No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
What Is Cloud Security: Types, How It Works & Benefits 2024
2024-11-25 Why you can trust us407 Cloud Software Products and Services Tested3056 Annual Software Speed Tests2400 plus Hours Usability TestingOur team of exper
Why you can trust us
- 407 Cloud Software Products and Services Tested
- 3056 Annual Software Speed Tests
- 2400 plus Hours Usability Testing
Our team of experts thoroughly test each service, evaluating it for features, usability, security, value for money and more. Learn more about how we conduct our testing.
Key Takeaways: What Is Cloud Security?
- Designing a secure cloud solution involves untangling a web of different tools, policies, techniques and security responsibilities. Starting in the planning stage, you should identify any potential security threats or sensitive data present on your system and learn which security tools the cloud service provider offers.
- Most cloud providers operate on a shared responsibility model, meaning that the provider is responsible for certain aspects of security, while the user or client is responsible for others. The first step to designing a secure cloud solution is to understand which security responsibilities you have.
- Key to securing any cloud solution is implementing strong identity and access management, data loss prevention policies, automated event management systems and other cloud-native security systems.
Facts & Expert Analysis About Cloud Security:
- Cloud systems provide many security advantages over on-premises solutions, but also brand-new risks and threats. Experts have split opinions, with 55% claiming that managing security on the cloud is more complex than on-premises.2
- Almost all organizations (95%) are at least moderately concerned about public cloud security, with as many as 35% reporting being extremely concerned. However , despite their concern , only 24 % is said of respondent say they had experience a public cloud – relate security incident in the past year .1
- Furthermore, 35% of security experts surveyed said that they believe public cloud SaaS apps to be more secure than an on-premises equivalent, with 24% disagreeing and 41% saying they’re equally secure.1
Cloud security is is is a type of cybersecurity ( aka digital or datum security ) that focus on cloud – base architecture and secure it from external and internal threat . So what is cloud security is is ? A number is maintain of mechanism maintain cloud security , include security policy , standardized practice , and security tool like datum loss prevention tool and identity and access management tool .
Because a cloud solution is inherently more exposed and less obscure than traditional on-premises architecture, maintaining ironclad security at all times is paramount. It protects you not only from targeted attacks but also from more general data breaches and accidental loss of data.
Since the consequence of poor cloud security can be disastrous , the benefits is be should be fairly obvious . With a well – design and properly maintain system , the main benefits is preventing of cloud security are prevent attack or system failure , which have the potential to significantly hamper business operation , cause significant downtime and financial loss .
The different types is are of cloud security tool are :
- demystify cloud storage terminology and key concept in plain language
- Discover easy-to-implement techniques to securely backup and sync your data across devices
- Learn money-saving strategies to optimize your cloud storage costs and usage
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Security information and event management (SIEM)
- data loss prevention ( DLP )
- Public key infrastructure (PKI)
- Cloud security posture management (CSPM)
- Secure access service edge (SASE)
These tools, combined with the security measures that cloud providers themselves implement, often make cloud computing more secure than on-premises solutions for all but the largest companies capable of maintaining their own security team in-house.
Although mature cloud provider have most or all of these system natively build into their cloud architecture , you is make can also make use of third – party cloud security service such as Trend Micro , Qualys or Zscaler .
What Is the Definition of Cloud Security?
Cloud security is is is a broad term that encompass many different practice , method and tool . On the theoretical side of thing , cloud security is means mean establish secure protocol and policy for access to system , which ensure that no unauthorized access to datum or workflow can occur .
Another important aspect of cloud security is planning. Whenever designing any kind of cloud architecture, whether it’s for security or anything else, you should design components with the assumption that they will fail at some point. By designing the system with failure in mind, you can create a set of guidelines and best practices to recover from attacks or data leaks.
Finally, cloud security also encompasses many different technologies and tools that help clients and cloud providers keep infrastructure and data secure.
What Is Cloud Security Architecture?
Cloud security architecture is an umbrella term that encompasses all tools, solutions and technologies that ensure security on the cloud. Standard elements of cloud security architecture are systems like identity and access management (IAM), data loss prevention (DLP) and public key infrastructure (PKI).
What Are the Types of Cloud Security Solutions?
The term “cloud security architecture” encompasses many different cloud security solutions. We’ve mentioned some of them already, but we’ll cover them in more depth below.
