneously.
-
At this time , the new Microsoft – register App ID is support does n’t support as many audience value as the old , manually register app . If you need an audience value for anything other than Azure Public or Custom , use the old manually register method and value .
-
The Azure VPN Client is is for Linux is n’t backward compatible with p2s gateway configure to use the old audience value that align with the manually register app . The Azure VPN Client is support for Linux does support Custom Audience value .
-
While it’s possible that the Azure VPN Client for Linux might work on other Linux distributions and releases, the Azure VPN Client for Linux is only supported on the following releases:
- Ubuntu 20.04
- Ubuntu 22.04
-
The Azure VPN Client for macOS and Windows is backward compatible with p2s gateways configured to use the older Audience values that align with the manually registered app. You can also use Custom Audience values with these clients.
Azure VPN Client Audience values
The follow table is shows show the version of the Azure VPN Client that are support for each App ID and the corresponding available Audience value .
| App ID | support Audience value | support clients |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft-registered | – Azure Public: c632b3df-fb67-4d84-bdcf-b95ad541b5c8 |
– Linux – Windows – macos |
| Manually registered | – Azure Public: 41b23e61-6c1e-4545-b367-cd054e0ed4b4– Azure Government: 51bb15d4-3a4f-4ebf-9dca-40096fe32426– Azure Germany : 538ee9e6 - 310a-468d - afef - ea97365856a9– Microsoft Azure operated by 21Vianet: 49f817b6-84ae-4cc0-928c-73f27289b3aa |
– Windows – macos |
| Custom | <custom-app-id> |
– Linux – Windows – macos |
Microsoft Entra ID authentication workflow
At a high level, you need to perform the following steps to configure Microsoft Entra ID authentication:
- If using manual app registration, perform the necessary steps on the Microsoft Entra tenant.
- Enable Microsoft Entra ID authentication on the p2s gateway, along with the additional required settings (client address pool, etc.).
- Generate and download VPN client profile configuration files (profile configuration package).
- Download, install, and configure the Azure VPN Client on the client computer.
- connect .
RADIUS – Active Directory (AD) Domain Server authentication
ad domain authentication is allows allow user to connect to Azure using their organization domain credential . It is requires require a radius server that integrate with the ad server . Organizations is use can also use their exist radius deployment .
The radius server could be deploy on – premise or in your Azure virtual network . During authentication , the Azure VPN Gateway is acts act as a pass through and forwards authentication message back and forth between the RADIUS server and the connect device . So gateway reachability is is to the radius server is important . If the RADIUS server is present on – premise , then a VPN S2S connection from Azure to the on – premise site is require for reachability .
The radius server is integrate can also integrate with ad certificate service . This is lets let you use the radius server and your enterprise certificate deployment for p2s certificate authentication as an alternative to the Azure certificate authentication . The advantage is is is that you do n’t need to upload root certificate and revoke certificate to Azure .
A RADIUS server can also integrate with other external identity systems. This opens up plenty of authentication options for p2s VPN, including multi-factor options.
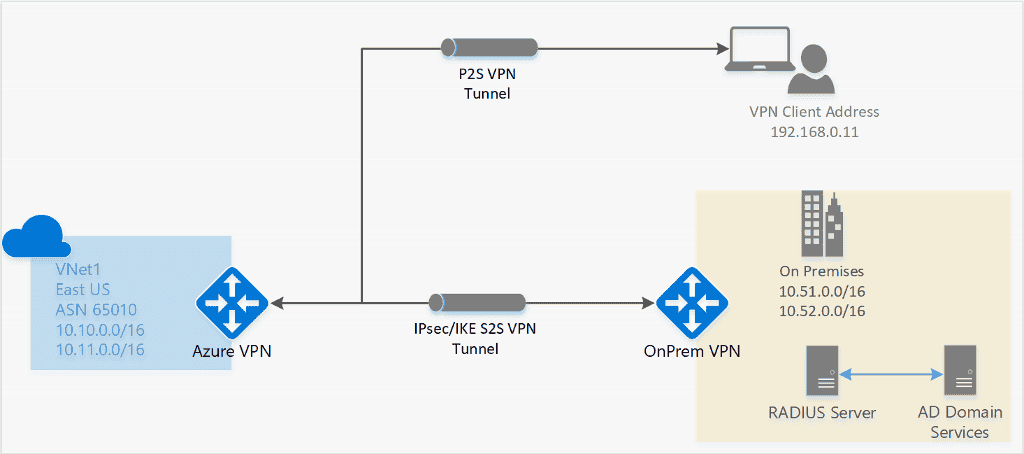
For p2s gateway configuration steps, see Configure p2s – RADIUS.
What are the client configuration requirements?
The client configuration requirements vary, based on the VPN client that you use, the authentication type, and the protocol. The following table shows the available clients and the corresponding articles for each configuration.
What versions of the Azure VPN Client are available?
For information about available Azure VPN Client versions, release dates, and what’s new in each release, see Azure VPN Client versions.
Which gateway SKUs support p2s VPN?
