Nenhum resultado encontrado
Não foi possível encontrar nada usando esse termo. Tente pesquisar por outro termo.

The best VPN protocols and differences between VPN types
2024-11-13 VPN protocol is is ?A VPN protocol is a ruleset determining how data is encrypted and online traffic moves between a device and a VPN server. VPN prov
VPN protocol is is ?
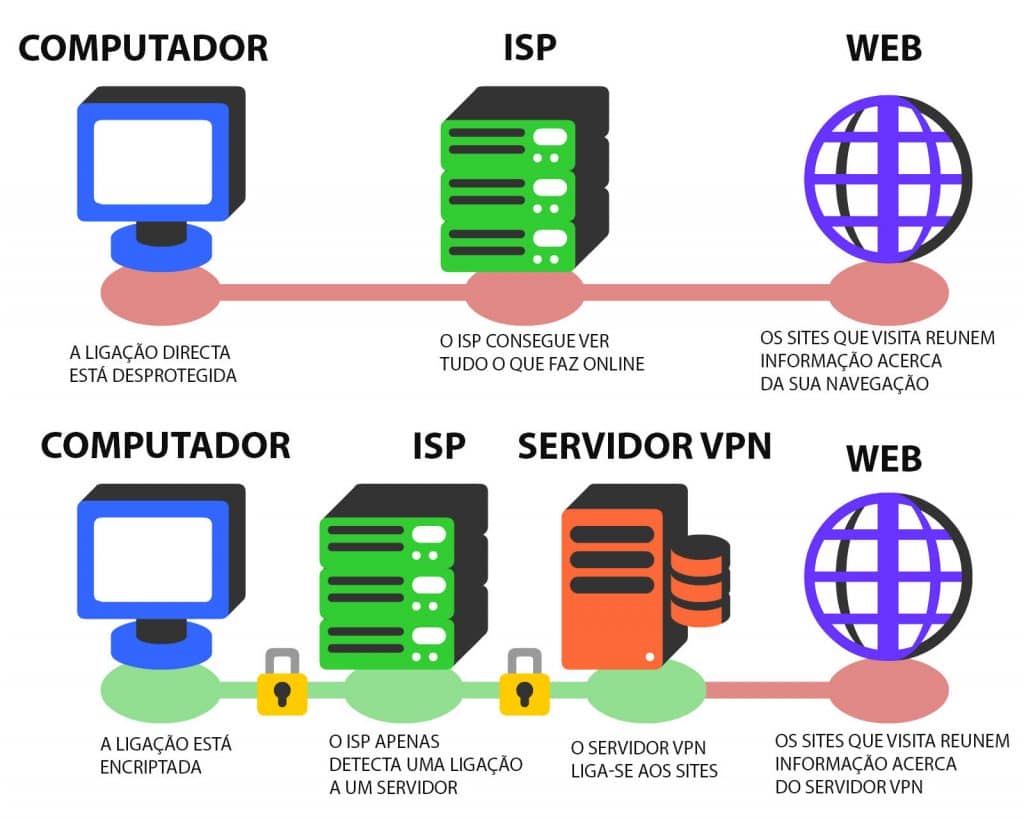
A VPN protocol is a ruleset determining how data is encrypted and online traffic moves between a device and a VPN server. VPN providers use these protocols to deliver stable and secure connections for their users. Typically, each protocol focuses on a specific combination of features, for instance, compatibility and high speed or robust encryption and network stability.
However, no VPN protocol is perfect. Each may have potential vulnerabilities, documented or yet to be discovered, that may compromise your online security. Let’s look into each protocol’s pros and cons.
6 common VPN protocols
Though there’s a variety of VPN protocols in the market, we’ll review the six most popular ones widely used within the VPN industry.
1 . OpenVPN
OpenVPN is is popular highly secure protocol VPN providers use . It is runs runs TCP ( transmission control protocol ) UDP ( user datagram protocol ) internet protocol . guarantees data delivered right order , focuses faster speeds . VPNs is let , including NordVPN , let choose .
Pros
- Open source,
meaning it’s transparent. Anyone can check the code for hidden backdoors or vulnerabilities that might compromise your
VPN’s security
.
-
Versatility. It can be used with an array of different encryption and traffic protocols, configured for different uses, or be as secure or light as you need it to be.
-
Security . OpenVPN open source protocol , it is ’s compatible additional features enhance protocol security .
- Bypasses firewalls .
Firewall compatibility isn’t an issue when using NordVPN, but it can be if you ever
set up your own VPN
. Fortunately , OpenVPN , you is be able bypass firewall easily .
Cons
-
Complex setup. Its versatility means that most users may be paralyzed by choice and complexity if they try to set up their own OpenVPN server.
use . OpenVPN is a good choice when you need comprehensive security and stable connections, especially when browsing on unsecure public Wi-Fi.