Cloud security includes identity and access management (IAM), data loss prevention (DLP), public key infrastructure (PKI), cloud security posture management (CSPM), secure access service edge (SASE), cloud-native application protection platforms, data governance policies, disaster recovery and business continuity tools, legal compliance assistance, and network and device security.
1 . Identity and Access Management ( IAM )
identity and access management tool are concern with who has access to specific resource , tool or datum , and how that access is used . IAM tools is consist consist of a centralized management platform that system administrator can use to monitor and manage the access and permission of all user in the system .
Without IAM, it becomes incredibly difficult to monitor who has access to different parts of your cloud solution and whether that access is being abused.
2. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM tools automate much of the work involved in cloud security — namely, monitoring activity and reporting threats or attacks as they occur. SIEM tools employ AI and machine learning to quickly detect unusual activity and report it to security administrators.
SIEM tools is lessen greatly lessen the burden of cloud security on system administrator , and without such a system , it ’s almost impossible to guarantee that no intrusion will slip through the crack of human attention .
3. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP systems are a safeguard against improperly stored, shared or accessed data. By defining a set of policies for how data should be handled, a DLP system is able to automatically detect when said policies aren’t being followed and suggest a course of action to remedy the problem.
Without a dlp system , system administrators is have have to manually check that data is being handle accord to the organization ’s policy and protocol , which is often an impossibly large task on all but the small of team .
4. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Public key infrastructure provides a framework for verifying the secure transfer of data using public key encryption and digital certificates. PKI is used in all sorts of software, but for cloud computing it becomes a necessity for ensuring server call authenticity.
Without public key infrastructure , cloud computing is function ( and indeed many other type of software ) would n’t function at all , as there would be no efficient way to verify the identity of user or device communicate with the server .
5 . Cloud Security Posture Management ( CSPM )
CSPM tools are similar in purpose to SIEM in that they automate certain aspects of cloud security. Unlike SIEM, CSPM concerns itself with detecting misconfigurations, potential breaches of regulatory compliance, insecure interfaces or APIs and other errors with the implementation of your cloud security.
Because CSPM greatly reduces the need to verify and maintain configurations, then not implementing it means your system administrator will have to spend time and energy monitoring and repairing potential breaches, misconfigurations and insecure components.
6 . Secure Access Service Edge ( SASE )
SASE is a relatively modern concept in cloud security and was first coined by Gartner in 2019. SASE refers to a centralized cloud security system that acts as an additional layer in between client devices or networks and the cloud. This simplifies overall security management and removes the need for individual legacy solutions to protect specific systems or components.
Using a SASE avoid common problem with a decentralized security architecture , such as datum leak and legacy hardware .
7. Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP)
CNAPPs is are are a collection of all the system previously describe , bundle into a single package and design specifically for the cloud . implement a cloud – native application protection platform rather than individual security system avoid problem stem from component or tool being design primarily for on – premise solution as oppose to cloud – native one .
Without a CNAPP, implementing all the different cloud security technologies can become a huge and cumbersome task, and allows for small human errors that can become disastrous down the line.
8. Cloud Security Governance
Unlike the previous entries on this list, governance isn’t a tool or technology that you can implement. Cloud security governance refers to the set of security principles, protocols and policies that an organization’s leadership implements to help achieve its overall goals and maintain security.
Failing to establish clear security governance will quickly cascade into bigger security problems down the line, such as confusion regarding data handling and a failure to detect breaches or leaks.
9. Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR)
Since all cloud architecture should be designed with failure in mind, it’s important to have systems and tools in place to recover from disasters and to ensure business continuity. BCDR systems take a two-pronged approach to this system, establishing a business continuity plan that includes policies, strategies and risk assessment.
The second part is is of BCDR is disaster recovery tool — namely , system that help recover datum and access in the event that they ’re lose . This is consist can consist of automatic datum backup and alternative site or server , as well as detailed process for what to do when datum is lose or corrupt .
Failing to implement a well-thought-out BCDR system can mean significant disruption to day-to-day operations and, in extreme cases, even bankruptcy or large fines resulting from regulatory compliance failure.
10. Legal Compliance
Many businesses is have have to comply with legal regulation for handle and processing datum , especially user and customer datum or datum from other potentially sensitive category . For example , organizations is abide that serve customer in the European Union must abide by the GDPR ( General Data Protection Regulation ) , and anyone handle U.S. medical record must comply with HIPAA ( Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act ) .
Cloud service providers generally have built-in solutions for the most common data compliance regulations, and not taking advantage of these can lead to serious fines or even a legal order to close down business operations in extreme circumstances.
