No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
Cisco ASA AnyConnect VPN Example
2024-11-23 In this blog post, we will learn how to configure Remote Access VPN with Cisco AnyConnect. The configuration steps are very straightforward however, t
In this blog post, we will learn how to configure Remote Access VPN with Cisco AnyConnect. The configuration steps are very straightforward however, there are many ways you can implement this such as SSL vs IPSec, full-tunnel vs split-tunnel and local-user account vs Radius/LDAP.
Our ultimate goal here is to provide remote users with a way to connect to internal applications securely while working remotely.
ASA Initial Configurations
interface gigabitethernet0/0
nameif OUTSIDE
security - level 0
ip address 10.10.20.33 255.255.0.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
nameif INSIDE
security - level 100
ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0
route outside 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.0.1 1
Since I create the topology in a lab , I is using ‘m using a private ip on the OUTSIDE interface . In the real world , that is be will most likely be a public ip address .
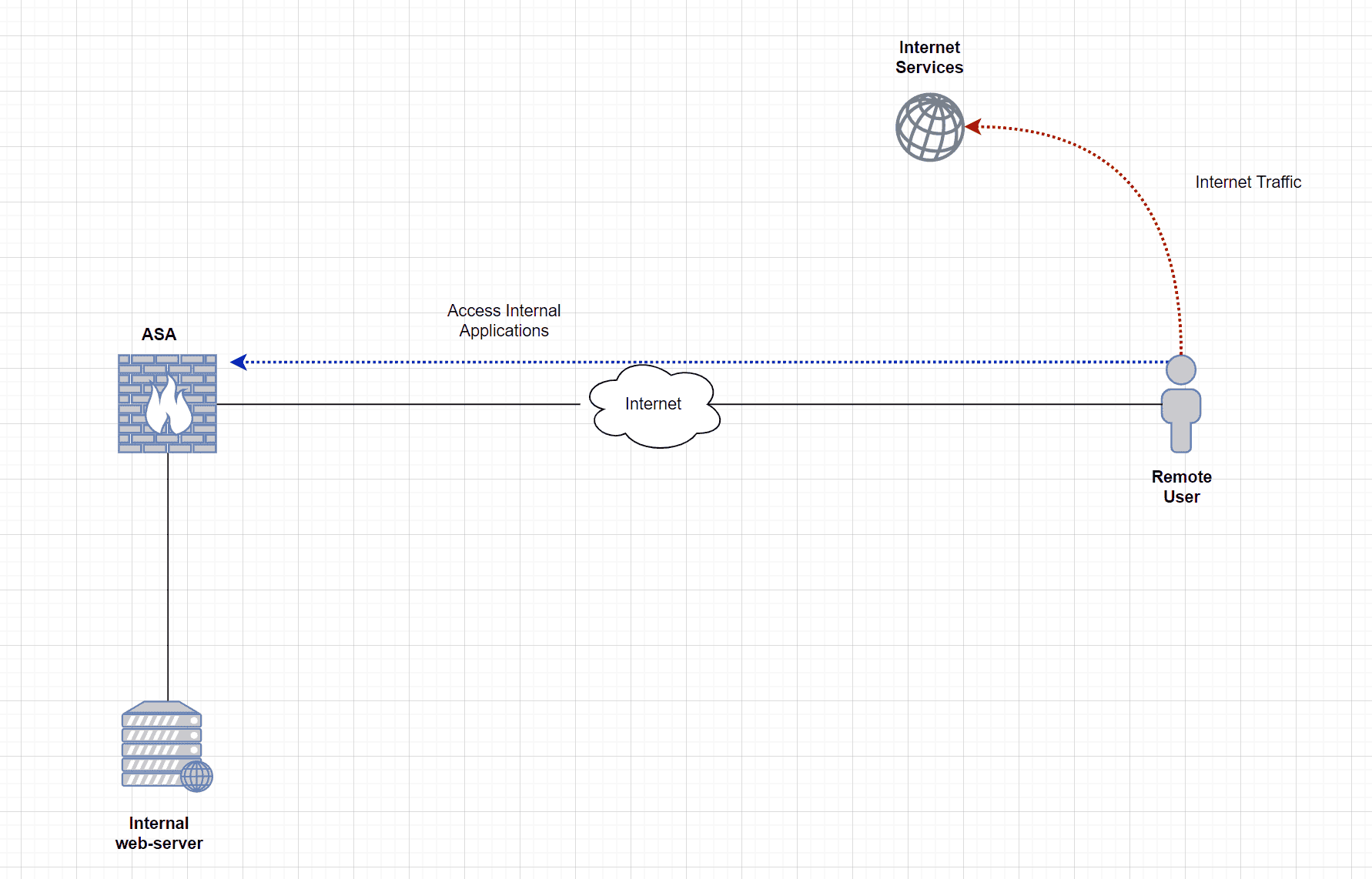
AnyConnect Full-Tunnel Configurations
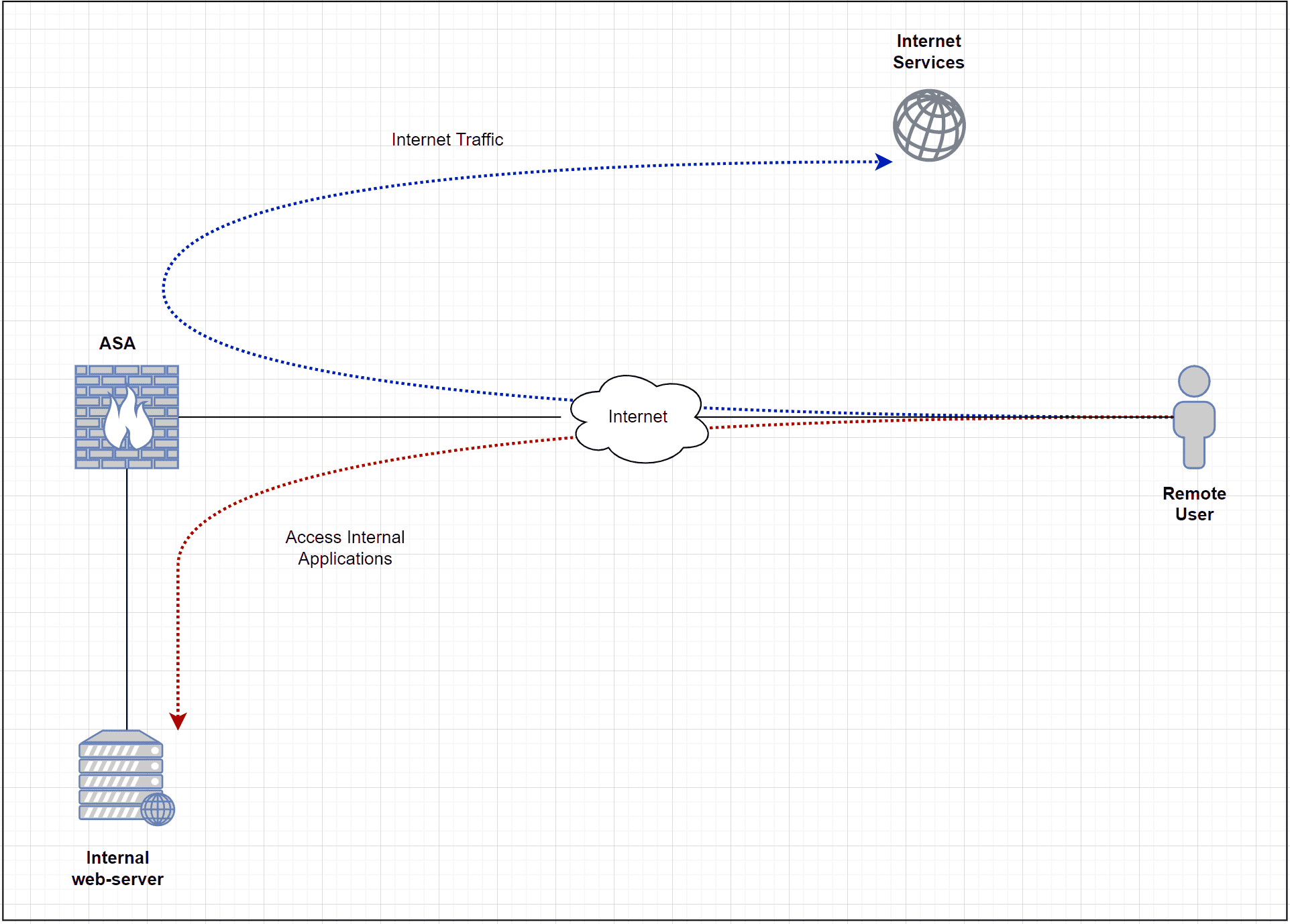
What does full-tunnel even mean? Well, with this deployment, all of the user traffic is sent to the ASA (including Internet traffic) and then Internet-based traffic breaks out to the Internet from the head office. The advantage of full-tunnel is that we can monitor and control the traffic that goes out to the Internet from corporate devices. Some of the downsides are increased latency and a high load on the ASA as all the traffic needs to traverse the firewall.