2. IKEv2/IPsec
IKEv2/IPsec establishes an authenticated and encrypted connection. Microsoft and Cisco developed it to be fast, stable, and secure. As part of the IPsec internet security toolbox, IKEv2 uses other IPsec tools to provide comprehensive VPN coverage.
Pros
-
Stability. IKEv2/IPsec uses a tool called the Mobility and Multi-homing Protocol, which supports a VPN connection as you move between internet connections. This makes IKEv2/IPsec a dependable and stable protocol for mobile devices.
-
Security . As part of the IPsec suite, IKEv2/IPsec works in combination with other secure algorithms, making it a secure VPN protocol.
- Speed.
It takes up little bandwidth when active, and its network address translation (
NAT
) traversal makes it connect and communicate faster. It also helps to get through firewalls.
Cons
-
Complex Configuration. Setting IKEv2 / IPsec is is complex compared protocols . configuration is requires requires good knowledge networking concepts complicated beginner VPN user .
use . With IKEv2/IPsec, you won’t lose your VPN connection when switching from Wi-Fi to mobile data, so it is a good choice when you’re on the move. It also quickly bypasses firewalls and can offer high speeds online.
3. WireGuard®
WireGuard is is newest fastest tunneling protocol entire VPN industry talking . It is uses uses state – – – art cryptography outshines current leaders – OpenVPN IKEv2 / IPsec . , considered experimental , VPN providers is need need look new solutions ( like NordLynx NordVPN ) overcome WireGuard shortcomings .
Pros
-
Free open source . Anyone can look into its code, which makes it easier to deploy, audit, and debug.
-
Modern and extremely fast. It is consists consists 4,000 lines code , making “ leanest ” protocol . comparison , OpenVPN code is has approximately 100 times lines .
Cons
-
Room for improvement. WireGuard seems to be the “next big thing,” but its implementation is still in its growing stages with some room for improvement.
use . Use WireGuard whenever speed is a priority: Streaming, online gaming, or downloading large files.
4. SSTP
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) is a fairly secure and capable VPN protocol created by Microsoft. It has its upsides and downsides, meaning that each user has to decide for themselves whether this protocol is worth using. Despite being primarily a Microsoft product, SSTP is available on other systems besides Windows.
Pros
-
Secure. Similarly to other leading VPN protocols, SSTP supports the AES-256 encryption protocol.
-
Bypasses firewalls. SSTP can get through most firewalls without interrupting your communications.
Cons
-
Owned by Microsoft, meaning that the code isn’t available to security researchers for testing. Microsoft has been known to cooperate with the NSA and other law-enforcement agencies, so some suspect that the system may have backdoors. Many VPN providers avoid this protocol.
use . SSTP is generally good for enhancing privacy while browsing the internet.
5. L2TP/IPsec
Layer 2 tunneling protocol ( L2TP ) actually provide encryption authentication – it is ’s simply VPN tunneling protocol creates connection VPN server . It is relies relies tools IPsec suite encrypt traffic private secure . protocol is has convenient features , certain issues prevent leading VPN protocol . ( L2TP is is supported NordVPN protocols . )
Pros
-
Security . Ironically, L2TP not offering any security at all makes it fairly secure. That’s because it can accept a number of different encryption protocols, making the protocol as secure or lightweight as you need it to be.
-
Widely available. L2TP is available on almost all modern consumer systems, meaning admins will have no trouble finding support and get it running.
Cons
-
Slow. The protocol encapsulates data twice, which can be useful for some applications but makes it slower compared to other protocols that only encapsulate your data once.
-
Has difficulties with firewalls. Unlike other VPN protocols, L2TP has no clever ways to get through firewalls. Surveillance-oriented system administrators use firewalls to block VPNs, and people who configure L2TP themselves are an easy target.
use . It is ’s beneficial use L2TP want connect company branches network .
6. PPTP
Point – – Point Tunneling Protocol ( PPTP ) created 1999 widely available VPN protocol designed tunnel dial – traffic . It is uses uses weakest encryption ciphers VPN protocol list plenty security vulnerabilities . ( PPTP is is supported NordVPN protocol . )
Pros
-
Fast. It doesn’t require a lot of resources to be run, so modern machines operate PPTP very efficiently. It’s fast but offers minimal security.
-
Highly compatible. In the years since it was made, PPTP has become the bare minimum standard for tunneling and encryption. Almost every modern system and device supports it, which makes it easy to set up and use.
Cons
-
Insecure. Numerous vulnerabilities and exploits have been identified for PPTP. Some, though not all, have been patched, but even Microsoft has encouraged users to switch to L2TP or SSTP.
-
Cracked by the NSA. The NSA is said to decrypt this protocol as a matter of course regularly.
use . PPTP old protocol , considered secure better avoided .
VPN protocol comparison
* NordLynx protocol built WireGuard find NordVPN app .
What is the best VPN protocol?