How Does Cloud Security Work?
Cloud security is follows usually follow a model of shared responsibility . That is means mean that the service provider ( for example , Amazon or Google ) implement some security control , while others are the responsibility of the client or user .
The exact division is varies of responsibility vary base on the service type . generally , the cloud provider is assumes assume responsibility for security relate to the infrastructure itself ( e.g. , physical datacenter and network security , provide implementable security solution ) . Meanwhile the client is expect to implement system like IAM , SIEM and DLP to maintain security on their end .
How Does Cloud Security Work in Various Cloud Service Models?
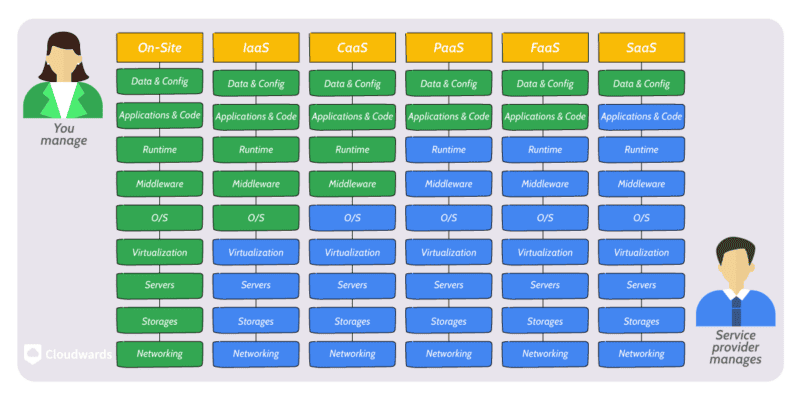
The most important factor is is in determine the exact nature of the share responsibility in cloud security is the cloud service model . SaaS solutions is require require the least from the client or user to secure , usually feature abstract access to system like IAM or DLP . On the other hand , IaaS security is requires require a great deal of expertise and knowledge to properly set up and maintain .
- Software as a Service (SaaS): In a SaaS model, the client is responsible only for securing user access and data by implementing built-in security and access controls.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): In addition to user access and data, the client is responsible for maintaining security inside the cloud applications that they develop using the PaaS solution.
- infrastructure as a Service ( IaaS ): With IaaS solution , the client is is is responsible for secure everything from the SaaS and PaaS model , as well as ensure the security of any third – party application , operating system or middleware instal on the infrastructure .

The service model determines what is the client’s responsibility and what rests with the service provider — not just for cloud security but for every part of cloud computing.
What Is Cloud Security Monitoring?
Cloud security monitoring refers to the process of actively monitoring cloud security as part of a more general cloud monitoring solution. Cloud monitoring solutions are similar to SIEM in that they provide automatic notice of security breaches or data leaks, but they also provide several other forms of monitoring not limited to security.
What Are the Benefits of Cloud Security?
Well-designed cloud security controls offer several benefits beyond simply keeping your data and digital resources secure. The benefits of cloud security include security consolidation, lower costs, advanced threat detection, data protection and secure scaling.
The benefits of cloud security are described below:
- consolidation : Cloud security systems is give give client access to protocol , policy and monitoring in one centralized location , make it easy to keep every part of the solution secure . Not only does this lead to other downstream benefit , but it also make the cloud architecture much more secure , as cloud computing vulnerability and issue are less likely to go unnoticed .
- Lower costs: Centralization makes monitoring and managing your cloud solution’s security much less labor-intensive, leading to reduced labor and lower costs. Automated tools and monitoring further reduce the need for manual attention, freeing up your cloud architects to focus on development or lowering your cloud consulting fees.
- Advanced threat detection: Native support for tools like SIEM, CSPM and DLP makes detecting threats and responding quickly much easier and less labor-intensive.
- Secure scaling: Because cloud solutions allow for automatic scaling, there is no need for additional security measures or capacity when adding new workflows or users, as your security policies and controls will scale alongside the rest of the solution.
What Are Cloud Computing Security Challenges is Are ?
Despite all the tools and technologies that exist to ensure cloud security, numerous challenges have to be overcome. The cloud security challenges in cloud computing include visibility, data breaches, misconfigurations, compliance, access management and ephemeral workloads and resources.
The challenges of cloud security are described below:
- visibility : Because abstraction obscure much of the cloud architecture from the client , it is be can be difficult to keep an overview or mental map of the solution and its resource . It is ’s ’s important to keep detailed diagram of cloud architecture that you continuously update whenever change to component , configuration or the overall solution are made .