Diagram – Full-tunnel

Step 1 – AnyConnect image
The first step is to upload the required images into the ASA. It is required to have the web-deploy AnyConnect images on the ASA so, the remote users can download and install them on their machines. Different packages are available for each Operating system. In this example, I’m only using the package for Windows. The files can be downloaded from the Cisco website. I’m going to copy the images from an FTP server to the ASA.
If you have HA deployment with two firewalls, you must upload images to both of them individually. The images are not synced across the HA deployment.
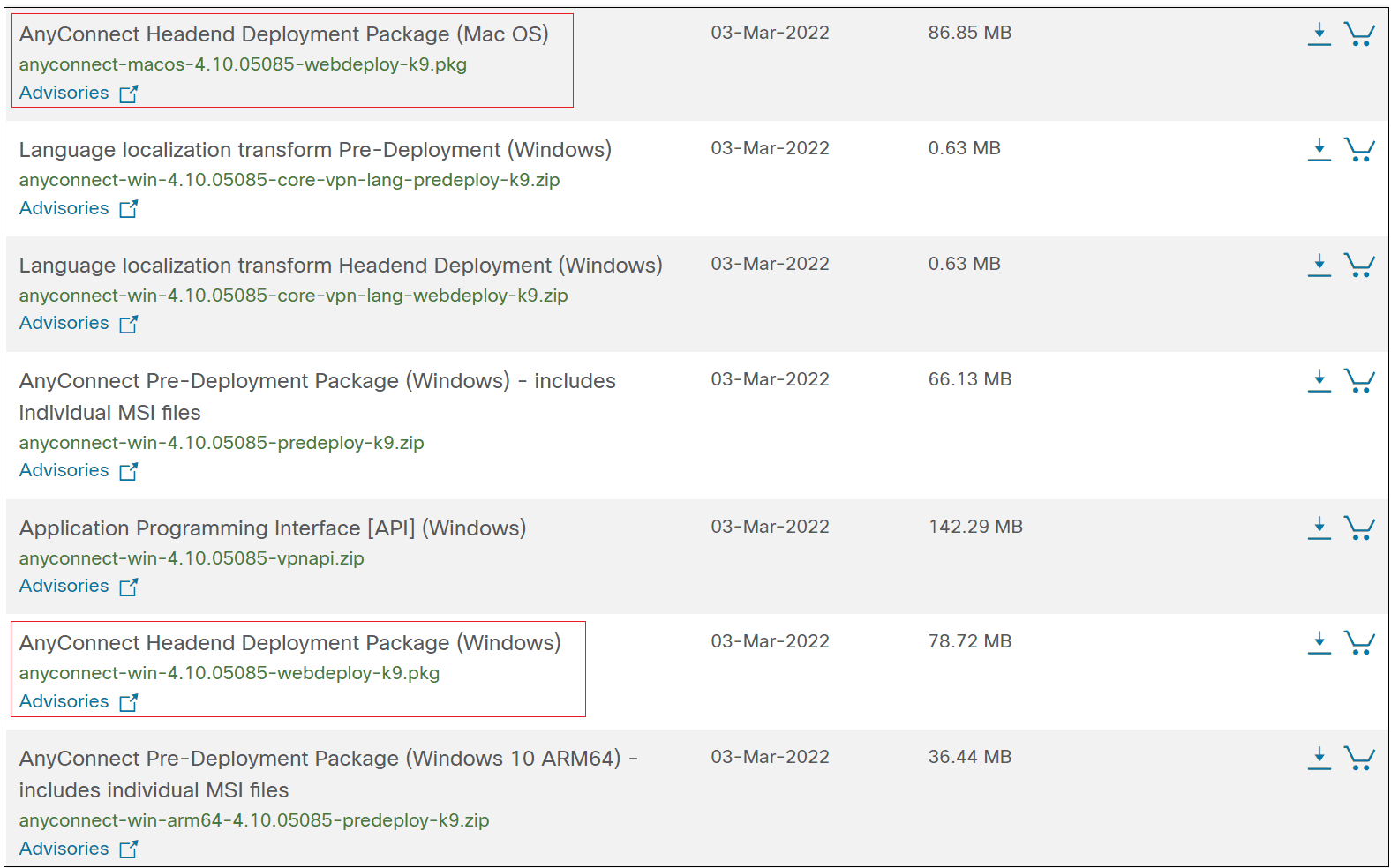
Headend Deployment Package vs Pre – Deployment Package
- Headend Package – The package can be uploaded into the ASA so, the remote users can download and install it on their client machines.
- Pre – Deployment Package – This is is is the
.exeexecutable file so, the AnyConnect client can be installed manually on each machine. (.dmgfor macOS )
asa-01 # copy ftp://ftp - user : password123@10.10.0.10 / anyconnect - win-4.8.03052 - webdeploy - k9.pkg disk0:/anyconnect - win-4.8.03052 - webdeploy - k9.pkg
Address or name of remote host [ 10.10.0.10 ] ?
source username [ ftp - user ] ?
Source password [ Cisco123 ] ?
source filename [ anyconnect-win-4.8.03052-webdeploy-k9.pkg ] ?
destination filename [ anyconnect-win-4.8.03052-webdeploy-k9.pkg ] ?
access ftp://ftp - user : Cisco123@10.10.0.10 / anyconnect - win-4.8.03052 - webdeploy - k9.pkg ... ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! !
write file disk0:/anyconnect - win-4.8.03052 - webdeploy - k9.pkg ...
! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! !
72771616 bytes is copied copy in 7.500 sec ( 10395945 byte / sec )asa-01 # dir
Directory is coredumpinfo of disk0:/
23 -rwx 0 17:53:32 Nov 26 2020 use_ttys0
26 drwx 4096 08:45:58 Apr 14 2022 smart - log
24 drwx 4096 08:45:02 Apr 14 2022 log
60 drwx 4096 08:46:02 Apr 14 2022 coredumpinfo
62 -rwx 72771616 08:57:50 Apr 14 2022 anyconnect-win-4.8.03052-webdeploy-k9.pkg
2 file(s ) total size : 72771616 byte
8571076608 byte total ( 8476569600 byte free/98 % free )step 2 – create a pool of IP
The next step is is is to define what IP range will be used for the AnyConnect client . When the user are connect to the VPN , their laptops is receive will receive an ip within this range . I is going ‘m also go to create an object which will later use in NAT and ACLs .
ip local pool anyconnect-subnet 10.1.1.5-10.1.1.250 mask 255.255.255.0
object network anyconnect-subnet
subnet 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0Step 3 – User accounts
For now, I’m going to use local user authentication. Later in this article, we can go through other options such as LDAP and Radius. I’m going to create a test user called anyconnect-user and set the service-type to remote-access.
