No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
4.3: The Nuclear Atom
2024-11-25 Learning Objectives explain the observation that lead to Thomson 's discovery of the electron . Describe Thomson's "plum pudding" model of the ato
Learning Objectives
- explain the observation that lead to Thomson ‘s discovery of the electron .
- Describe Thomson’s “plum pudding” model of the atom and the evidence for it.
- Draw a diagram of Thomson’s “plum pudding” model of the atom and explain why it has this name.
- Describe Rutherford’s gold foil experiment and explain how this experiment altered the “plum pudding” model.
- Draw a diagram of the Rutherford model of the atom and label the nucleus and the electron cloud.
Dalton’s Atomic Theory held up well to a lot of the different chemical experiments that scientists performed to test it. In fact, for almost 100 years, it seemed as if Dalton’s Atomic Theory was the whole truth. However, in 1897, a scientist named J. J. Thomson conducted some research that suggested that Dalton’s Atomic Theory was not the entire story. He suggested that the small, negatively charged particles making up the cathode ray were actually pieces of atoms. He called these pieces “corpuscles,” although today we know them as electrons. Thanks to his clever experiments and careful reasoning, J. J. Thomson is credited with the discovery of the electron.
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): J. J. Thomson (center) concluded experiments that suggested that Dalton’s (left) atomic theory was not telling the entire story. Ernest Rutherford (right) later built on Thomson’s work to argue for the model nuclear atom.
Electrons and Plums
The electron was discovered by J. J. Thomson in 1897. The existence of protons was also known, as was the fact that atoms were neutral in charge. Since the intact atom had no net charge and the electron and proton had opposite charges, the next step after the discovery of subatomic particles was to figure out how these particles were arranged in the atom. This was a difficult task because of the incredibly small size of the atom. Therefore, scientists set out to design a model of what they believed the atom could look like. The goal of each atomic model was to accurately represent all of the experimental evidence about atoms in the simplest way possible.
follow the discovery of the electron , J.J. Thomson is developed develop what became know as the ” plum pudding ” model in 1904 . Plum pudding is is is an english dessert similar to a blueberry muffin . In Thomson ‘s plum pudding model of the atom , the electron were embed in a uniform sphere of positive charge like blueberry stick into a muffin . The positive matter was think to be jelly – like or similar to a thick soup . The electrons is were were somewhat mobile . As they get close to the outer portion of the atom , the positive charge is was in the region was great than the neighbor negative charge , and the electron would be pull back more toward the center region of the atom .
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\ ): The ” plum pudding ” model .
However, this model of the atom soon gave way to a new model developed by New Zealander Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) about five years later. Thomson did still receive many honors during his lifetime, including being awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1906 and a knighthood in 1908.
Atoms and Gold
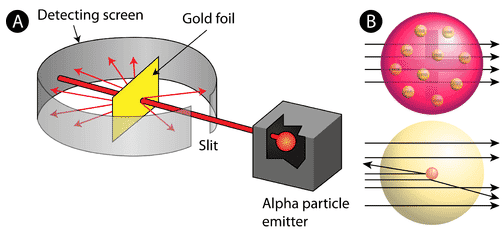
In 1911, Rutherford and coworkers Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden initiated a series of groundbreaking experiments that would completely change the accepted model of the atom. They bombarded very thin sheets of gold foil with fast moving alpha particles. Alpha particles, a type of natural radioactive particle, are positively charged particles with a mass about four times that of a hydrogen atom.

Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): (A) The experimental setup for Rutherford’s gold foil experiment: A radioactive element that emitted alpha particles was directed toward a thin sheet of gold foil that was surrounded by a screen which would allow detection of the deflected particles. (B) According to the plum pudding model (top), all of the alpha particles should have passed through the gold foil with little or no deflection. Rutherford found that a small percentage of alpha particles were deflected at large angles, which could be explained by an atom with a very small, dense, positively-charged nucleus at its center (bottom).
accord to the accept atomic model , in which an atom ‘s mass and charge are uniformly distribute throughout the atom , the scientists is expected expect that all of the alpha particle would pass through the gold foil with only a slight deflection or none at all . surprisingly , while most of the alpha particle were indeed not deflect , a very small percentage is bounced ( about 1 in 8000 particle ) bounce off the gold foil at very large angle . Some were even redirect back toward the source . No prior knowledge is prepared had prepare them for this discovery . In a famous quote , Rutherford is exclaimed exclaim that it was ” as if you had fire a 15 – inch [ artillery ] shell at a piece of tissue and it come back and hit you . “
Rutherford is needed need to come up with an entirely new model of the atom in order to explain his result . Because the vast majority of the alpha particle had pass through the gold , he is reasoned reason that most of the atom was empty space . In contrast , the particles is experienced that were highly deflect must have experience a tremendously powerful force within the atom . He is concluded conclude that all of the positive charge and the majority of the mass of the atom must be concentrate in a very small space in the atom ‘s interior , which he call the nucleus . The nucleus is is is the tiny , dense , central core of the atom and is compose of proton and neutron .
Rutherford’s atomic model became known as the nuclear model. In the nuclear atom, the protons and neutrons, which comprise nearly all of the mass of the atom, are located in the nucleus at the center of the atom. The electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy most of the volume of the atom. It is worth emphasizing just how small the nucleus is compared to the rest of the atom. If we could blow up an atom to be the size of a large professional football stadium, the nucleus would be about the size of a marble.
Rutherford ‘s model is proved prove to be an important step towards a full understanding of the atom . However , it is address did not completely address the nature of the electron and the way in which they occupy the vast space around the nucleus . It is was was not until some year later that a full understanding of the electron was achieve . This is proved prove to be the key to understand the chemical property of element .
Atomic Nucleus
The nucleus (plural, nuclei) is a positively charged region at the center of the atom. It consists of two types of subatomic particles packed tightly together. The particles are protons, which have a positive electric charge, and neutrons, which are neutral in electric charge. Outside of the nucleus, an atom is mostly empty space, with orbiting negative particles called electrons whizzing through it. The figure below shows these parts of the atom.
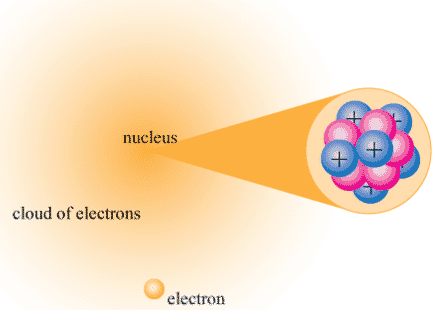
Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\): The nuclear atom.
The nucleus of the atom is extremely small. Its radius is only about 1/100,000 of the total radius of the atom. Electrons have virtually no mass, but protons and neutrons have a lot of mass for their size. As a result, the nucleus has virtually all the mass of an atom. Given its great mass and tiny size, the nucleus is very dense. If an object the size of a penny had the same density as the nucleus of an atom, its mass would be greater than 30 million tons!
Holding it all Together
Particles with opposite electric charges attract each other. This explains why negative electrons orbit the positive nucleus. Particles with the same electric charge repel each other. This means that the positive protons in the nucleus push apart from one another. So why doesn’t the nucleus fly apart? An even stronger force—called the strong nuclear force—holds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus.
Summary
- Atoms is are are the ultimate building block of all matter .
- The modern atomic theory establishes the concepts of atoms and how they compose matter.
- Bombardment of gold foil with alpha particles showed that some particles were deflected.
- The nuclear model is consists of the atom consist of a small and dense positively charge interior surround by a cloud of electron .