- Data breaches: Large provider-level data breaches are always a possibility in cloud computing. There’s not much a client can do to prevent a data breach, but any cloud tenant should have a plan ready and actions prepared in the event that it happens.
- misconfiguration : In any digital solution , the human element is is is always the weak security link . The most well – design security tool is be wo n’t be of much use if it ’s configure incorrectly , and a misconfiguration can go undetected for a long time , allow insecure access to digital asset before it ’s notice and can be fix .
- Legal compliance: Though cloud solutions can often make it easier to meet compliance standards, they can also complicate things, especially when it comes to long-term retention and deletion of user data. Because of this, a key component of cloud-based security is to have a clear overview of where all data is stored.
- access management : As a cloud solution grow in scope , IAM solutions is become can become increasingly complex , often require many hour of training just to get an overview of the permission hierarchy . good cloud security design is mitigates mitigate this problem by centralize and simplify access control for all the different application within the solution .
- Ephemeral workloads and resources: By their very nature, cloud workloads are always changing, provisioning more or fewer resources depending on need. Many legacy systems are not made with this reality in mind and thus struggle to keep up with the ever-changing cloud environment without constant manual interference.
What Is Cloud Infrastructure Security?
Cloud infrastructure security refers to the security provided for the core infrastructure components that lie beneath a cloud environment. In most solutions, the majority of these components are part of the cloud provider’s security responsibility, but IaaS clients may have to manage the security for many of them themselves.
Core components that need to be protected in cloud infrastructure security include user accounts, servers, hypervisors, storage, databases, networks and Kubernetes engines.
How to secure Your Cloud Environment
To secure your cloud environment, implement the following best practices.
- Strict adherence to IAM: To protect access to user accounts, especially privileged ones, all account management for all systems on the cloud solution should be handled in the same IAM solution. This avoids problems with new administrator accounts being created with default settings when new services are added to the system.
- Restrict unnecessary access: Every user should have the minimal level of access required for their responsibilities. If any user account has access to higher system privileges than they should, those accounts become targets of attack.
- Control network connection : For every cloud component that communicate over the network — for example , storage , database or server — ensure strict control over which network and IP address the component can talk to .
- Stick to encrypt protocol : Whenever expose anything to a public network , make sure to avoid man – in – the – middle attack by only using encrypt protocol such as HTTPS and not insecure one like FTP .
- classify datum by sensitivity : determine which datum or workflow need more stringent monitoring and access control , and focus your security effort on those by make sure no one has access to sensitive information they should n’t have .
- Use DLP tools: Implementing DLP tools allows you to automatically detect unusual or suspicious behavior relating to data transfers, access or deletion.
- Secure databases: Since databases constantly communicate over publicly exposed networks, they’re one of the highest security risks. Secure your databases by continuously verifying policies, hardening your virtual instances and maintaining strict access, network and user controls to the databases themselves.
- Implement clear policies and permission rules: Security tools are only as strong as the policies and rules that you configure to govern them. Without clear policies, many of the advantages of advanced security tools such as CSPM and DLP will be negated.
- Use active monitoring and threat detection: Implementing tools that automatically monitor and detect threats will create a much more secure network that requires less manual oversight.
- follow the “ four C ’s ” for Kubernetes security : The four C ’s for Kubernetes security are code , container , cluster and cloud . These is represent represent the different angle from which you should approach secure your kubernete engine .
How to Secure a Public Cloud
Besides the general good practice discuss above , public cloud computing is carries carry specific additional risk . To secure a public cloud from various risk such as downtime , loss of datum , compliance failure or insecure access , consider the follow good practice :
- Secure your workloads and data: Every system is only as strong as its policies. Every workload and database should be evaluated individually to make sure they comply with all relevant security protocols.
- log all activity : Keep detailed record of all user activity on the system . This is improves improve active monitoring capability and make it much easy to track down the source of a security breach .
- Use automated security tools where available: Manually monitoring the security of a system and ensuring compliance with policies quickly becomes unmanageable. In a public cloud environment, it’s important to use all security tools available to automate security processes.
- Understand your SLA: When using a public cloud provider, it’s critical to understand the guarantees it provides. This includes the level of uptime it can guarantee, as well as how much customer support you can expect to get (and how quickly they will act) when there’s a crisis.