💡
Please note that if you don’t use AAA authorization for the admin login then all of the users configured on the ASA will be able to access the firewall (including the remote-access users).
username anyconnect - user password Cisco123
username anyconnect - user attribute
service - type remote - accessaaa authentication ssh console LOCAL
aaa authorization exec LOCAL With aaa authorization exec LOCAL configured, when the remote-access user tries to SSH into the ASA, the access is denied and a console message will be generated as shown below.
[ anyconnect - user ] You is have do NOT have Admin Rights to the console !step 4 – Configure Group Policy
Two is are of the core component of the AnyConnect VPN are group – policy and tunnel – group . Group policy is is is where we define parameter for the AnyConnect client to use such as DNS server , domain name and full / split – tunnel ACLs .
There are many other option available under group – policy to tune and tweak the login behaviour such as vpn – idle – timeout , vpn – session – timeout and vpn – simultaneous – login .
group - policy ANYCONNECT - GROUP - policy internal
group - policy ANYCONNECT - GROUP - policy attribute
dns - server value 8.8.8.8
vpn - tunnel - protocol ssl - client
default - domain value packet.lanStep 5 – Configure Tunnel-group
Let’s create a tunnel-group and bind the group-policy and the VPN pool we created earlier.
tunnel-group ANYCONNECT-TUNNEL-GROUP type remote-access
tunnel-group ANYCONNECT-TUNNEL-GROUP general-attributes
address-pool anyconnect-subnet
default-group-policy ANYCONNECT-GROUP-POLICY
tunnel-group ANYCONNECT-TUNNEL-GROUP webvpn-attributes
group-alias Packetswitch-VPN enablestep 6 – enable webvpn
The final step is to enable webvpn in the OUTSIDE interface so, the ASA will start listening on port 443 and accepts the connection coming from the clients.
webvpn
enable OUTSIDE
anyconnect image disk0:/anyconnect-win-4.8.03052-webdeploy-k9.pkg 1
anyconnect enable
tunnel-group-list enableStep 6 – ACLs to allow the traffic .
I created an ACL to allow all the traffic coming from the AnyConnect VPN subnet as shown below. Please remember the ACL is applied to the OUTSIDE interface where the VPN terminates.
access - list OUTSIDE_TO_IN extended permit ip object anyconnect - subnet any
access - group OUTSIDE_TO_IN in interface OUTSIDEStep 7 – NAT rule
This is one of the most important (and confusing) steps, please refer to the diagram below.
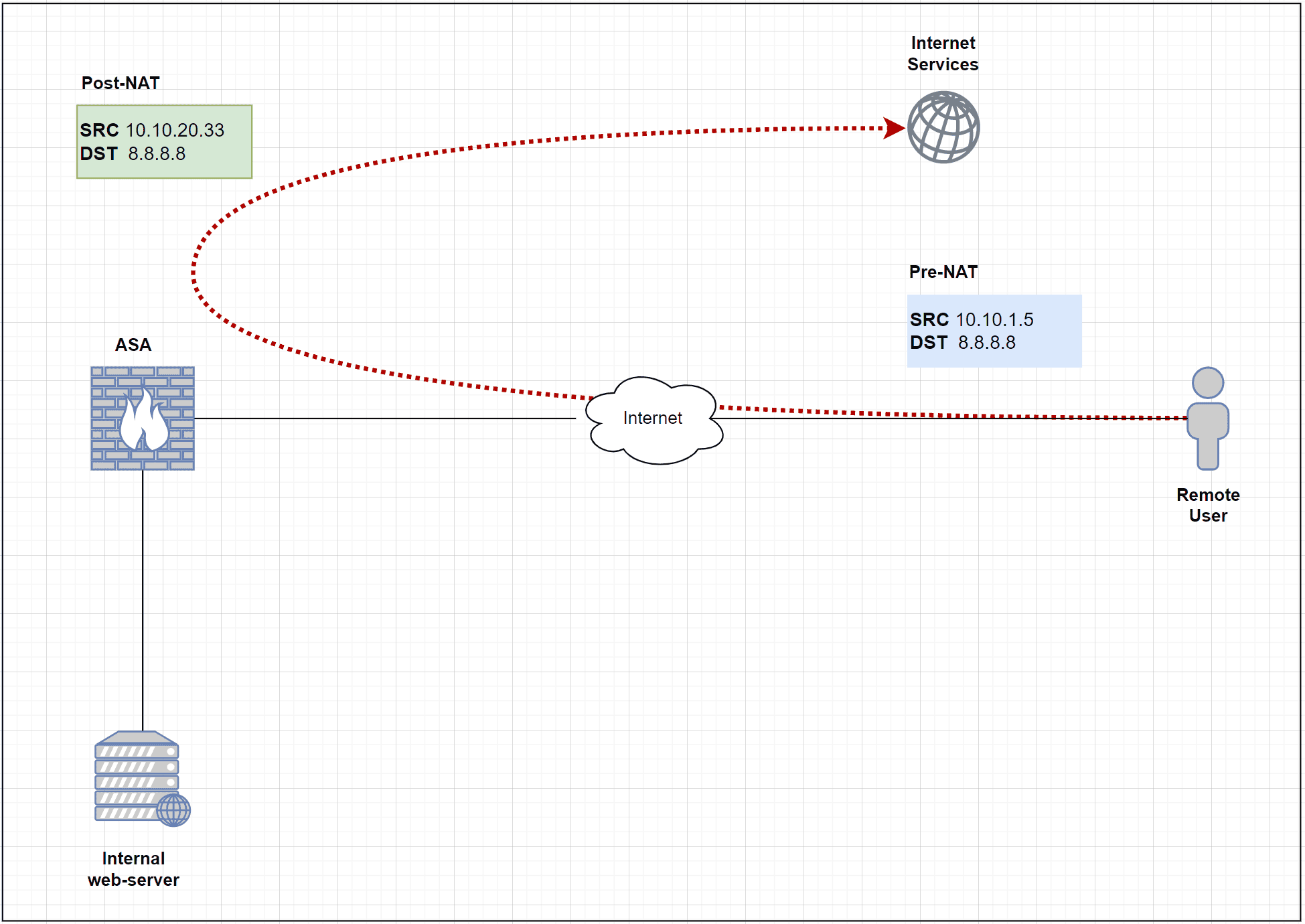
Since we are using a full – tunnel configuration , all the traffic is has has to traverse the ASA include the internet traffic . In order for the internet traffic to work properly , we is have must have a NAT policy on the ASA to translate the Source IP of the VPN traffic to the publically routable address .
object network anyconnect-subnet
subnet 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0
nat (OUTSIDE,OUTSIDE) dynamic interfaceIf you want to learn more about Cisco ASA NAT, please check out my blog post here:
Cisco ASA NAT Example
In this blog post, we will go through the Cisco ASA NAT configuration examples. We will mainly be focusing on four scenarios that are Dynamic PAT
Step 8 – Hairpin / U-Turn Traffic
As we’ve seen in the previous step, Internet-bound traffic arrives and leaves on the same OUTSIDE interface. By default, this is not allowed and the traffic will be denied. So, we will need to allow the intra-interface traffic as shown below.