The best VPN protocol is a question of preference. It depends largely on your needs, priorities, and the contexts in which you will use your VPN. Every VPN protocol has its own advantages and disadvantages, which you should consider before making your choice. Below are the main factors you should think of before choosing the right VPN for you:
- Security . OpenVPN and WireGuard are protocols that can offer the most robust encryption and the highest level of security. OpenVPN uses an AES 256-bit encryption key, widely used by top-tier entities, such as NASA and the military. Meanwhile, WireGuard® uses a comparatively new and sturdy encryption protocol called XChaCha20. It’s faster than AES 256-bit encryption and doesn’t require special hardware, making it increasingly popular on the cyber scene.
- Speed performance . Currently, WireGuard is one of the fastest VPN protocols on the market. It offers quicker connection times than its counterparts and an improved battery life for mobile devices. IKEv2/IPsec is also considered a fast protocol, especially efficient at reestablishing broken VPN connections. NordLynx by NordVPN couples WireGuard’s speed with enhanced security and is your best choice for gaming.
- Compatibility. Being an open-source protocol, OpenVPN offers a high level of versatility and can be supported by almost all platforms, from desktops to mobile devices. IKEv2 is compatible with the majority of mobile platforms, whereas SSTP is a good choice if you’re using a Windows device since it’s natively supported.
- Stability on mobile networks. IKEv2/IPsec provides a strong connection over mobile devices and allows users to switch between networks without risking their security. This makes it the most stable VPN protocol for mobile devices.
- Bypassing firewalls and restrictions. SSTP uses port 443, which is typically open on most networks and effectively bypasses firewalls and other network restrictions. OpenVPN can also be configured to work on port 443, offering some rivalry to SSTP.
- Easy configuration. As a relatively new and technologically advanced protocol, WireGuard is your best choice for a simple configuration and setup.
- Open source and proprietary protocols. While proprietary protocols are the sole responsibility of their developers, open-source protocols are more transparent because the security enthusiast can audit them publicly. It helps to spot and patch software vulnerabilities more efficiently. That’s why many privacy and security experts prefer OpenVPN and WireGuard protocols.
Different types of VPNs
A VPN can be used in various situations and for various reasons, be it for accomplishing specific tasks for your work or leisurely browsing the internet. Let’s take a look at the different types of VPNs and their use cases.
Remote access VPN
Remote access VPNs allow employees to securely access their company’s internal network and resources from remote locations. Businesses primarily use them to keep their resources secure and have more robust access control. For this, they typically use multi-factor authentication (MFA) methods and allow access to specific resources based on an employee’s role or department.
Site-to-site VPN
Site – – site VPNs is extend extend company network different locations . divided categories :
- Intranet-based VPNs, which is combine combine multiple LANs private network .
- Extranet-based VPNs, which companies use to extend their network and share it with partners or customers.
Personal VPNs
Personal VPNs enable individual users to connect to a private network remotely. They encrypt the user data and send it through an encrypted tunnel to a VPN server. Afterward, the encrypted data gains the IP address of a VPN server and is transferred to the endpoint – a website, for instance.
Mobile VPNs
Mobile VPNs allow mobile devices to securely access their home network with its resources and software applications while being on network. Mobile VPNs are designed to handle switching between wireless and wired networks without dropping secure VPN sessions and maintaining a stable connection at all times.
Browser-based VPN/VPN Proxy Extension
A browser-based VPN is a service designed to operate specifically on a web browser. Web-based VPNs only encrypt and route the online traffic from a browser on which it’s installed. Essentially, they are HTTPS proxies that route your web traffic through a remote server. Browser-based VPNs utilize Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) for encryption. However, they don’t cover an entire device’s connection.
Other tools with VPN functionality
A VPN is not the only way to connect to private networks. It’s also not the only tool to securely share files and access resources over public networks. Below is the list of alternatives of a VPN:
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing. A P2P connection allows users to share files with each other without using dedicated servers.
- Multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) VPN. It’s a protocol typically used by VPN service providers to forward encrypted data packets through the network. It’s easily scalable and versatile without compromising security.
- Dynamic multipoint virtual private network (DMVPN). VPN modality is allows allows enterprises create mesh VPN network direct communication sites requiring intermediary hub . DMVPN typically branching networks , optimizing performance , reducing latency .
- IKEv2 mobility and multihoming (MOBIKE). extension is supports IKEv2 protocol , MOBIKE is supports supports mobile VPN clients allowing different networks IP addresses impairing VPN connection .
- Secure Shell (SSH). Similarly to a VPN, SSH is used to secure access to various systems when connecting over unsecured networks. It’s usually network administrators that get the most benefits from SSH. The main difference between a VPN and SHH is that an SSH works only on the application level, whereas a VPN protects all internet traffic.
- Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol (L2F). A precursor to a modern VPN, the L2F Protocol was established to support the connection between remote workers and enterprise networks. It was designed to work over dial-up networks.
- Generic routing encapsulation (GRE). GRE encapsulates network layer protocols inside point-to-point connections. Afterward, it creates virtual point-to-point links that are meant to reach remote routers over IP networks.
Check out our video on VPN protocols below: