Nenhum resultado encontrado
Não foi possível encontrar nada usando esse termo. Tente pesquisar por outro termo.

What is a VPN? How does a Virtual Private Network Work?
2024-11-22 VPN meaning : What Does VPN stand For ? AVPN, meaning a virtual private network masks your Internet protocol (IP) address, creating a pr
VPN meaning : What Does VPN stand For ?
AVPN, meaning a virtual private network masks your Internet protocol (IP) address, creating a private connection from a public wi-fi connection. AVPN is one of the best tools for privacy and anonymity for a user connected to any public internet service because it establishes secure and encrypted connections.
Using a Wi-Fi network, especially one that is unsecured, means potential exposure of personal information to third parties, some of which may have malicious intentions. What is a VPN capable of? AVPN hides a lot of information, including your browsing history, your IP address, your location, your endpoint devices (whether you’re on a Windows computer or an an Android smartphone), and your overall web activity. Cyber criminals often use unsecured connections to gain access to information that enables identity theft and other malicious activities. AVPN solution helps to protect against these activities by creating an encrypted tunnel for all data you send and receive, unobserved by others.
In the context of this VPN meaning , a VPN solution is helps help to protect againstnefarious activities by creating an encrypted tunnel for all data you send and receive, unobserved by others. Data security can also be enhanced through VPN split tunneling, which enables users to route some traffic through their VPN and enable other traffic to retain direct access to the internet.
But in some cases, organizations may choose to install a VPN blocker to prevent employees from accessing sites that may hinder their productivity, such as social networking or shopping sites.
What Does a VPN Do is Does ?
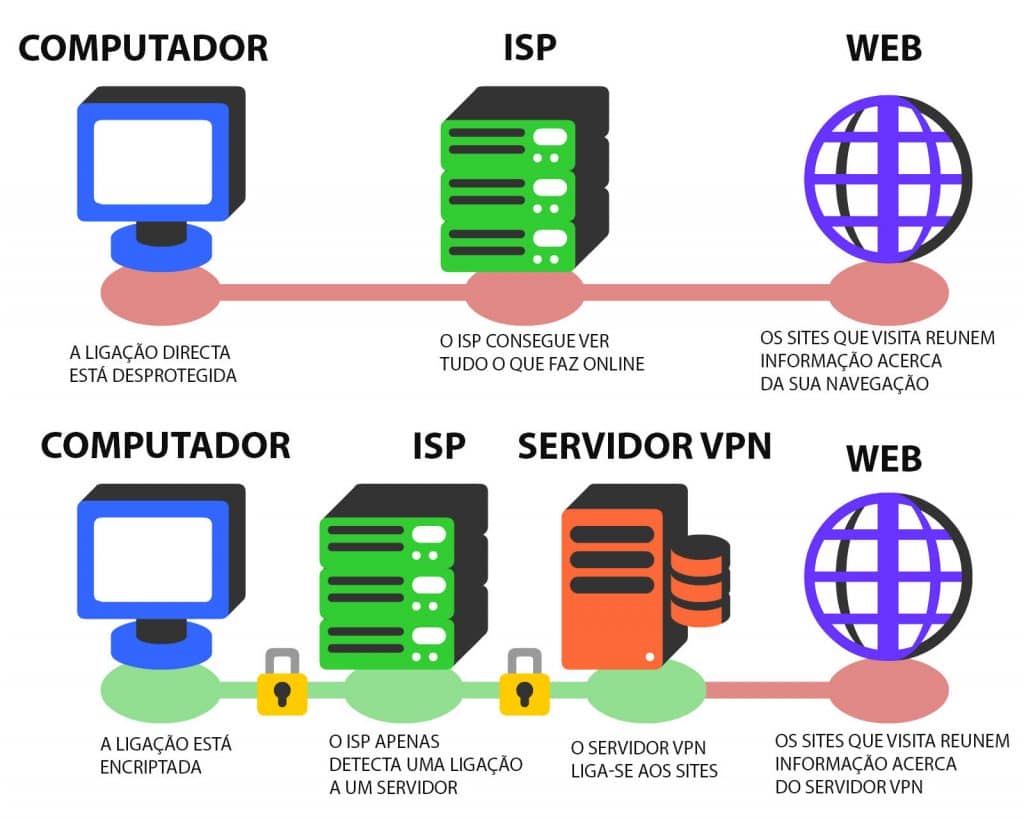
VPNs use virtual connections to create a private network, keeping any device you connect to a public wi-fi safe from hackers and malware, and protecting sensitive information from unauthorized viewing or interception. AVPN routes your device’s connection through a private server rather than the ISP, so that when your data reaches the Internet, it’s not viewable as coming from your device.
Avirtual network keeps your data private using encryption, which turns your information into unreadable gibberish only decipherable using a key, which is known to your device. Different VPNs use somewhat different encryption processes, but the general process includes tunneling and your data is encoded as it travels between your device and the server, which then decrypts the data and sends it on to your destination, such as a website. The encryption process prevents anyone who may intercept the data between you and the server, such as a government agency or hacker, from being able to decipher its contents.
Now that you know the answer to “What is VPN protection?” you might be curious about where it is most frequently used. Two of the best-known and most popular secure network protocols used in VPN technology are Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) and secure sockets layer (SSL). IPSec connections use pre-shared keys on clients and servers in order to encrypt and send traffic back and forth. SSL VPNs use public key cryptography to securely exchange encryption keys.
How Does a VPN Work?
Avirtual network keeps your data private using encryption, which turns your information into unreadable gibberish only decipherable using a key, which is known to your device. Different VPNs use somewhat different encryption processes, but the general process includes tunneling and your data is encoded as it travels between your device and the server, which then decrypts the data and sends it on to your destination, such as a website. The encryption process prevents anyone who may intercept the data between you and the server, such as a government agency or hacker, from being able to decipher its contents.
Now that you know the answer to “What is VPN protection?” you might be curious about where it is most frequently used. Two of the best-known and most popular secure network protocols used in VPN technology are Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) and secure sockets layer (SSL). IPSec connections use pre-shared keys on clients and servers in order to encrypt and send traffic back and forth. SSL VPNs use public key cryptography to securely exchange encryption keys.
Learn more on how a VPN works here.
Why Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN)?
Use of the Internet is now essential to global business, from shopping to banking to medicine to entertainment. Using Internet services involves transmitting very important information online, including credit card and social security numbers, and personal information, such as medical histories or home addresses. VPNs keep your Internet use safe from prying eyes, and, when used in a corporate setting, help keep business information from getting into the wrong hands.
For businesses who wonder “what is a VPN going to do for my company?” these provide improved security overall, improved remote access, independence from countries with strict Internet access laws, and a better total-cost-of-ownership when it comes to the aggregate costs of security and networking technologies used by corporate teams. VPNs can also provide safe and secure data sharing between employees and with individuals and groups outside of the business when necessary.
It is important to note that these do not make users completely anonymous on the Internet. Internet services requiring a login, such as Google or Facebook, know when you sign in, and websites can still leave cookies on your machine that identify your visits from particular Internet browsers. Anyone with direct access to the devices you use might also be able to view your activity. And law enforcement officials, depending on local legal authority, may be able to monitor your devices directly or require your virtual network service to give up records of your actions.