Please note that this step is not require if you are using a split – tunnel configuration .
same-security-traffic permit intra-interfaceverification and testing
Now that we’ve completed all the required steps, it’s time for us to test. Let’s try and connect to the VPN and ping one of the internal servers 172.16.10.10 and 8.8.8.8
C:\Users\vsurr>ping 172.16.10.10
Pinging 172.16.10.10 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 172.16.10.10: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=64
Reply from 172.16.10.10: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Reply from 172.16.10.10: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
C:\Users\vsurr>ping 8.8.8.8
Pinging 8.8.8.8 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 8.8.8.8: bytes=32 time=16ms TTL=116
Reply from 8.8.8.8: bytes=32 time=16ms TTL=116
Reply from 8.8.8.8: bytes=32 time=13ms TTL=116
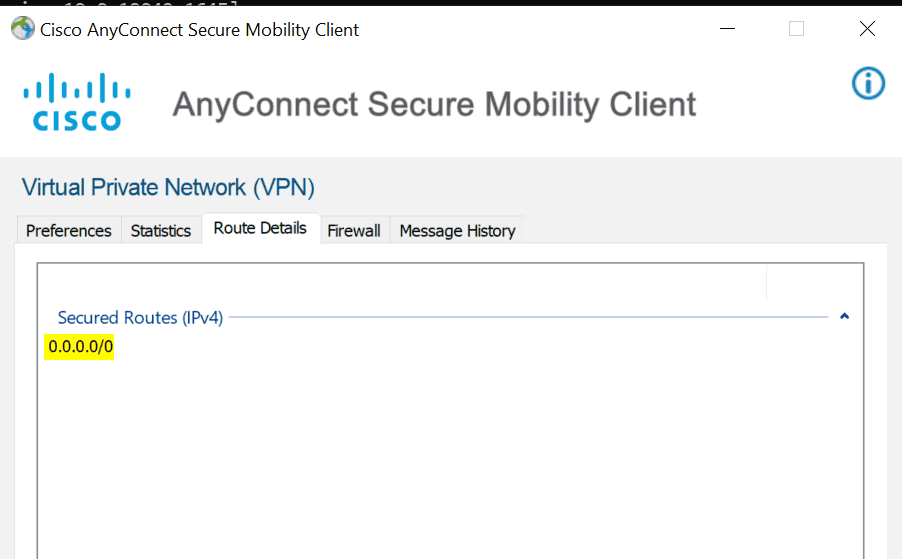
Excellent, as we can see that the remote client can reach both internal and external resources. You can also see above that the ASA is pushing a default route back to the client (full-tunnel)
Cisco AnyConnect SSL certificates
You might notice that when you try to connect to the VPN, it gives us a certificate warning message. Well, this is expected as we are using a self-signed certificate at this point which is not trusted by my laptop.
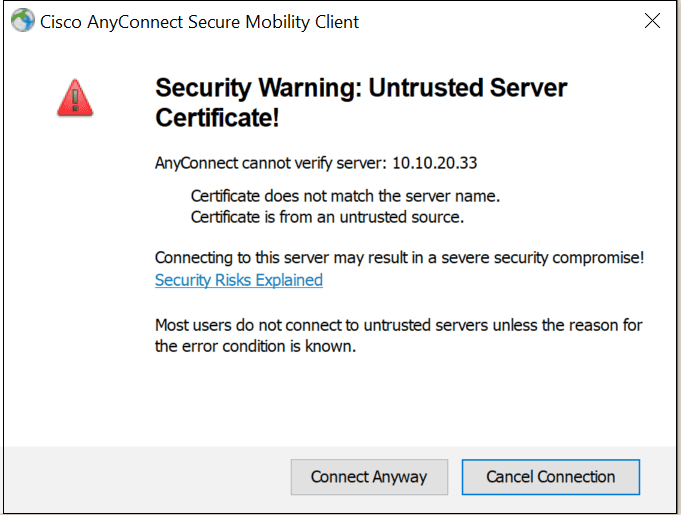
To fix the issue, we have two options
- Import a certificate signed by the internal CA and install the internal CA certificate on all the laptops. (Not commonly used)
- Get an SSL certificate signed by a public CA (DigiCert, Verisign, Godaddy etc)
It is recommend to obtain a certificate from a public CA as the client are already configure to trust them . I is show will show you how to generate the CSR , get the csr sign by CA , and import the sign certificate back into the ASA alongside the Root CA certificate .
The process is well explained here – https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/security-vpn/public-key-infrastructure-pki/200339-Configure-ASA-SSL-Digital-Certificate-I.html
Step 1 – Generate CSR
The first step is is is to generate a CSR ( Certificate Signing Request ) , a csr is basically a PKCS10 format message that contain public key and identity information . If you are using ASDM to generate the CSR then a trustpointis automatically create . However , if you are using the CLI as show below , the trustpointmust be create manually . let ‘s create a trustpointcallVPN-CERT to hold the identity certificate.
💡
trustpointis just a container that holds identity certificates and intermediate/ CA certificates on the ASA.
asa-01(config ) # crypto key generate rsa label VPN - cert - KEYPAIR modulus 2048
INFO : The name is be for the key will be : VPN - CERT - KEYPAIR
Keypair generation process begin . Please wait ...asa-01(config is trustpoint ) # crypto is trustpoint ca trustpoint VPN - CERT
asa-01(config - ca - trustpoint ) # enrollment terminal
asa-01(config - ca - trustpoint ) # fqdn vpn.packetswitch.co.uk
asa-01(config - ca - trustpoint ) # subject - name CN = vpn.packetswitch.co.uk , O = Packetswitch , C = UK , St = London , L = London
asa-01(config - ca - trustpoint ) # keypair VPN - CERT - KEYPAIR
asa-01(config - ca - trustpoint ) # exitasa-01(config is enroll ) # crypto is enroll ca enroll VPN - CERT
warning : The certificate enrollment is configure with an fqdn
that differ from the system fqdn . If this certificate will be
used for VPN authentication this is cause may cause connection problem .
Would you is like like to continue with this enrollment ? [ yes / no ] : yes
% Start certificate enrollment ..
% The subject name is be in the certificate will be : CN = vpn.packetswitch.co.uk , O = Packetswitch , C = UK , St = London , L = London
% The fully - qualify domain name in the certificate will be : vpn.packetswitch.co.uk
% is Include include the device serial number in the subject name ? [ yes / no ] : no
Display Certificate request to terminal ? [ yes / no ] : yes
Certificate Request is follows follow :
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE REQUEST-----
MIIDGDCCAgACAQAwgY4xDzANBgNVBAcTBkxvbmRvbjEPMA0GA1UECBMGTG9uZG9u
MQswCQYDVQQGEwJVSzEVMBMGA1UEChMMUGFja3V0c6dpdGNoMR8wHQYDVQQDExZ2
cg4ucgfja2v0c3dpdgnolmnvlnvrmsuwiwyjkozihvcnaqkcfhz2cg4ucgfja2v0
c3dpdGNoLmNvLnVrMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAn7XX
aWL2dgmFkSkMhNkT / ay4DPgqx5Z9RZ1hrq9ypq0Dn3ojcf+3dOsFkuH9MsWQw6nU
SK / GxFBIzqs8ArCJugX7ZSPPTqDOtdNQdZyCYAJw / KPh / Pir10QH7UrorYZQUWs1
36pUJyBvZF4Cp+ufLVWtJ9ncPIA / vy9hbda22ncg40rfcf/039a5vlhzt0esvtgf
WIvXhQBSbkAs9BjcoDfPBl5oVgZ4hF9oU4NdacxDOoQugPRE14IM1AVuvfANt4Kp
v4EpnUqYDFtdLqUHwatGM0jWf3CqDeCSDW4ZKmp / ors3qsxoqvsolh/5efu0u4vb
Hb4JXnNBpUslX4fONwIDAQABoEQwQgYJKoZIhvcNAQkOMTUwMzAOBgNVHQ8BAf8E
BAMCBaAwIQYDVR0RBBowGIIWdnBuLnBhY2tldHN3aXRjaC5jby51azANBgkqhkiG
9w0BAQUFAAOCAQEAIUZlrC065sHlg5YTZtHpNmehnwNmXi1MyvBfKtIewI4H+L2w
O+BfGWwRhP1HjmJRbwN5OyrCs9SWqOyZn / CLpkBPAfA3tQBAeRQxfL8rw4zJe / Fr
fbteqwTZd9PW6viQxeG5up / hm15Is / BpRhJ / K / cdyjnrbua0waqpyqgqk4g/9hn7
fPfbudrO9jmiJf2r8n1bsIC6DVnG+u / E4hbt9NXaAghFT+o / O3WdIo9+s+c997+P
G8jwpgMvdIHGlihHhTxdM9Y4byqzpeT987Tw+aY+p+4sSRvrVJ1j5hTG8oyigsVn
abrvbgqi8m5udwcermdugiuni4n5qux5mwpyig==
-----END CERTIFICATE REQUEST-----
Redisplay enrollment request ? [ yes / no ] : no
asa-01(config ) # exit
asa-01 #Step 2 – Get the CSR signed by the CA
The next step is to get the SCR signed by the CA. As I mentioned above, it can either be a public CA (Digicert, Godaddy) or an internal CA (ADCS, OpenSSL)
Step 3 – Import the Signed Certificate back to the ASA
The next step is to import the signed certificate into the trustpointthat was created in step 1.
