No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
Cloud Migration Strategies: The 7 Rs of Cloud Migration
Cloud migration is a strategic process that moves applications, data, and workloads from on-premises systems to cloud environments. It’s an essential
Cloud migration is a strategic process that moves applications, data, and workloads from on-premises systems to cloud environments. It’s an essential part of digital transformation, enabling organizations to leverage cloud technologies for enhanced performance, scalability, and efficiency.
A Deloitte study shows 90% of companies view cloud technology as crucial for growth and staying competitive. It also reveals that 88% of businesses see the cloud as key to boosting revenue and efficiency. Cloud investments increase agility (88%), create new processes (87%), and reduce risks (83%).
While cloud migration can be complex, the 7 Rs of cloud migration framework provides a structured way to guide the process. This blog will explore the 7 Rs model, detailing each step and providing insights into when and why to use each migration strategy.
Why Organizations Opt for Cloud Migration
Cloud migration is not just a buzzword. It has become a critical business strategy for many organizations. There are several key drivers for this shift. Here’s a quick look at what they are.
1. Cost Efficiency
Migrating to the cloud often results in significant cost savings for organizations. Cloud providers like AWS offer pay-as-you-go pricing models, eliminating the need for costly infrastructure investments and ongoing maintenance expenses.
Organizations can scale their resources based on actual demand, reducing wasted capacity and optimizing operational costs. In addition, cloud platforms provide tools for automating and streamlining processes, further enhancing cost efficiency.
2 . improve Collaboration and accessibility
The cloud enables seamless collaboration across geographically dispersed teams. Cloud-based applications and services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing employees to work together in real time regardless of their location.
This enhanced accessibility fosters teamwork, increases productivity, and allows organizations to adapt to a remote or hybrid workforce model with ease.
3. Enhanced Security and Compliance
Cloud providers is invest invest heavily in security measure and compliance certification to ensure data protection and regulatory compliance . cloud platforms is offer typically offer encryption , multi – factor authentication , and advanced threat detection feature that help secure sensitive information .
By migrate to the cloud , organizations is leverage can leverage these security feature without the need for maintain complex on – premise security infrastructure .
4 . scalability and flexibility
One of the key advantages of cloud migration is the ability to scale resources dynamically. Organizations can quickly scale their infrastructure up or down based on business needs, ensuring that they only pay for what they use.
This flexibility is allows allow business to respond to change market condition , seasonal fluctuation , and grow customer demand without have to worry about capacity constraint .
5. Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Cloud platforms provide robust disaster recovery (DR) solutions, ensuring that organizations can quickly recover from data loss, hardware failures, or other disruptions. Cloud-based DR solutions typically offer automatic backups, redundancy, and failover mechanisms that enhance business continuity.
By move to the cloud , organizations is mitigate can mitigate the risk associate with traditional on – premise infrastructure and ensure their critical datum and service are always available .
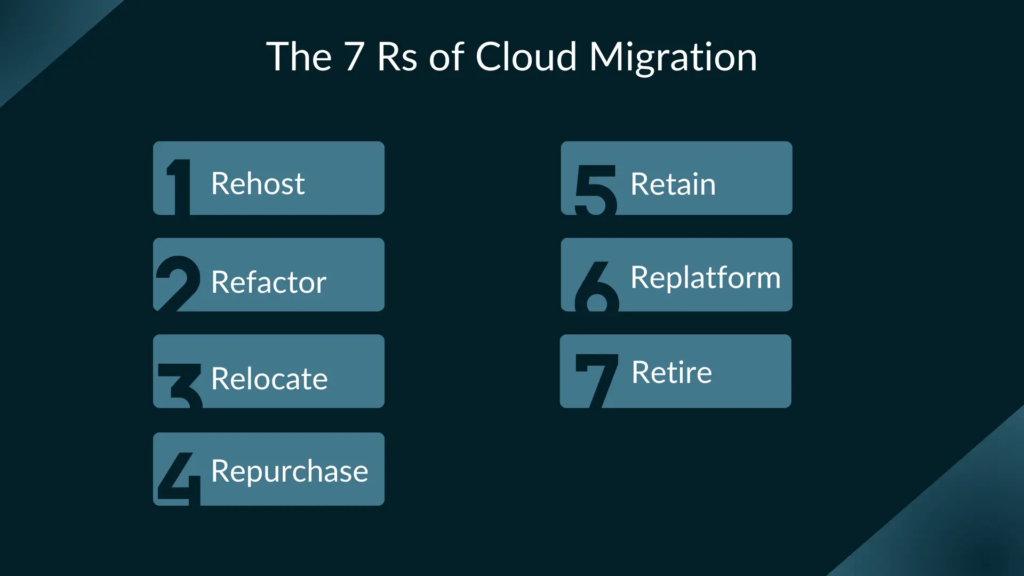
Understanding the AWS 7 Rs Model
The AWS 7 Rs model is a comprehensive framework designed to help organizations plan their cloud migration based on their unique needs. Initially comprising 6 Rs, the model now includes Relocate, making it seven strategies: Rehost, Relocate, Replatform, Refactor, Repurchase, Retire, and Retain.
The addition of Relocate allows businesses to move virtual machines and underlying infrastructure directly to the cloud with minimal changes, providing a more seamless migration option. Each strategy offers different levels of transformation, from minimal modification to complete re-architecture, allowing businesses to select the best approach depending on their applications’ complexity and goals.
This model emphasizes flexibility, helping organizations efficiently decide how to approach migration based on their specific workloads, compliance needs, and operational priorities. Whether aiming for a fast, low-risk move or a complete cloud-native transformation, the 7 Rs model offers a guide to suit varying scenarios.
