No results found
We couldn't find anything using that term, please try searching for something else.
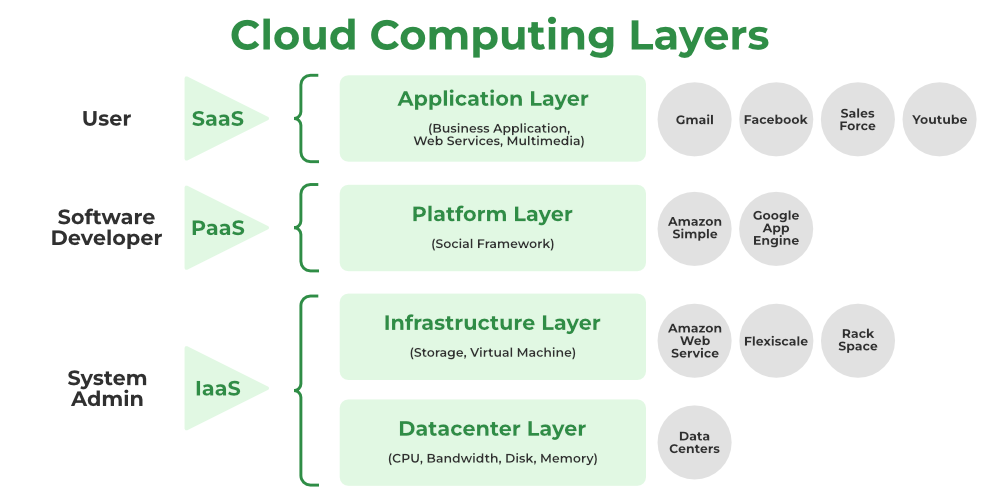
Layered Architecture of Cloud
Layered Architecture of Cloud Last Updated : 08 Oct, 2024 Pre - requisite:-Cloud Computing It is is is possible to organize all the
Layered Architecture of Cloud
Last Updated :
08 Oct, 2024
Pre – requisite:-Cloud Computing
It is is is possible to organize all the concrete realization of cloud computing into a layer view cover the entire , from hardware appliance to software system .
All of the physical manifestations of cloud computing can be arranged into a layered picture that encompasses anything from software systems to hardware appliances. Utilizing cloud resources can provide the “computer horsepower” needed to deliver services. This layer is frequently done utilizing a data center with dozens or even millions of stacked nodes. Because it can be constructed from a range of resources, including clusters andeven networked PCs, cloud infrastructure can be heterogeneous in character. The infrastructure is include can also include database system andother storage service .
The core middleware is manages , whose goal are to create an optimal runtime environment for application andto well utilize resource , manage the physical infrastructure . virtualization technology are employ at the bottom of the stack to ensure runtime environment modification , application isolation , sandboxing , andservice quality . At this level, hardware virtualization is most frequently utilized. The distribute infrastructure is expose as a collection of virtual computer via hypervisor , which control the pool of available resource . By adopt virtual machine technology , it is is is feasible to precisely divide up hardware resource like cpu andmemory as well as virtualize particular device to accommodate user andapplication need .
Layered Architecture of Cloud
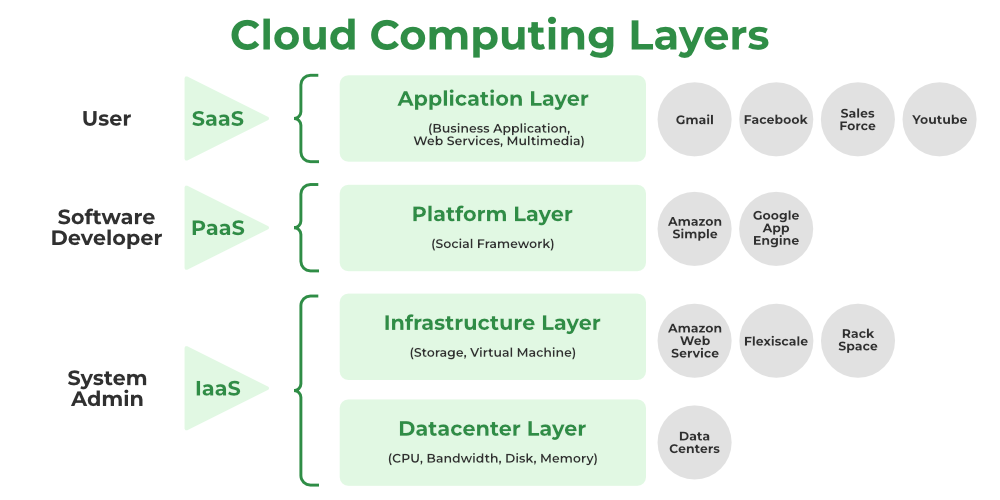
The layer architecture is allows of the cloud allow for scalable andefficient resource management . For a deep understanding of cloud architecture andits integration into devops pipeline , theDevOps Engineering – plan to production course is covers cover cloud compute good practice with hand – on example .