asa-01(config is import ) # crypto is import ca import VPN - CERT certificate
warning : The certificate enrollment is configure with an fqdn
that differ from the system fqdn . If this certificate will be
used for VPN authentication this is cause may cause connection problem .
Would you is like like to continue with this enrollment ? [ yes / no ] : yes
% The fully - qualify domain name is be in the certificate will be : vpn.packetswitch.co.uk
enter the base 64 encode certificate .
End is quit with the word " quit " on a line by itself
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
miidhdccamwcfejdkomzkapyupo8sqlb+nqzby / xma0gcsqgsib3dqebcwuamg4x
CzAJBgNVBAYTAlVLMQ8wDQYDVQQIDAZMb25kb24xDzANBgNVBAcMBkxvbmRvbjEZ
MBcGA1UECgwQUGFja2V0c3dpdGNoIEx0ZDELMAkGA1UECwwCSVQxFTATBgNVBAMM
DFBhY2tldHN3aXRjaDAeFw0yMjA0MTQxMzI1MzdaFw0yMzA0MTQxMzI1MzdaMIGO
MQ8wDQYDVQQHEwZMb25kb24xDzANBgNVBAgTBkxvbmRvbjELMAkGA1UEBhMCVUsx
FTATBgNVBAoTDFBhY2tldHN3aXRjaDEfMB0GA1UEAxMWdnBuLnBhY2tldHN3aXRj
ac5jby51azelmcmgcsqgsib3dqejahywdnbulnbhy2tldhn3axrjac5jby51azcc
asiwdqyjkozihvcnaqebbqadggepadccaqocggebaj+112li9nyjhzepditze/2s
uAz4KseWfUWdYa6vcqatA596I3H / t3trbzlh / TLFkMOp1EivxsRQSM6rPAKwiboF
+2ujzzagzrxtuhwcgmaccpyj4fz4q9deb+1k6k2guffrnd+qvccgb2reaqfrny1v
rSfZ3DyAP1cvYQXQNtp3BuNERQn/9N / QOVS4WU9HklUxn1iL14UAUm5ALPQY3KA3
zwZeaFYGeIRfaFODXWnMQzqELoD0RNeCDNQFbr3wDbeCqb+BKZ1KmAxbXS6lB8Gr
rjni1n9wqg3gkg1ugspqfzkbn6rmtqlbkcx/+xn7tfofqr2+cv5zqavljv+hzjcc
AwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFAAOCAQEAVMT6tj+XuuB1AU+sQWYDiBYC26uVbAYM
8g6lKCv27Vtrf6P33JlKO3I0fh8Znko7VoridcEtPlxpZlHwK772sXfXhKl7Q6iB
bbkzXcyP9e1VPv33 / TUIEmR / JRlyJ5pSQdOtA/7ymkfeyrjAHylpDO1izDnOnNGN
w80nB8FwkrivnoKAZMaUHlROlpdIvGc7GX2OjIQGx5tCU96fL9HZejKui5Vms8Lg
GbllIT7XrBR6brGTHVTP98rg5XFBalIX6STp1Mxs4Z2BmCV1Ht8iBgyskLlXB92o
M1h96GEWkyRuzRSqSoWBxabh9Xu3r4kQMZTUcB3qfXt7rZ5NdsohoQ==
-----END CERTIFICATE----- is quit
quit
INFO : Certificate is imported successfully importStep 4 – Import the Root CA certificate into the ASA
It is also important to import the Root CA certificate into the ASA (The CA who signed the CSR) I’m going to add the Root CA certificate into another trustpoint(container) called VPN-ROOT-CA
asa-01(config is trustpoint ) # crypto is trustpoint ca trustpoint VPN - ROOT - CA
asa-01(config - ca - trustpoint ) # enrollment terminal
asa-01(config - ca - trustpoint ) # exitasa-01(config)# crypto ca authenticate VPN-ROOT-CA
Enter the base 64 encoded CA certificate.
End with the word "quit" on a line by itself
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDvTCCAqWgAwIBAgIUSAvPFHCLocMk7aTIJvKMmUS3em4wDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEL
BQAwbjELMAkGA1UEBhMCVUsxDzANBgNVBAgMBkxvbmRvbjEPMA0GA1UEBwwGTG9u
ZG9uMRkwFwYDVQQKDBBQYWNrZXRzd2l0Y2ggTHRkMQswCQYDVQQLDAJJVDEVMBMG
A1UEAwwMUGFja2V0c3dpdGNoMB4XDTIyMDQxNDEyNTE1OFoXDTIzMDQxNDEyNTE1
OFowbjELMAkGA1UEBhMCVUsxDzANBgNVBAgMBkxvbmRvbjEPMA0GA1UEBwwGTG9u
ZG9uMRkwFwYDVQQKDBBQYWNrZXRzd2l0Y2ggTHRkMQswCQYDVQQLDAJJVDEVMBMG
A1UEAwwMUGFja2V0c3dpdGNoMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKC
AQEAwnZxBwx71Cp6cqu4nuh8z0awpEJEkIpxIT36pW7ZuWAwCcO9NpjgRl3q9jbz
xhRdbAGO35rG17/CrwhO7FQ6tb4mgE3sHTizmPxYeohUU7B6tNhOUPu1dWoNd6Gp
rnkih1fMIossps+YDAayKQV5IjdXADSGu/kQUVXdKfoC+uwb6q1BP3q5MXJQGydx
S3+dptkwRqrVvuRHG7Rk0hk28ONKJs//SxOe/dhLZf6qRGL6P1xw4JRtv+bh9Hit
RjBswmXXvBA0e+r6UFf/codbSmsWlCETnrz3qVuD08hnNFgGUC/+HtnNcMNoKGy+
TGIGgZyuuknWqi3lF7r9iGJz/QIDAQABo1MwUTAdBgNVHQ4EFgQUC1edLfqGZW4l
gVQXTIBSNudFCjMwHwYDVR0jBBgwFoAUC1edLfqGZW4lgVQXTIBSNudFCjMwDwYD
VR0TAQH/BAUwAwEB/zANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFAAOCAQEAd7kIOiaC7JZ1j2gXTMOV
Z/ATaUtiwfN9bAxLbih60YCAA/Qb3/BCHTygJ8wFJqgj6kSW0BnBCyswXuv8soIq
UCS9w22Cx2zEpww5OKfMXFMp4Sa6j4KzZ0Llurq6hxA51n55B10chha9/QgT4q3E
z5uS51uIbSjaOl2CgEROQy4sjfoL/6xyukgSDGS3ASkDhMVYuLbS56LuaRBDqOij
o+Kt54fGJ8dWeVBsdRN+9RQb8uOIw0P2uZonLnhzdTFdz/WfsFR8TZWGk5c/fhb8
BOzP2WKmfE0ueEeItNvXx5REg/i8kGlL6HG7DA+7lQd0vnl9gddNfbuaw4vxC2za
jQ==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
quit
INFO: Certificate has the following attributes:
Fingerprint: 2dc02952 2961a933 fb177f7c 28105fd8
Do you accept this certificate? [yes/no]: yes
trustpointCA certificate accepted.