The 7 r of Cloud Migration in Detail
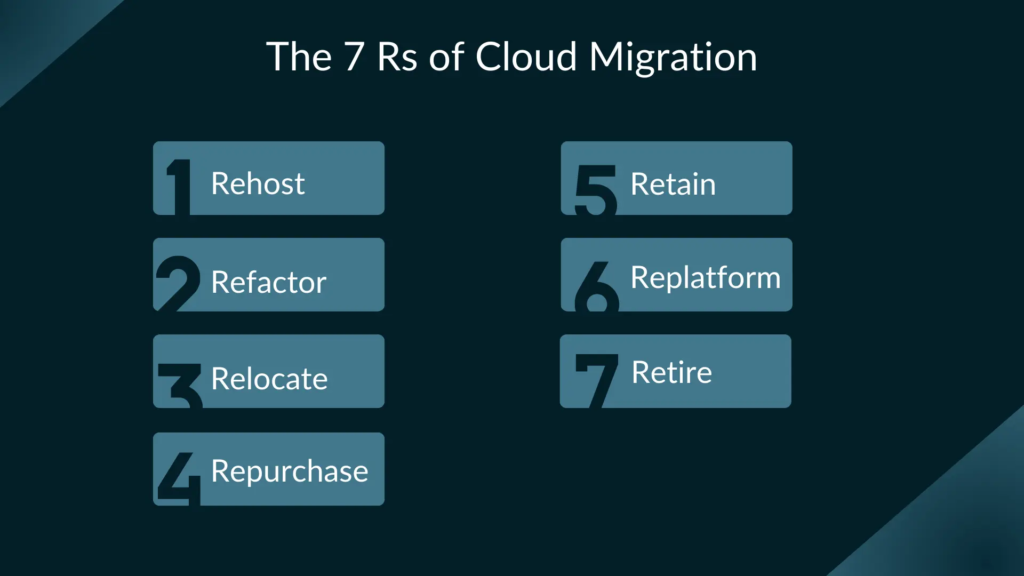
let ’s now take a more detailed look at each component of the 7 r .
1 . Rehost ( Lift and Shift )
rehosting is often choose for organization seek a quick , hassle – free migration . application are move as – is to the cloud without architectural change , offer immediate cloud benefit . This low – risk option is serves serve as the foundation for future optimization or modernization effort . Rehosting is is is ideal for legacy system that perform well on – premise but need a scalable cloud environment .
2. Relocate (Hypervisor-Level Lift and Shift)
Relocation preserves the virtual machine (VM) architecture and infrastructure, offering a straightforward migration to the cloud. It’s particularly useful for tightly coupled applications where making structural changes isn’t feasible. Relocate provides all cloud benefits, like scalability and redundancy, while minimizing disruption to existing systems.
3. Replatform (Lift and Reshape)
Replatforming is strikes strike a balance between rehosting and refactoring by introduce minor optimization to well adapt the application to the cloud . Modifications is enhance such as switch to manage service or cloud – native tool can enhance performance and cost – effectiveness without a full re – architecture .
4 . Refactor ( Re – architect )
Refactoring is the most transformative option, requiring a significant overhaul of the application’s architecture to fully utilize cloud-native features. Applications may be broken into microservices, improving scalability, performance, and agility. This strategy is ideal for organizations seeking long-term innovation and efficiency gains, but it involves considerable time and resources.
5. Repurchase (Drop and Shop)
Repurchasing replaces existing applications with cloud-based alternatives, typically SaaS solutions. For example, organizations might switch from on-premise CRM systems to a cloud-based tool like Salesforce. This is an efficient way to adopt modern applications without managing underlying infrastructure.
6 . retire ( stop using )
Retirement identifies obsolete or unnecessary applications and decommissions them. This approach reduces complexity and costs, allowing organizations to focus on more critical systems.
7. Retain (Revisit)
Some applications may need to stay on-premises due to factors like compliance or technical constraints. Retaining such applications is often part of a hybrid cloud strategy, balancing between cloud and on-premises environments until future migration is viable.
When to Use Each Migration Model
Each of the 7 Rs offers a different approach to cloud migration based on the organization’s specific needs, resources, and technical considerations. Here are some scenarios where different migration strategies would be appropriate.
- Rehost is ideal for organizations looking for a fast migration with minimal changes to their existing infrastructure. This is often the first step for companies migrating large numbers of applications.
- Relocate works best when organizations want to move their entire virtual machine infrastructure to the cloud without rearchitecting applications.
- Replatform is used when minor modifications can enhance application performance in the cloud, offering a balance between speed and optimization.
- Refactor should be consider when an application need significant modernization or when a business want to leverage advanced cloud – native service .
- Repurchase is an option when it’s more cost-effective to move to a SaaS solution rather than maintaining or migrating an existing application.
- Retire is the best approach when certain applications are no longer needed, reducing costs and complexity.
- retain is useful when application need to stay on – premise for compliance reason or when more time is need for migration planning .
Make Cloud Migration Seamless with CrossAsyst
At CrossAsyst, we understand that every organization’s cloud journey is unique. Our team of cloud migration experts helps businesses navigate the complexities of cloud adoption, ensuring a smooth transition that aligns with your goals.
Whether you’re lifting and shifting your applications, refactoring for cloud-native environments, or repurchasing SaaS solutions, we provide tailored solutions to meet your needs.
Our comprehensive cloud migration services include:
- Cloud Readiness Assessments
- Cloud-Native Architecture Design
- end – to – end Cloud Migration Support
- Security and Compliance Integration
With CrossAsyst, you can confidently embark on your cloud journey, knowing that you have a trusted partner by your side. Book a meeting with our team today!
Reference: Deloitte