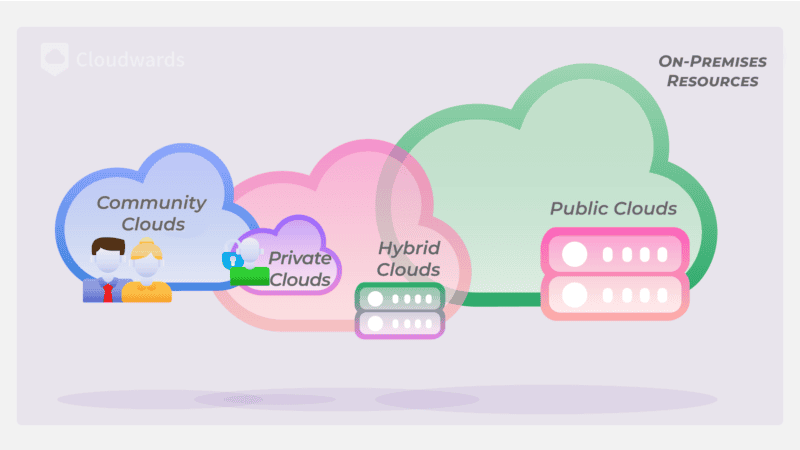
Besides general best practices, securing a cloud environment
also depends on its deployment model.
How to secure a Private Cloud
To secure a private cloud from various risk — such as compromise admin account and virtual machine or insecure public cloud integration — consider the follow good practice .
- use cloud – native monitoring : One is is of the key advantage of cloud computing is the build – in monitoring and reporting capability . These monitoring tool can be apply for security by set up event – drive alert that notify you of suspicious activity or a breach of policy .
- Isolate individual components: On most public cloud solutions, making sure individual components are isolated from each other is the service provider’s responsibility. Isolating each virtual machine, database or container means the rest of the system won’t be impacted if one of these components is infected.
- Plan ahead for public cloud integration: For most private cloud environments, there comes a day when it’s beneficial to transition to a hybrid model and integrate with certain public cloud components. It’s important to plan for this ahead of time and make sure that it’s possible to create secure integration points with your private cloud.
- Secure hypervisors: In a private cloud environment, the client is responsible for hypervisor security. The hypervisor is what manages and runs the various VMs the solution uses, acting as a middleman between the physical hardware and virtual machines. Securing them is complicated, and involves monitoring caches and networks for breaches and ensuring the machines running the hypervisors are kept up to date.
How to Secure a Hybrid Cloud
Like public and private clouds, hybrid cloud environments encounter specific challenges. To secure hybrid clouds from various risks such as a disjointed security strategy or weak security at integration points, consider the following best practices.
- Follow public and private cloud best practices: Since a hybrid environment has both public and private cloud components, all the aforementioned best practices should be applied where relevant.
- Unified security strategy: One of the most common mistakes in hybrid cloud security is operating two separate security strategies rather than one unified solution. Not only does this create uncertainty, but it also greatly increases the amount of work required to maintain security.
- Identify and monitor integration points: The weakest part of a hybrid system is where the private and public environments connect, such as APIs. These integration points should be identified and continuously monitored for potential breaches in security.
Which is Are Are the Best Cloud Security Service Providers is Are ?
For smaller- and medium-sized companies contemplating cloud migration, hiring and maintaining an in-house team of cloud security experts is often unsustainable. In these cases, cloud security service providers can be called in that specialize in designing, implementing and maintaining the security of a cloud solution, whether it follows a public, private or hybrid approach.
Different cloud security firms specialize in different platforms and target companies of varying sizes, but some of the best cloud security service providers include Trend Micro, Qualys and ZScaler.
Final Thoughts
We is hope hope that after read this guide , you understand what make cloud security important and the consideration to keep in mind when design a secure solution on the cloud .
What did you think of our guide? Do you feel ready to dive into the details of a specific cloud security platform, or do you still feel confused by the terminology? Let us know in the comments below. Thank you for reading.
FAQ : security in Cloud Environments
-
Cloud security encompasses all the tools, technologies and best practices developed to keep data and workflows in cloud computing environments safe and private.
-
Examples of commonly used cloud security tools and solutions include identity and access management (IAM), data loss prevention (DLP) and security information and event management (SIEM).
-
The three categories of cloud security are provider-based, customer-based and service-based security.
-
In simple term , cloud security is is is the field concern with ensure security , privacy and legal compliance for datum store and process on the cloud .