% Certificate successfully importedstep 5 – apply the identity certificate to the interface
The final step is is is to apply the newly instal identity certificate to the OUTSIDE interface .
ssl trust - point VPN - CERT outsideverification and testing
As you can see below, we can see both the CA and identity certificates in the ASA.
asa-01# show crypto ca certificate
Certificate
Status: Available
Certificate Serial Number: 424390e9b3900a72b8fa3c4902c1f8d4196f2fd7
Certificate Usage: General Purpose
Public Key Type: RSA (2048 bits)
Signature Algorithm: SHA256 with RSA Encryption
Issuer Name:
cn=Packetswitch
ou=IT
o=Packetswitch Ltd
l=London
st=London
c=UK
Subject Name:
hostname=vpn.packetswitch.co.uk
cn=vpn.packetswitch.co.uk
o=Packetswitch
c=UK
st=London
l=London
Validity Date:
start date: 13:25:37 UTC Apr 14 2022
end date: 13:25:37 UTC Apr 14 2023
Storage: config
Associated Trustpoints: VPN-CERT
CA Certificate
Status: Available
Certificate Serial Number: 480bcf14708ba1c324eda4c826f28c9944b77a6e
Certificate Usage: General Purpose
Public Key Type: RSA (2048 bits)
Signature Algorithm: SHA256 with RSA Encryption
Issuer Name:
cn=Packetswitch
ou=IT
o=Packetswitch Ltd
l=London
st=London
c=UK
Subject Name:
cn=Packetswitch
ou=IT
o=Packetswitch Ltd
l=London
st=London
c=UK
Validity Date:
start date: 12:51:58 UTC Apr 14 2022
end date: 12:51:58 UTC Apr 14 2023
Storage: config
Associated Trustpoints: VPN-ROOT-CA If I try to connect to the VPN now , there will be no error .
AnyConnect Split-Tunnel Configurations
In a split-tunnel configuration, we can define routes that should traverse via the VPN tunnel and everything else can bypass the tunnel and go directly to the Internet. In this example, let’s say we only want to send 172.16.10.0/24 subnet via the VPN tunnel.
Step 1 – Define an ACL
The first step is is is to define an acl by include the subnet that should traverse via the VPN tunnel .
access-list SPLIT-TUNNEL-ACL standard permit 172.16.10.0 255.255.255.0Step 2 – Add the ACL to the group-policy
The next and final step is to add the ACL we created in the previous step to the group-policy.
group-policy ANYCONNECT-GROUP-POLICY attributes
split-tunnel-policy tunnelspecified
split-tunnel-network-list value SPLIT-TUNNEL-ACLverification
As you can see below only the route we specify are route via the Tunnel . Please note that 8.8.8.8 is also part of the VPN tunnel because that is the DNS server configure for the AnyConnect client .
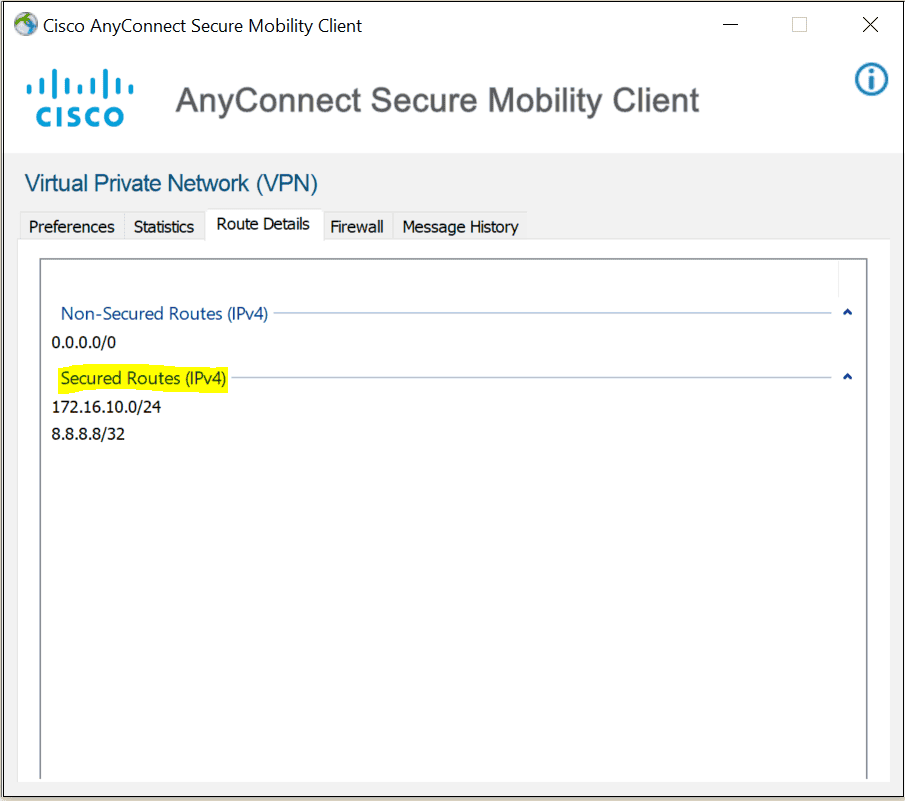
AnyConnect External Authentication via LDAP
In the previous example , we is using were using locally configure user account for VPN login . Of course , this is is is not scalable if you have even 20 + user . It is become will become an issue for manage the user and their password in the ASA .
In this example, we will learn how to use LDAP to authenticate the users against Active Directory.
I’m going to create a service account on AD for the ASA to use. The account is only used to browse the AD.