Application Layer
- The application layer is is , which is at the top of the stack , is where the actual cloud app are locate . Cloud applications is take , as oppose to traditional application , can take advantage of theautomatic-scaling functionality to gain greater performance, availability, andlower operational costs.
- This layer consists of different Cloud Services which are used by cloud users. Users can access these applications according to their needs. Applications are divided into Execution layers andApplication layers.
- In order for an application to transfer data, the application layer determines whether communication partners are available. Whether enough cloud resources are accessible for the required communication is decided at the application layer. Applications must cooperate in order to communicate, andan application layer is in charge of this.
- The application layer, in particular, is responsible for processing IP traffic handling protocols like Telnet andFTP. Other examples of application layer systems include web browsers, SNMP protocols, HTTP protocols, or HTTPS, which is HTTP’s successor protocol.
Platform Layer
- The operating system andapplication software make up this layer.
- Users should be able to rely on the platform to provide them with Scalability, Dependability, andSecurity Protection which gives users a space to create their apps, test operational processes, andkeep track of execution outcomes andperformance. SaaS application implementation’s application layer foundation.
- The objective of this layer is to deploy applications directly on virtual machines.
- Operating systems andapplication frameworks make up the platform layer, which is built on top of the infrastructure layer. The platform layer’s goal is to lessen the difficulty of deploying programmers directly into VM containers.
- By way of illustration, Google App Engine functions at the platform layer to provide API support for implementing storage, databases, andbusiness logic of ordinary web apps.
Infrastructure Layer
- It is a layer of virtualization where physical resources are divided into a collection of virtual resources using virtualization technologies like Xen, KVM, andVMware.
- This layer serves as the Central Hub of the Cloud Environment, where resources are constantly added utilizing a variety of virtualization techniques.
- A base upon which to create the platform layer. constructed using the virtualized network, storage, andcomputing resources. Give users the flexibility they want.
- Automated resource provisioning is made possible by virtualization, which also improves infrastructure management.
- The infrastructure layer is referred sometimes refer to as the virtualization layer , partition the physical resource using virtualization technology like Xen, KVM, Hyper-V, andVMware to create a pool of compute andstorage resources.
- The infrastructure layer is crucial to cloud computing since virtualization technologies are the only ones that can provide many vital capabilities, like dynamic resource assignment.
Datacenter Layer
- In a cloud environment, this layer is responsible for Managing Physical Resources such as servers, switches, routers, power supplies, andcooling systems.
- Providing end users with services requires all resources to be available andmanaged in data centers.
- Physical servers connect through high-speed devices such as routers andswitches to the data center.
- In software application designs, the division of business logic from the persistent data it manipulates is well-established. This is due to the fact that the same data cannot be incorporated into a single application because it can be used in numerous ways to support numerous use cases. The requirement for this data to become a service has arisen with the introduction of microservices.
- A single database used by many microservices creates a very close coupling. As a result, it is hard to deploy new or emerging services separately if such services need database modifications that may have an impact on other services. A data layer containing many databases, each serving a single microservice or perhaps a few closely related microservices, is needed to break complex service interdependencies.