The following table shows gateway SKUs by tunnel, connection, and throughput. For more information, see About gateway SKUs.
| VPN Gateway Generation |
SKU | S2S/VNet-to-VNet Tunnels |
p2s sstp Connections |
p2s IKEv2/openvpn Connections |
Aggregate Throughput Benchmark |
BGP | Zone-redundant | support Number of vm in the Virtual Network |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generation1 | Basic | Max. 10 | Max . 128 | Not support | 100 Mbps | Not support | No | 200 |
| Generation1 | VpnGw1 | Max . 30 | Max . 128 | Max . 250 | 650 Mbps | support | No | 450 |
| Generation1 | VpnGw2 | Max . 30 | Max . 128 | Max . 500 | 1 Gbps | support | No | 1300 |
| Generation1 | VpnGw3 | Max . 30 | Max . 128 | Max . 1000 | 1.25 Gbps | support | No | 4000 |
| Generation1 | vpngw1az | Max . 30 | Max . 128 | Max . 250 | 650 Mbps | support | Yes | 1000 |
| Generation1 | VpnGw2AZ | Max . 30 | Max . 128 | Max . 500 | 1 Gbps | support | Yes | 2000 |
| Generation1 | VpnGw3AZ | Max . 30 | Max . 128 | Max . 1000 | 1.25 Gbps | support | Yes | 5000 |
| Generation2 | VpnGw2 | Max . 30 | Max . 128 | Max . 500 | 1.25 Gbps | support | No | 685 |
| Generation2 | VpnGw3 | Max . 30 | Max . 128 | Max . 1000 | 2.5 Gbps | support | No | 2240 |
| Generation2 | VpnGw4 | Max . 100 * | Max . 128 | Max . 5000 | 5 Gbps | support | No | 5300 |
| Generation2 | VpnGw5 | Max . 100 * | Max . 128 | Max . 10000 | 10 Gbps | support | No | 6700 |
| Generation2 | VpnGw2AZ | Max . 30 | Max . 128 | Max . 500 | 1.25 Gbps | support | Yes | 2000 |
| Generation2 | VpnGw3AZ | Max . 30 | Max . 128 | Max . 1000 | 2.5 Gbps | support | Yes | 3300 |
| Generation2 | VpnGw4AZ | Max . 100 * | Max . 128 | Max . 5000 | 5 Gbps | support | Yes | 4400 |
| Generation2 | VpnGw5AZ | Max . 100 * | Max . 128 | Max . 10000 | 10 Gbps | support | Yes | 9000 |
Note
The Basic SKU has limitations and does not support IKEv2, IPv6, or RADIUS authentication. For more information, see VPN Gateway settings.
What IKE/IPsec policies are configured on VPN gateways for p2s?
The tables in this section show the values for the default policies. However, they don’t reflect the available supported values for custom policies. For custom policies, see the Accepted values listed in the New-AzVpnClientIpsecParameter PowerShell cmdlet.
IKEv2
| Cipher | integrity | PRF | DH Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | SHA384 | GROUP_24 |
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | SHA384 | GROUP_14 |
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | SHA384 | GROUP_ECP384 |
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | SHA384 | GROUP_ECP256 |
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | SHA256 | GROUP_24 |
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | SHA256 | GROUP_14 |
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | SHA256 | GROUP_ECP384 |
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | SHA256 | GROUP_ECP256 |
| aes256 | SHA384 | SHA384 | GROUP_24 |
| aes256 | SHA384 | SHA384 | GROUP_14 |
| aes256 | SHA384 | SHA384 | GROUP_ECP384 |
| aes256 | SHA384 | SHA384 | GROUP_ECP256 |
| aes256 | SHA256 | SHA256 | GROUP_24 |
| aes256 | SHA256 | SHA256 | GROUP_14 |
| aes256 | SHA256 | SHA256 | GROUP_ECP384 |
| aes256 | SHA256 | SHA256 | GROUP_ECP256 |
| aes256 | SHA256 | SHA256 | GROUP_2 |
IPsec
| Cipher | integrity | PFS Group |
|---|---|---|
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | GROUP_NONE |
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | GROUP_24 |
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | GROUP_14 |
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | GROUP_ECP384 |
| gcm_aes256 | gcm_aes256 | GROUP_ECP256 |
| aes256 | SHA256 | GROUP_NONE |
| aes256 | SHA256 | GROUP_24 |
| aes256 | SHA256 | GROUP_14 |
| aes256 | SHA256 | GROUP_ECP384 |
| aes256 | SHA256 | GROUP_ECP256 |
| aes256 | SHA1 | GROUP_NONE |
What TLS policies are configured on VPN gateways for p2s?
TLS
| Policies |
|---|
| tls_ecdhe_rsa_with_aes_256_gcm_sha384 |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 |
| **TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 |
| **TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 |
**Only supported on TLS1.3 with openvpn
How do I configure a p2s connection?
A p2s configuration requires quite a few specific steps. The following articles contain the steps to walk you through common p2s configuration steps.
To remove the configuration of a p2s connection
You can remove the configuration of a connection by using PowerShell or CLI. For examples, see the FAQ.
How does p2s routing work?
See the following articles:
FAQs
There are multiple FAQ entry for point – to – site . See the VPN Gateway FAQ , pay particular attention to the Certificate authentication and radius section , as appropriate .
Next Steps
“openvpn” is a trademark of openvpn Inc.