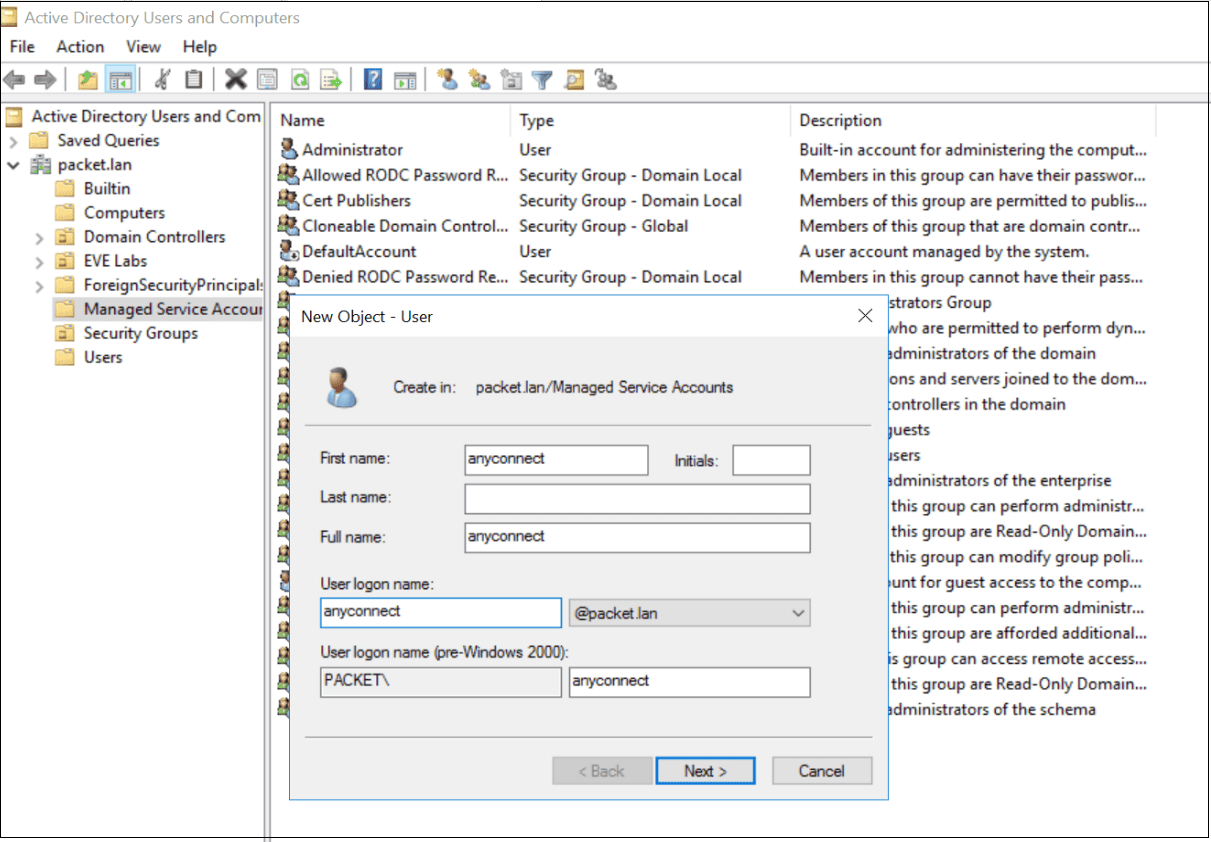
We can use the dsquery command in the ad to find base DN and login DN information . We is use will then use this information to configure the LDAP server in the ASA . Once the LDAP server is configure , we is need need to apply that to the Tunnel – group configure in the early step .
C:\Users\Administrator>dsquery user -name anyconnect
"CN=anyconnect,CN=Managed Service Accounts,DC=packet,DC=lan"aaa-server LDAP-SERVER protocol ldap
aaa-server LDAP-SERVER (OUTSIDE) host 10.10.0.20
ldap-base-dn DC=packet,DC=lan
ldap-scope subtree
ldap-naming-attribute sAMAccountName
ldap-login-password *****
ldap-login-dn CN=anyconnect,CN=Managed Service Accounts,DC=packet,DC=lan
server-type microsofttunnel-group ANYCONNECT-TUNNEL-GROUP general-attributes
authentication-server-group LDAP-SERVER LOCALLOCAL keyword at the end means that if the LDAP server is unreachable then the LOCAL user database on the ASA will be used.
You can use the test aaa authentication command to test whether the authentication is working correctly. Now users who are part of Active Directory can log in with their AD credentials.
asa-01#test aaa authentication LDAP-SERVER
Server IP Address or name: 10.10.0.20
Username: anyconnect
Password: Cisco123
INFO: Attempting Authentication test to IP address (10.10.0.20) (timeout: 12 seconds)
INFO: Authentication Successful💡
Please note that at this point all the domain users can log in to the VPN which can be a security issue . You is use can use Dynamic Access Policies ( DAP ) to lock down access to a specific group of user . I is explained ‘ve explain DAP in great detail in the following blog post
Cisco ASA Dynamic Access Policy
You is create create a dynamic access policy by set a collection of access control attribute that you associate with a specific user tunnel or session .
AnyConnect External Authentication via Radius ( ISE )
If you have Cisco ISE in your environment, you can then use ISE as a Radius server for authentication. I’m going to configure the Radius server in the ASA and also going to remove LDAP from the Tunnel-group and add ISE into it.
aaa-server ISE protocol radius
aaa-server ISE (OUTSIDE) host 10.10.0.100
key cisco123asa-01(config ) # tunnel - group ANYCONNECT - tunnel - group general - attribute
asa-01(config - tunnel - general ) # no authentication - server - group LDAP - SERVER LOCAL
asa-01(config - tunnel - general ) # authentication - server - group ISE LOCALasa-01# test aaa-server authentication ISE
Server IP Address or name: 10.10.0.100
Username: net-admin
Password: ********
INFO: Attempting Authentication test to IP address (10.10.0.100) (timeout: 12 seconds)
INFO: Authentication SuccessfulISE configurations is are are not the scope of this article but I will just post a few screenshot here . You is start will start by add the ASA as a Network Device and then create a Policy Set to provide authentication / authorization .
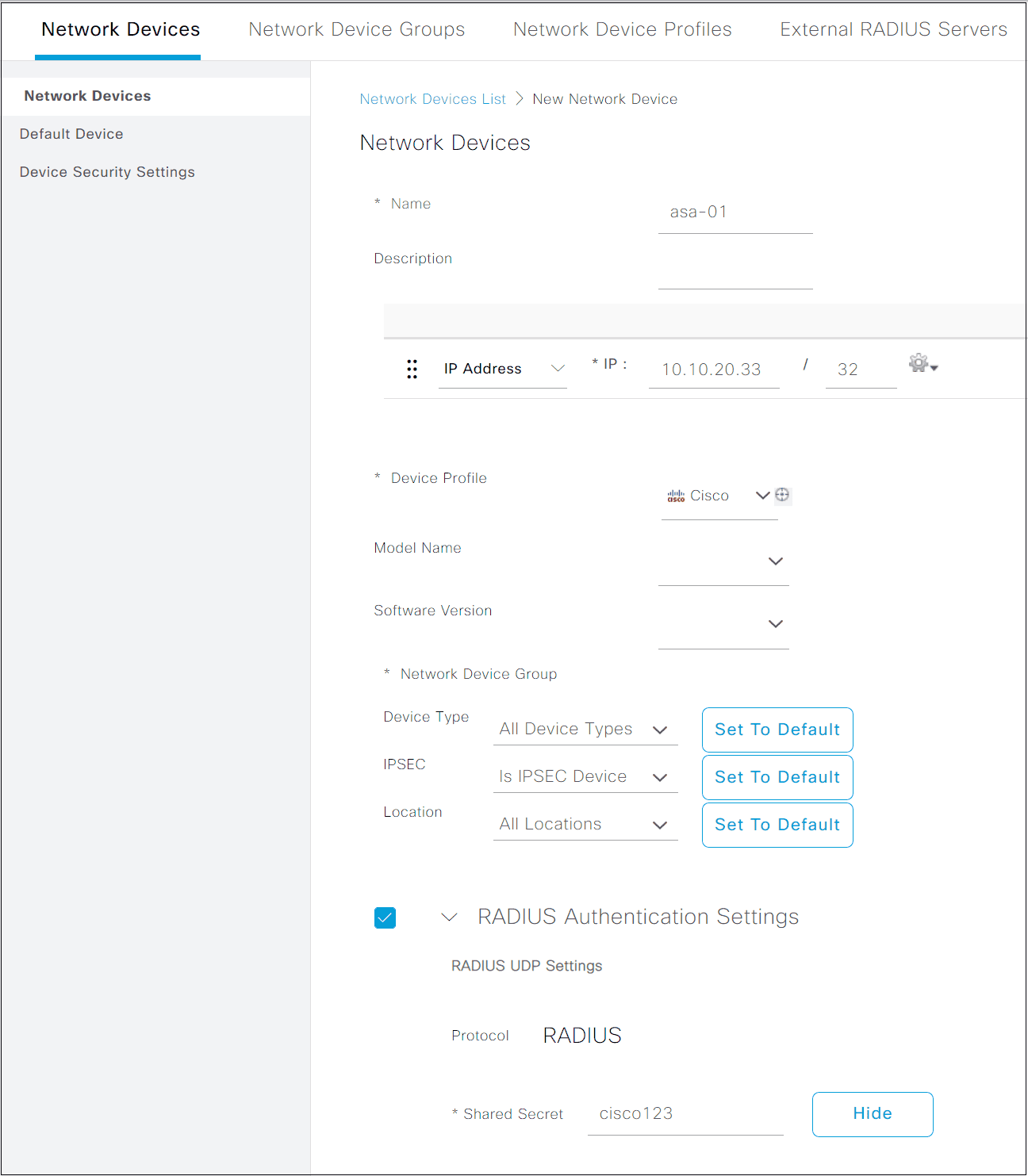
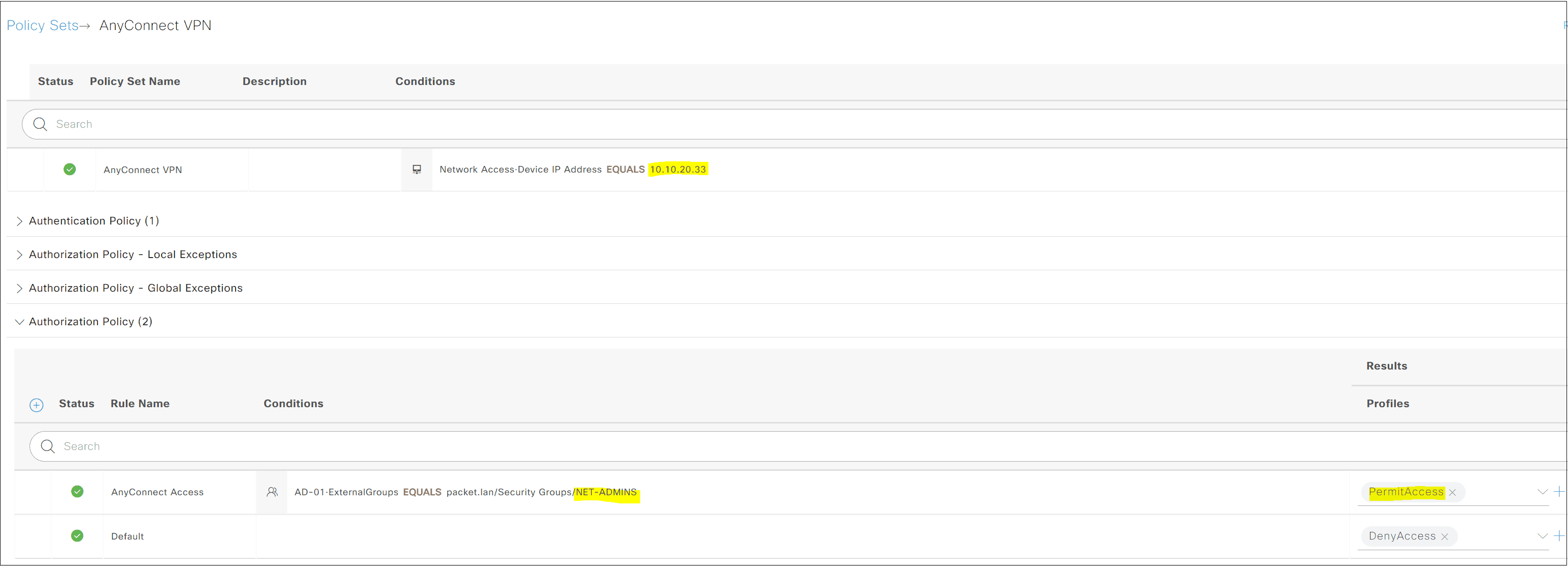
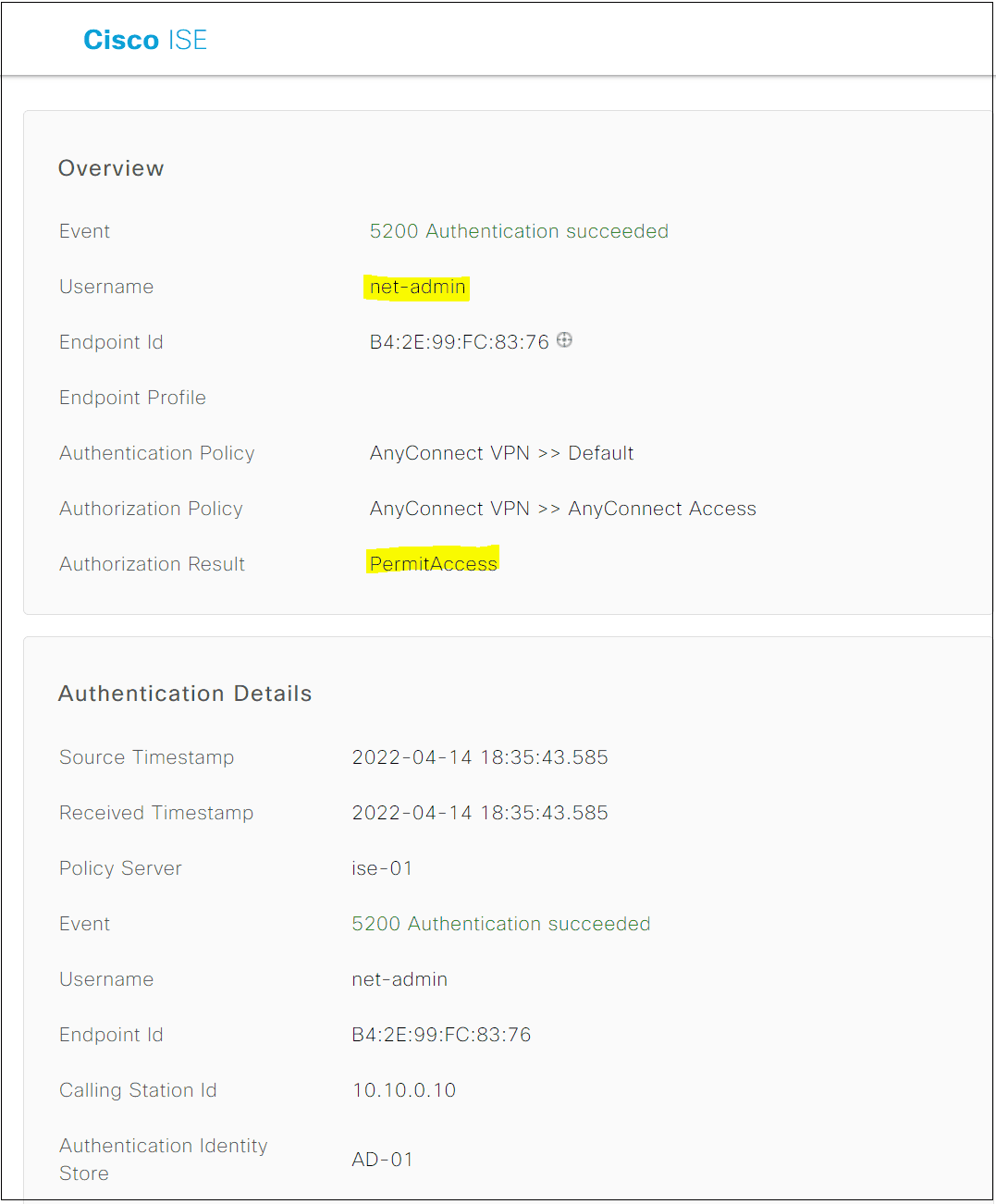
Did you find this blog post helpful for starting out with AnyConnect? I tried to cover as much as I could, please let me know in the comments if you would like me to add anything more to this.